Three security models are available: SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3. The security model combined with
the security level determine the security mechanism applied when the SNMP message is processed.
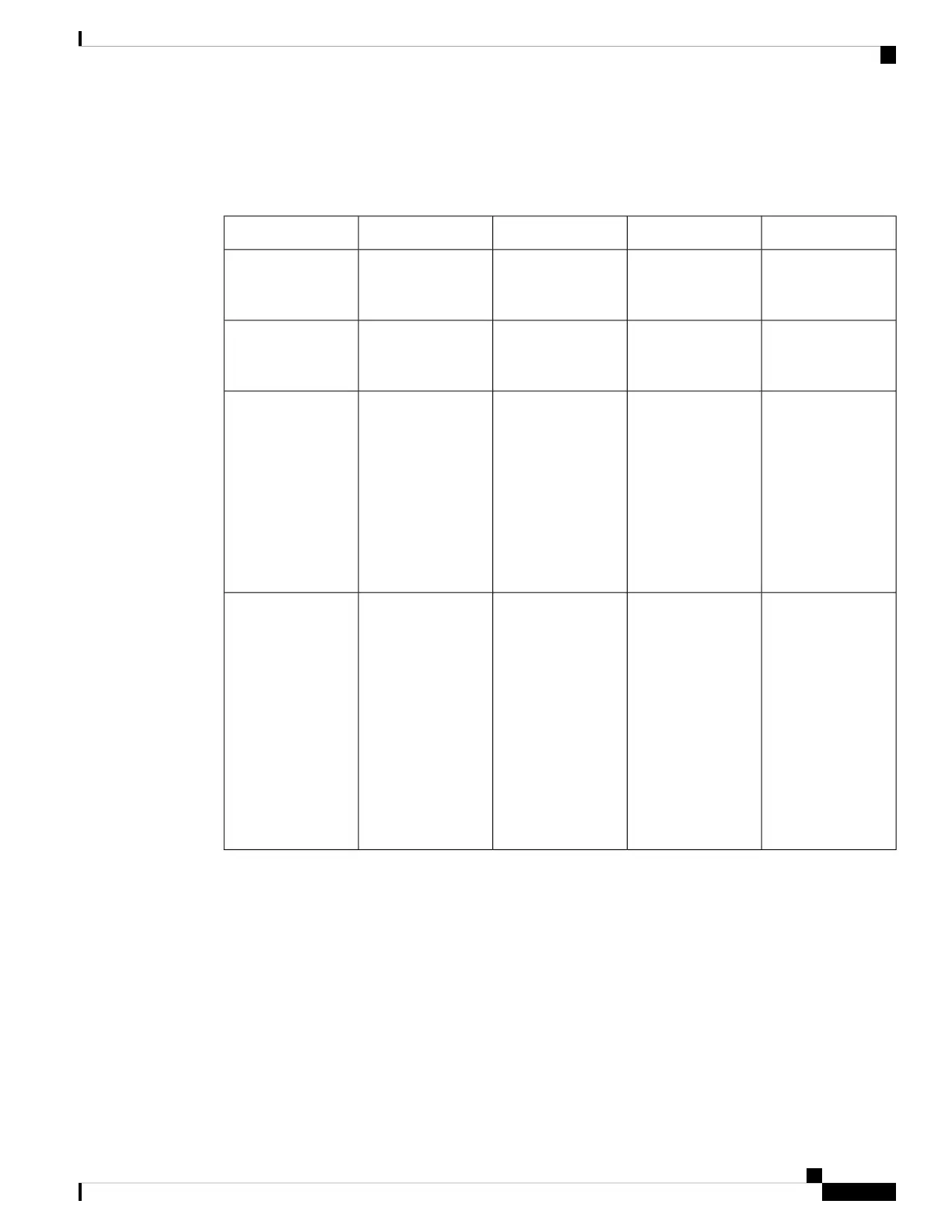
Table 18: SNMP Security Models and Levels
What HappensEncryptionAuthenticationLevelModel
Uses a community
string match for
authentication.
NoCommunity stringnoAuthNoPrivv1
Uses a community
string match for
authentication.
NoCommunity stringnoAuthNoPrivv2c
Provides
authentication based
on the Hash-Based
Message
Authentication Code
(HMAC) Message
Digest 5 (MD5)
algorithm or the
HMAC Secure Hash
Algorithm (SHA).
NoHMAC-MD5 or
HMAC-SHA
authNoPrivv3
Provides
authentication based
on the HMAC-MD5
or HMAC-SHA
algorithms. Provides
Data Encryption
Standard (DES)
56-bit encryption in
addition to
authentication based
on the Cipher Block
Chaning (CBC) DES
(DES-56) standard.
DESHMAC-MD5 or
HMAC-SHA
authPrivv3
User-Based Security Model
SNMPv3 User-Based Security Model (USM) refers to SNMP message-level security and offers the following
services:
• Message integrity—Ensures that messages have not been altered or destroyed in an unauthorized manner
and that data sequences have not been altered to an extent greater than can occur nonmaliciously.
• Message origin authentication—Confirms that the claimed identity of the user who received the data
was originated.
• Message confidentiality—Ensures that information is not made available or disclosed to unauthorized
individuals, entities, or processes.
Cisco Nexus 3548 Switch NX-OS System Management Configuration Guide, Release 7.x
93
Configuring SNMP
User-Based Security Model

 Loading...
Loading...











