Safety
information
Product
information
Mechanical
installation
Electrical
installation
Getting
started
Basic
parameters
Running
the motor
Optimization
NV Media Card
Operation
Onboard
PLC
Advanced
parameters
Technical
data
Diagnostics
UL listing
information
128 Unidrive M702 User Guide
Issue Number: 3
8.5 Switching frequency
The default switching frequency is 3 kHz (6 kHz in RFC-S mode),
however this can be increased up to a maximum of 16 kHz by Pr 05.018
(dependent on drive size). The available switching frequencies are
shown below.
Table 8-1 Available switching frequencies
* Size 5 - 575 V variant does not support 16 kHz switching frequency.
If switching frequency is increased from 3 kHz the following apply:
1. Increased heat loss in the drive, which means that derating to the
output current must be applied.
See the derating tables for switching frequency and ambient
temperature in section 12.1.1 Power and current ratings (Derating
for switching frequency and temperature) on page 227.
2. Reduced heating of the motor - due to improved output waveform
quality.
3. Reduced acoustic noise generated by the motor.
4. Increased sample rate on the speed and current controllers. A trade
off must be made between motor heating, drive heating and the
demands of the application with respect to the sample time required.
Table 8-2 Sample rates for various control tasks at each
switching frequency
8.6 High speed operation
8.6.1 Encoder feedback limits
The maximum encoder frequency should be prevented from exceeding
500 kHz. In RFC-A and RFC-S modes the maximum speed that can be
entered in to the speed reference clamps (Pr
01.006
and Pr
01.007
) can
be limited by the drive. This is defined by the following (subject to an
absolute maximum of 40,000 rpm):
Where:
ELPR is the equivalent encoder lines per revolution and is the
number of lines that would be produced by a quadrature encoder.
• Quadrature encoder ELPR = number of lines per revolution
• F and D encoder ELPR = number of lines per revolution / 2
• SINCOS encoder ELPR = number of sine waves per revolution
This maximum speed limit is defined by the device selected with the
speed feedback selector (Pr 03.026), and the ELPR set for the position
feedback device. In RFC-A mode it is possible to disable this limit via
Pr 03.024, so that the drive can be switched between operation with and
without feedback when the speed becomes too high for the feedback
device. The maximum speed limit is defined as above when Pr 03.024 =
0 and is 36,000 rpm when Pr 03.024 = 1,2, 3 or 4.
8.6.2 Field weakening (constant power) operation
(Open loop and RFC-A mode only)
The drive can be used to run an induction machine above synchronous
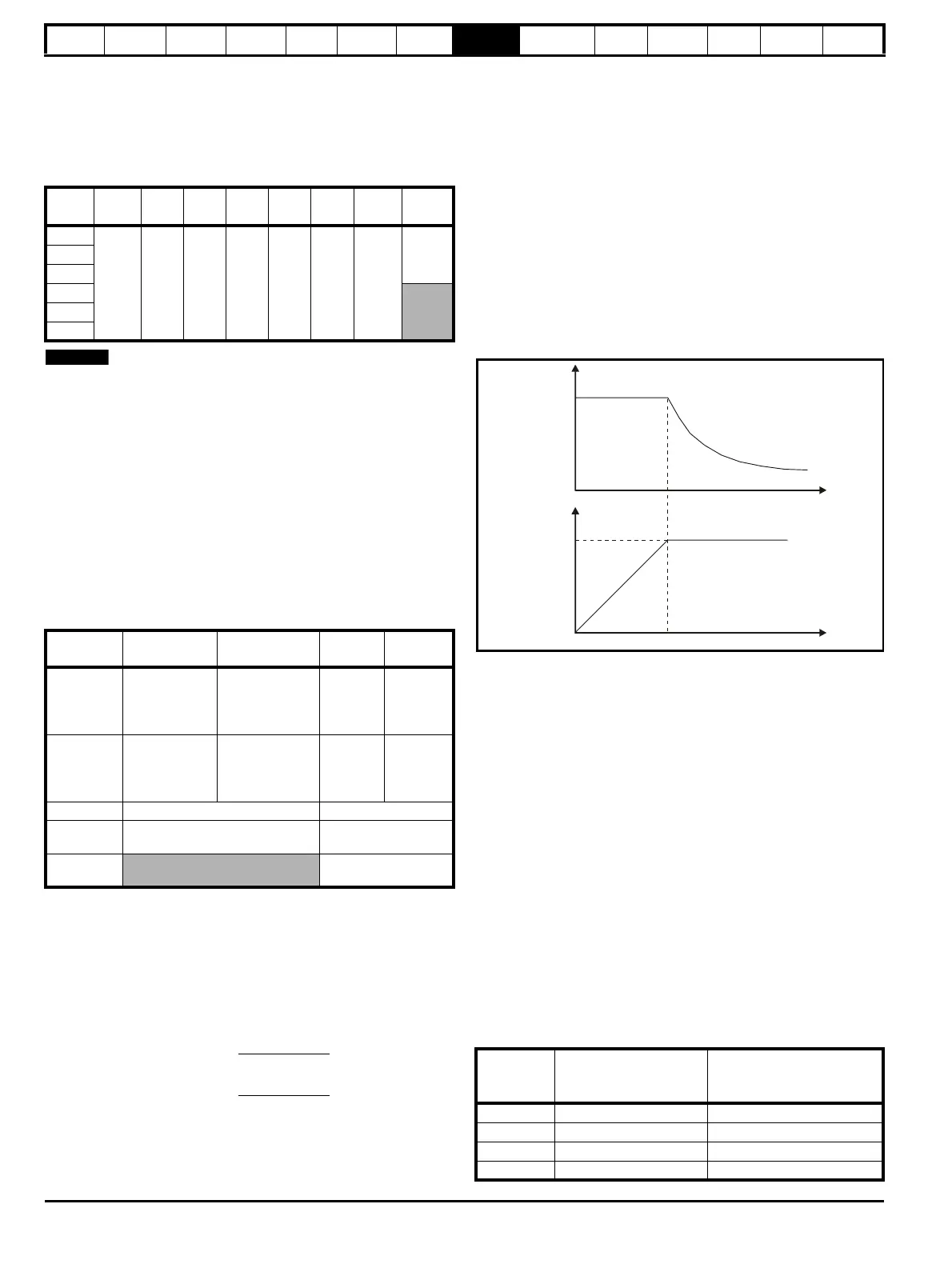
speed into the constant power region. The speed continues to increase
and the available shaft torque reduces. The characteristics below show
the torque and output voltage characteristics as the speed is increased
above the rated value.
Figure 8-3 Torque and rated voltage against speed
Care must be taken to ensure the torque available above base speed is
sufficient for the application to run satisfactorily.
The saturation breakpoint parameters (Pr 05.029, Pr 05. 030, Pr 05.062
and Pr 05.063) found during the autotune in RFC-A mode ensure the
magnetizing current is reduced in the correct proportion for the specific
motor. (In open loop mode the magnetizing current is not actively
controlled).
8.6.3 Permanent magnet motor high speed operation
High speed servo mode is enabled by setting Pr 05.022 =1. Care must
be taken when using this mode with permanent magnet motor to avoid
damaging the drive. The voltage produced by the permanent magnet
motor magnets is proportional to speed. For high speed operation the
drive must apply currents to the motor to counter-act the flux produced
by the magnets. It is possible to operate the motor at very high speeds
that would give a very high motor terminal voltage, but this voltage is
prevented by the action of the drive.
If however, the drive is disabled (or tripped) when the motor voltages
would be higher than the rating of the drive without the currents to
counter-act the flux from the magnets, it is possible to damage the drive.
If high speed mode is enabled the motor speed must be limited to the
levels given in the table below unless an additional hardware protection
system is used to limit the voltages applied to the drive output terminals
to a safe level.
Drive
size
Model
2
kHz
3
kHz
4
kHz
6
kHz
8
kHz
12
kHz
16
kHz
3
All
4
5*
6
7
8
Level
3, 6, 12
kHz
2, 4, 8, 16
kHz
Open
loop
RFC-A
RFC-S
Level 1
3 kHz - 167μs
6 kHz - 83 μs
12 kHz - 83 μs
2 kHz - 250 μs
4 kHz - 125 μs
8 kHz - 62.5 μs
16 kHz - 62.5 μs
Peak limit
Current
controllers
Level 2 250 μs
2 kHz - 500
μs
4 kHz - 250 μs
8 kHz - 250 μs
16 kHz - 250 μs
Current
limit and
ramps
Speed
controller
and ramps
Level 3 1 ms Voltage controller
Level 4 4 ms
Time critical user
interface
Background
Non-time critical user
interface
Maximum speed limit (rpm) =
500 kHz x 60
ELPR
=
3.0 x 10
7
ELPR
Drive
voltage
rating
Maximum motor speed
(rpm)
Maximum safe line to line
voltage at the motor
terminals (V rms)
200 400 x 1000 / (Ke x √2) 400 / √2
400 800 x 1000 / (Ke x √2) 800 / √2
575 955 x 1000 / (Ke x √2) 955 / √2
690 1145 x 1000 / (Ke x √2) 1145 / √2
Rated
voltage
Torq ue
Speed
Speed
Rated speed

 Loading...
Loading...











