Theory of Operations
84 Operator’s Manual
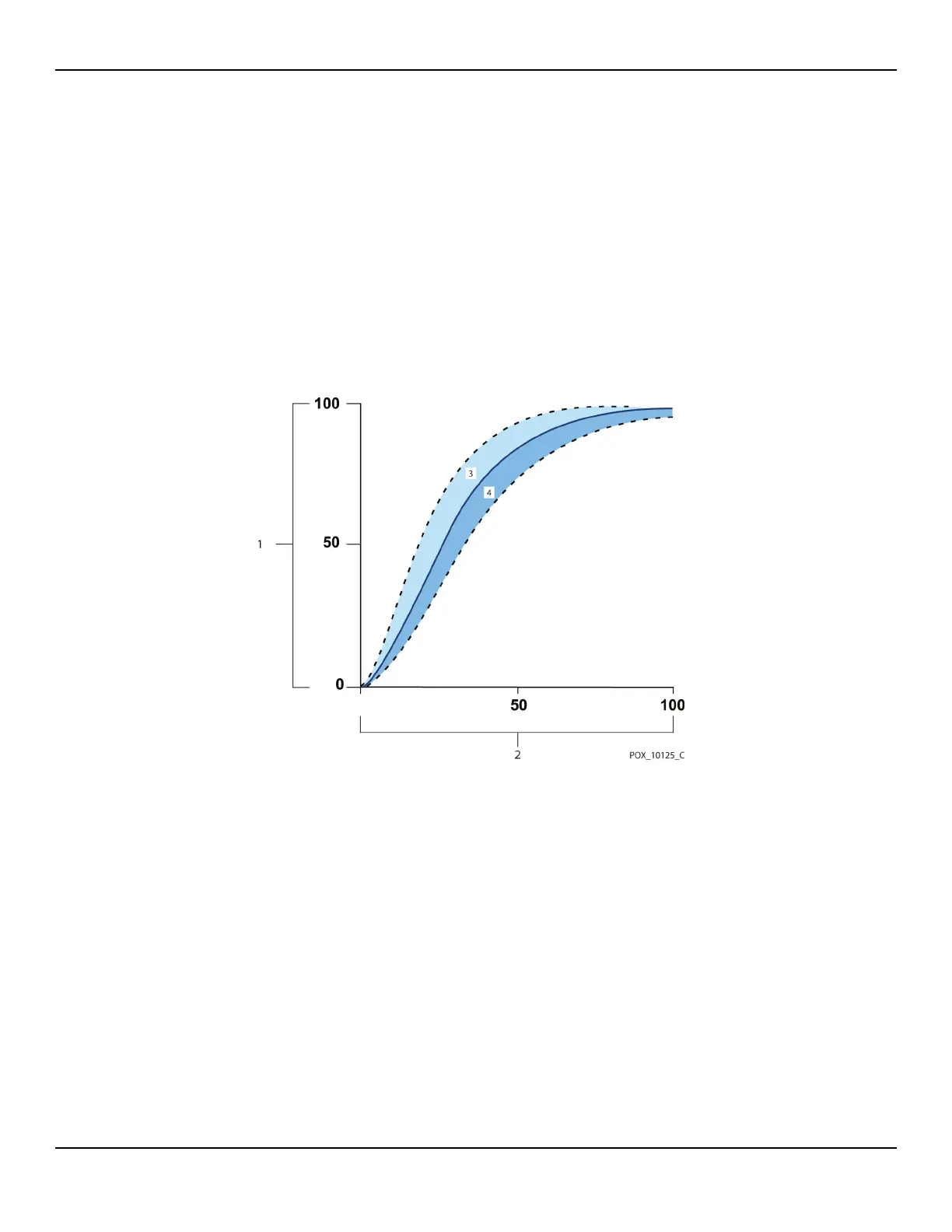
10.5.2 Measured versus Calculated Saturation
When calculating saturation from a blood gas partial pressure of oxygen (PO2),
the calculated value may differ from the SpO
2 measurement of a monitoring
system. This usually occurs when saturation calculations exclude corrections
for the effects of variables such as pH, temperature, the partial pressure of
carbon dioxide (PCO2), and 2,3-DPG, that shift the relationship between PO2
and SpO
2.
Figure10-1.Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
10.5.3
10.5.4
Data Update Period, Data Averaging, and Signal Processing
The advanced signal processing of the OxiMax™ algorithm automatically extends
the amount of data required for measuring SpO
2
and pulse rate depending on the
measurement conditions. The OxiMax™ algorithm automatically extends the
dynamic averaging time required beyond seven (7) seconds during degraded or dif-
ficult measurement conditions caused by low perfusion, signal artifact, ambient
light, electrocautery, other interference, or a combination of these factors, which
1 % Saturation Axis 3 Increased pH; Decreased temperature, PCO2, and 2,3-DPG
2 PO2 (mmHg) Axis 4 Decreased pH; Increased temperature, PCO2, and 2,3-DPG
 Loading...
Loading...