Choosing the operation mode Characteristics of server mode
FortiMail™ Secure Messaging Platform Version 4.0 Patch 1 Install Guide
Revision 2 73
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
FortiMail units operating in transparent mode provide a web-based user interface from
which email users can access personal preferences and email quarantined to their per-
recipient quarantine. However, FortiMail units operating in transparent mode do not locally
host mailboxes such as each email user’s inbox, which are instead stored on protected
email servers.
By default, FortiMail units operating in transparent mode are configured as a bridge, with
all network interfaces on the same subnet. You can configure out-of-bridge network
interfaces if you require them, such as if you have some protected email servers that are
not located on the same subnet.
Transparent mode usually requires no changes to an existing network. Requirements
include that the FortiMail unit must be physically inline between the protected email server
and all SMTP clients — unlike gateway mode, because FortiMail units operating in
transparent mode are invisible, clients cannot be configured to route email directly to the
FortiMail unit, and so it must be physically placed where it can intercept the connection.
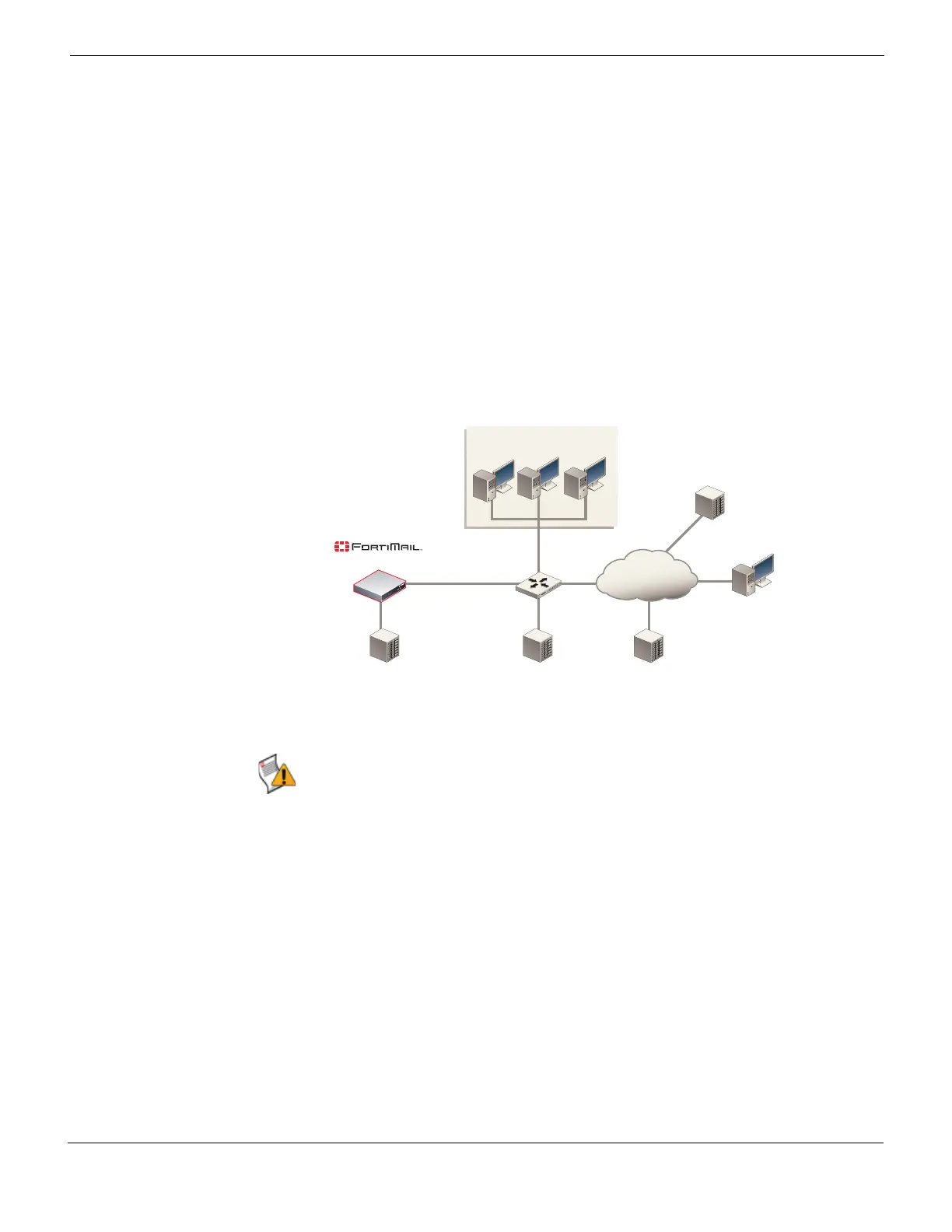
Figure 25: Example transparent mode topology
For example, a school might want to install a FortiMail unit to protect its mail server, but
does not want to make any changes to its existing DNS and SMTP client configurations or
other network topology. Therefore, the school installs the FortiMail unit in transparent
mode.
For sample deployment scenarios, see the chapter “Transparent mode deployment” on
page 119.
Characteristics of server mode
When operating in server mode, the FortiMail is a stand-alone email server. The FortiMail
unit receives email messages, scans for viruses and spam, then delivers email to its email
users’ mailboxes. External MTAs connect to the FortiMail unit, which itself is also the
protected email server.
External
Email Server
Local Email Users
Internet
Transparent Mode
Remote Email Users
Router
port2
port1
Internal Email Server
172.16.1.10
Protected Domain:
@example.com
Email Domain:
@example.com
Public DNS Server
example.com IN MX 10 mail.example.com
mail IN A 10.10.10.1
Private DNS Server
example.com IN MX 10 mail.example.com
mail IN A 172.16.1.10
10.10.10.1
Caution: Do not connect two ports to the same VLAN on a switch or the same hub. Some
Layer 2 switches become unstable when they detect the same media access control (MAC)
address originating on more than one network interface on the switch, or from more than
one VLAN.

 Loading...
Loading...











