3-55
Chapter 3 Starting and Stopping this Device
(3) Calculation Example Using the JTE Model
In some cases the high pressure flange is attached to the upper portion of the tank, and in some
cases the high pressure flange is attached to the lower portion of the tank.
(i)
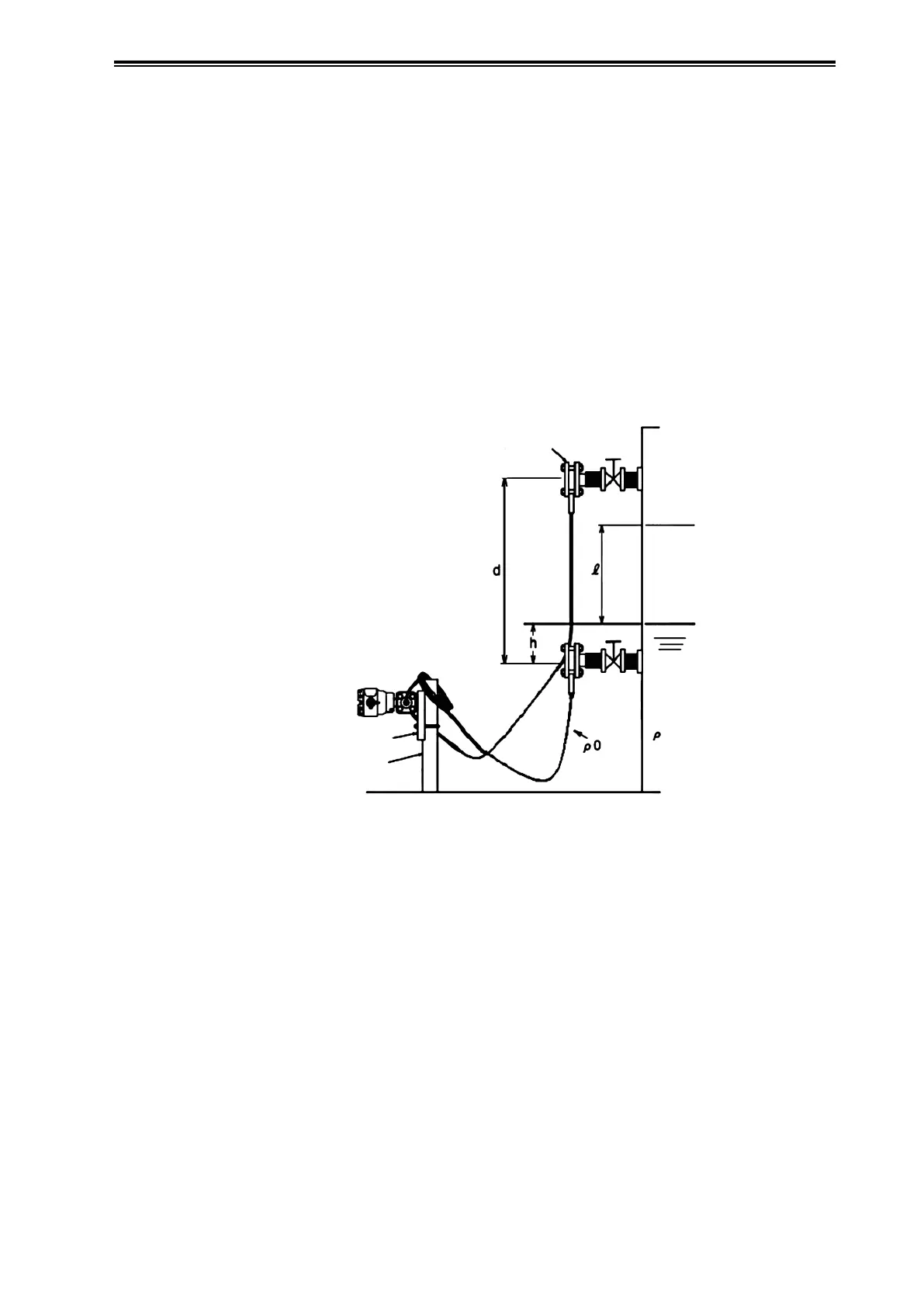
If the high pressure side flange is attached to the upper portion of the tank
Calculation of the setting range is described below.
In this calculation, density and distance are represented by the following symbols. In addition,
density is assumed to be constant during liquid level measurement.
ρ: Specific gravity of liquid in tank
ρ
0
: Specific gravity of sealed liquid
l: Distance between the 100% liquid level and the 0% liquid level (measurement range)
h: Distance between the 0% liquid level and the low pressure side mounting flange
d: Distance between the flanges
High Pressure
Side Mounting
Flange
100%
Liquid Level
0%
Liquid Level
Low Pressure
Side Mounting
Flange
Mounting
Bracket
Pipe
Stanchion
Sealed
Tank
Figure 3-20. Sealed Tank (Wet Leg)
0% liquid level differential pressure
LRV = d×ρ
0
- h×ρ
100% liquid level differential pressure
URV = d×ρ
0
- l×ρ - h×ρ
= d×ρ
0
- (l+h)×ρ
Accordingly,
Low limit (LRV): dρ
0
- hρ
High limit (URV): dρ
0
- (l+h)ρ
is the range to set.

 Loading...
Loading...