Chapter 6. Serial I/O, SNP & RTU Protocols
GFK-2222AD April 2018 205
6.1.6 Example COMMREQ Command Blocks for Serial Port Setup function
The following COMMREQ command blocks provide examples for configuring the various protocols. All
values are in decimal unless followed by an H indicating hexadecimal.
Note that an example is not provided for Message Mode, but it can be setup with a command block
similar to the one for Serial I/O, with a value of 7 for the protocol selector.
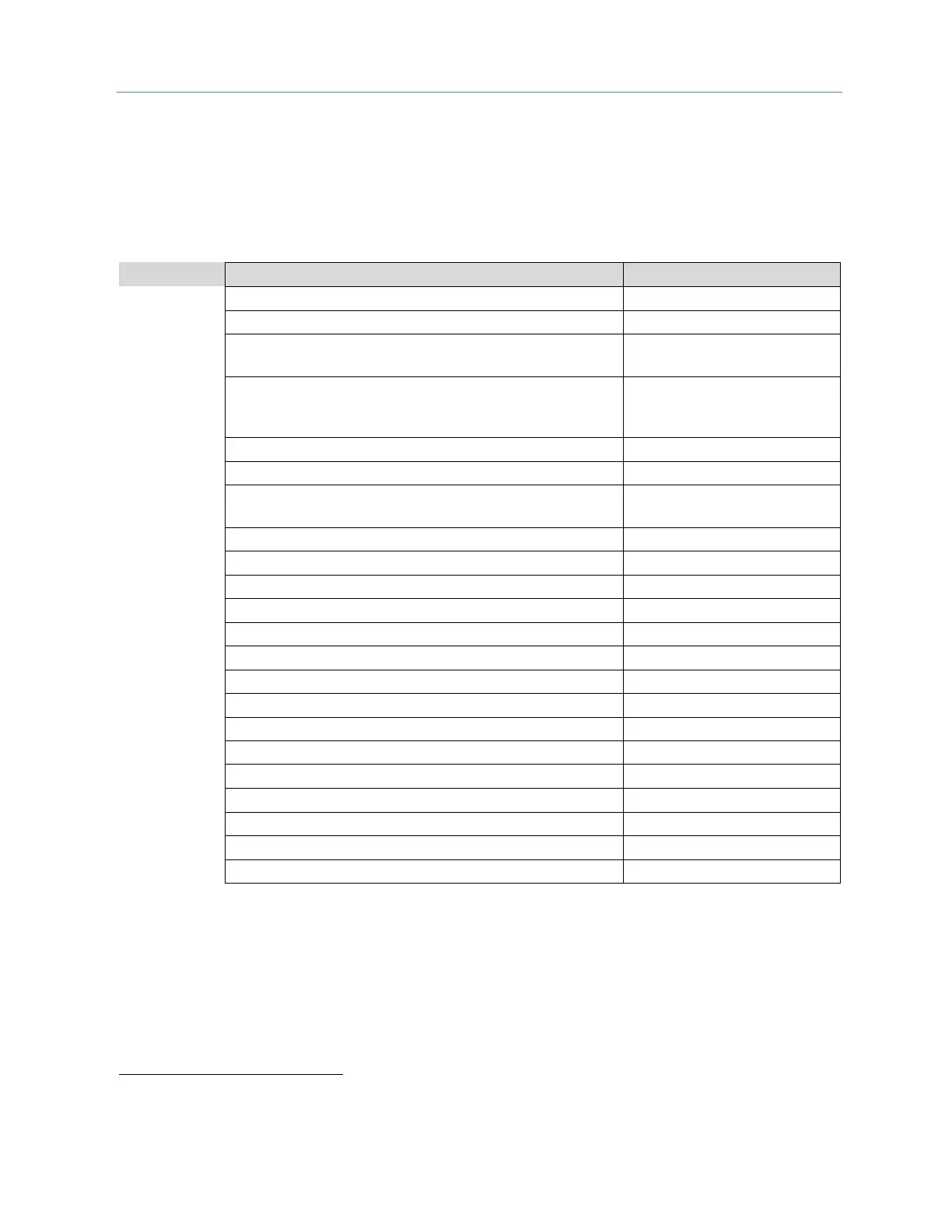
Example COMMREQ Command Block for Configuring SNP Protocol
0 = No Wait (WAIT mode not supported)
0008 = %R, register memory
Status Word Pointer Memory
Type
Zero-based number that gives the address of the COMMREQ
status word (for example, a value of 99 gives an address of
100 for the status word)
Status Word Pointer Offset
Maximum Communication Time
Command Word (serial port
setup)
See COMMREQ Command Block Parameter Values.
0 = None, 1 = Odd, 2 = Even
not used (SNP always chooses NONE by default)
0 = None, 1 = 10ms, 2 = 100ms, 3 = 500ms
0 = Long, 1 = Medium, 2 = Short, 3 = None
not used (SNP always chooses 8 bits by default)
0 = 1 Stop Bit, 1 = 2 Stop bits
not used (SNP always chooses 4-wire mode by default)
Device identifier bytes 1 and 2
Device identifier bytes 3 and 4
Device identifier bytes 5 and 6
Device identifier bytes 7 and 8
The device identifier for SNP Slave ports is packed into words with the least significant character in the least significant byte
of the word. For example, if the first two characters are “A” and “B,” the Address + 18 will contain the hex value 4241.
 Loading...
Loading...