56
This average, which is called the
central difference
, is expressed as:
uu
uu
uTo perform a differential calculation
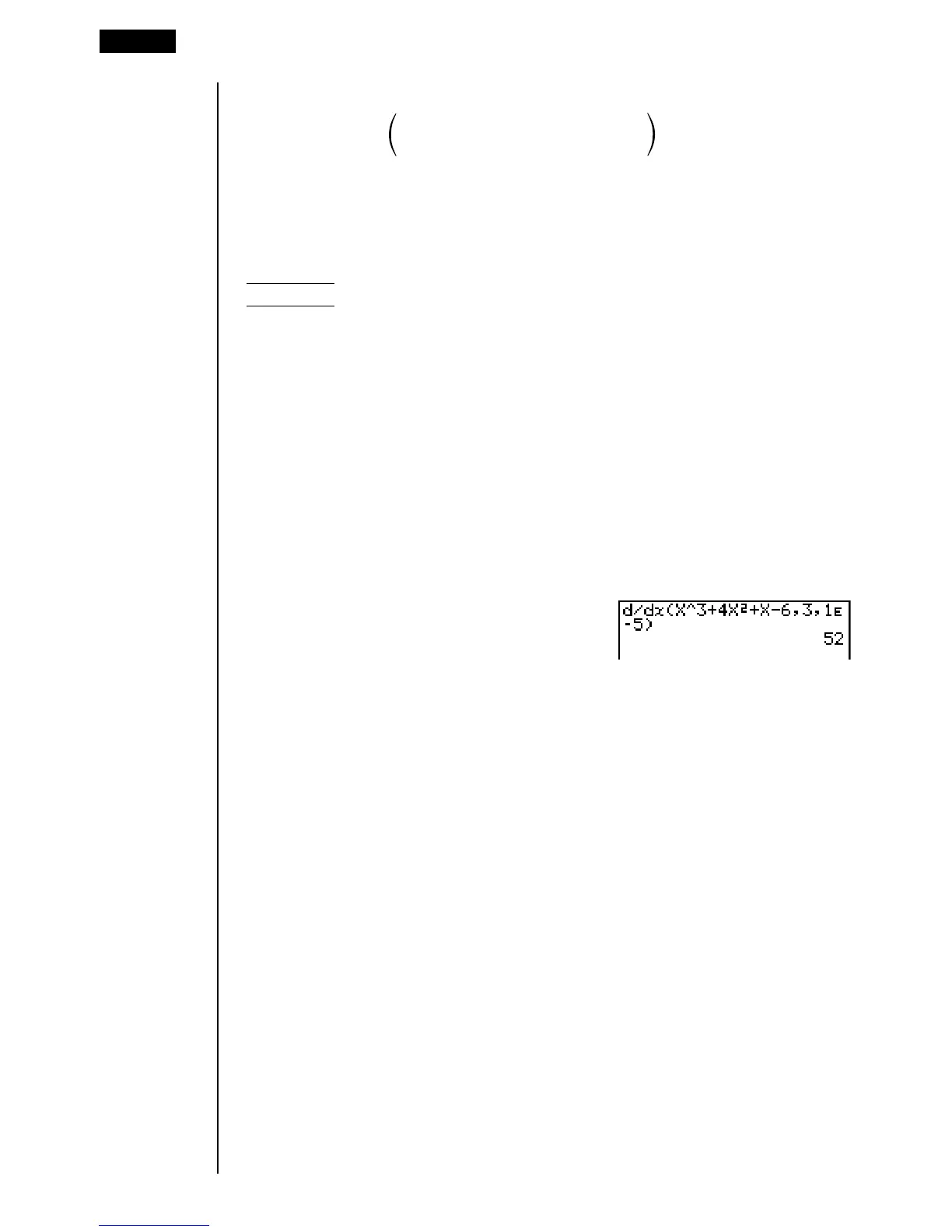
Example To determine the derivative at point x = 3 for the function
y = x
3
+ 4x
2
+ x – 6, when the increase/decrease of x is defined
as
AA
AA
Ax = 1E – 5
Input the function f(x).
AK4(CALC)2(d/dx)vMd+evx+v-g,
Input point x = a for which you want to determine the derivative.
d,
Input Ax, which is the increase/decrease of x.
bE-f)
w
•In the function f(x), only X can be used as a variable in expressions. Other
variables (A through Z, r,
θ
) are treated as constants, and the value currently
assigned to that variable is applied during the calculation.
•Input of Ax and the closing parenthesis can be omitted. If you omit Ax, the
calculator automatically uses a value for Ax that is appropriate for the deriva-
tive value you are trying to determine.
•Discontinuous points or sections with drastic fluctuation can adversely affect
precision or even cause an error.
3 - 2 Differential Calculations
1 f (a + Ax) – f (a) f (a) – f (a – Ax)
f '(a) = –– ––––––––––––– + –––––––––––––
2 Ax Ax
f (a + Ax) – f (a – Ax)
= –––––––––––––––––
2Ax
 Loading...
Loading...