RFI Filter
Type
Conduct emission. Maximum shielded cable length [m] Radiated emission
Industrial environment
Housing, trades and
light industries
Industrial
environment
Housing, trades and
light industries
EN 55011 Class A2 EN 55011 Class A1 EN 55011 Class B EN 55011 Class A1 EN 55011 Class B
Without
external
filter
With
external
filter
Without
external
filter
With
external
filter
Without
external
filter
With
external
filter
Without
external
filter
With
external
filter
Without
external
filter
With
external
filter
H3 RFI filter (Class A1/B)
20–60 hp
[15–45 kW]
3x200–
240 V IP20
50 20 Yes No
40–125 hp
[30–90 kW]
3x380–
480 V IP20
50 20 Yes No
1–25
[0.75–18.5
kW]
3x380–
480 V IP54
25 10 Yes
30–125 hp
[22–90 kW]
3x380–
480 V IP54
25 10 Yes No
Table 2.12 Test Results
2.8.3
General Aspects of Harmonics Emission
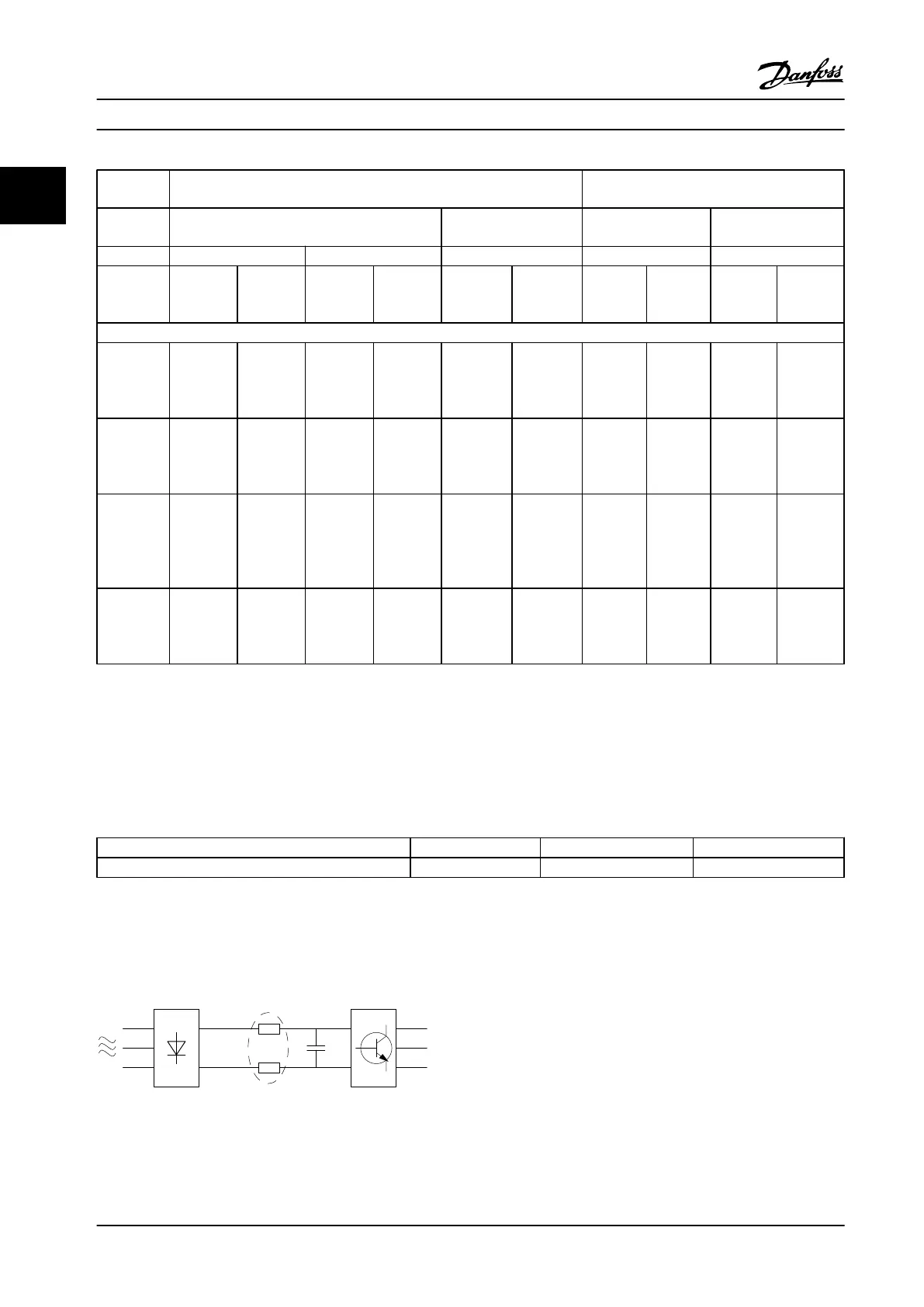
An adjustable frequency drive takes up a non-sinusoidal current from the line power, which increases the input current I
RMS
.
A non-sinusoidal current is transformed by means of a Fourier analysis and split up into sine-wave currents with different
frequencies, i.e., different harmonic currents I
n
with 50 Hz as the basic frequency:
I
1
I
5
I
7
Hz 50 250 350
Table 2.13 Harmonic Currents
The harmonics do not affect the power consumption directly but increase the heat losses in the installation (transformer,
cables). Consequently, in plants with a high percentage of rectifier load, maintain harmonic currents at a low level to
prevent an overload of the transformer and high temperature in the cables.
Figure 2.24 Harmonic Currents
Product Overview Design Guide
38 Danfoss A/S © Rev. 2014-01-14 All rights reserved. MG18C522
22

 Loading...
Loading...











