The role of DNS in email delivery Key concepts
FortiMail™ Secure Messaging Platform Version 4.0 Patch 1 Install Guide
16 Revision 2
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
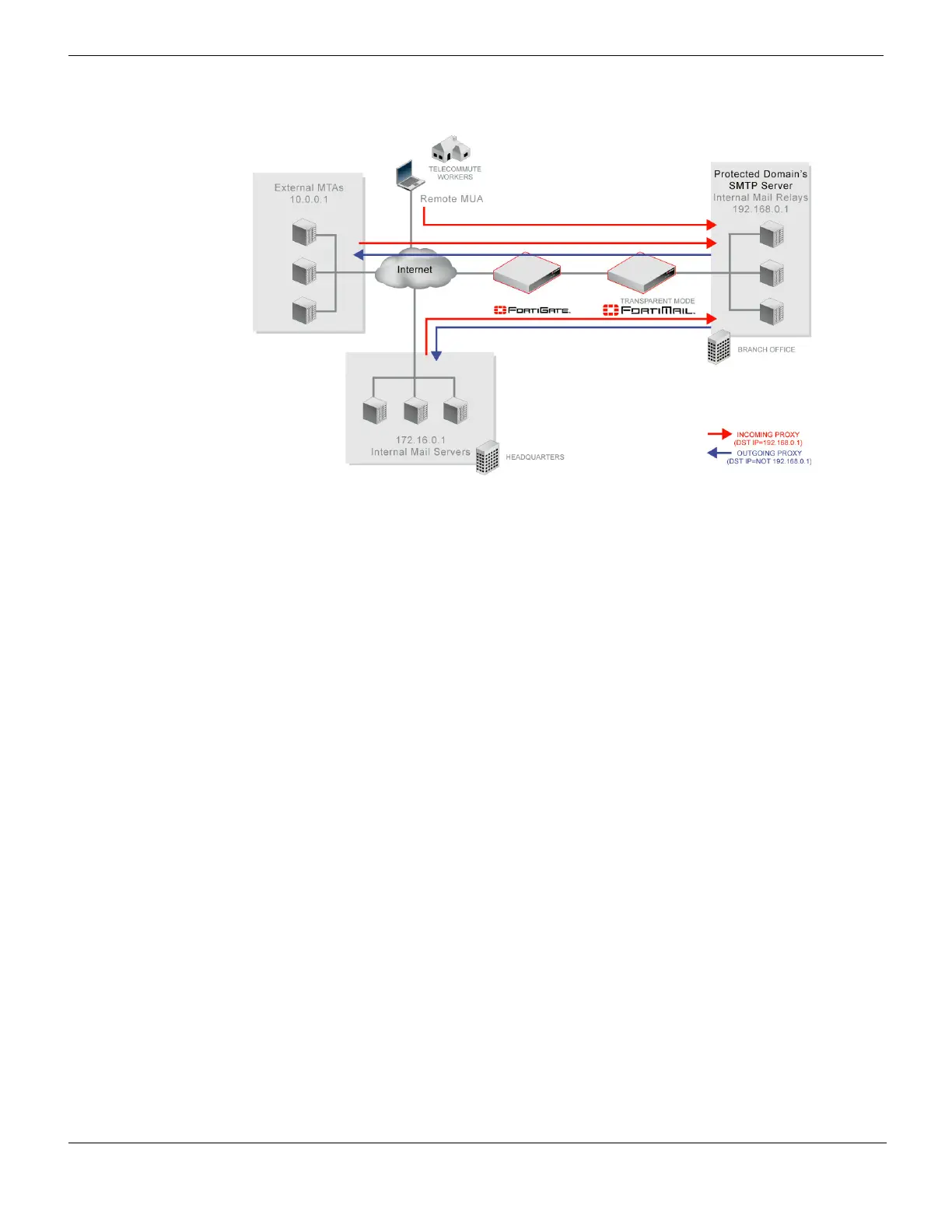
Figure 1: Incoming vs. outgoing SMTP connections
Directionality at the connection level may be different than directionality at the level of
email messages contained by the connection. It is possible that an incoming connection
could contain an outgoing email message, and vice versa.
For example, in Figure 1 on page 16, connections from the internal mail relays to the
internal mail servers are outgoing connections, but they contain incoming email
messages. Conversely, connections from remote MUAs to the internal mail relays are
incoming connections, but may contain outgoing email messages if the recipients’ email
addresses (RCPT TO:) are external.
Similarly to when determining the directionality of an SMTP connection, when determining
the directionality of an email message, FortiMail units examine the domain to which the
recipient belongs: if the domain to which the recipient email address belongs is a
protected domain, the email message is considered to be incoming; if the domain to which
the recipient email address belongs is not a protected domain, the email message is
considered to be outgoing.
The role of DNS in email delivery
SMTP can be configured to operate without DNS, using IP addresses instead of domain
names for SMTP clients, SMTP servers, and recipient email addresses. However, this
configuration is rare.
SMTP as it is typically used relies upon DNS to determine the mail gateway server (MX)
for a domain name, and to resolve domain names into IP addresses. As such, you usually
must configure email servers and FortiMail units to be able to query a DNS server.
In addition, you may also be required to configure the DNS server with an MX record, an A
record, and a reverse DNS record for protected domain names and for the domain name
of the FortiMail unit itself.

 Loading...
Loading...











