Published 08-25-09, Control # 077-04 1-17
RT9130E SERVICE MANUAL INTRODUCTION
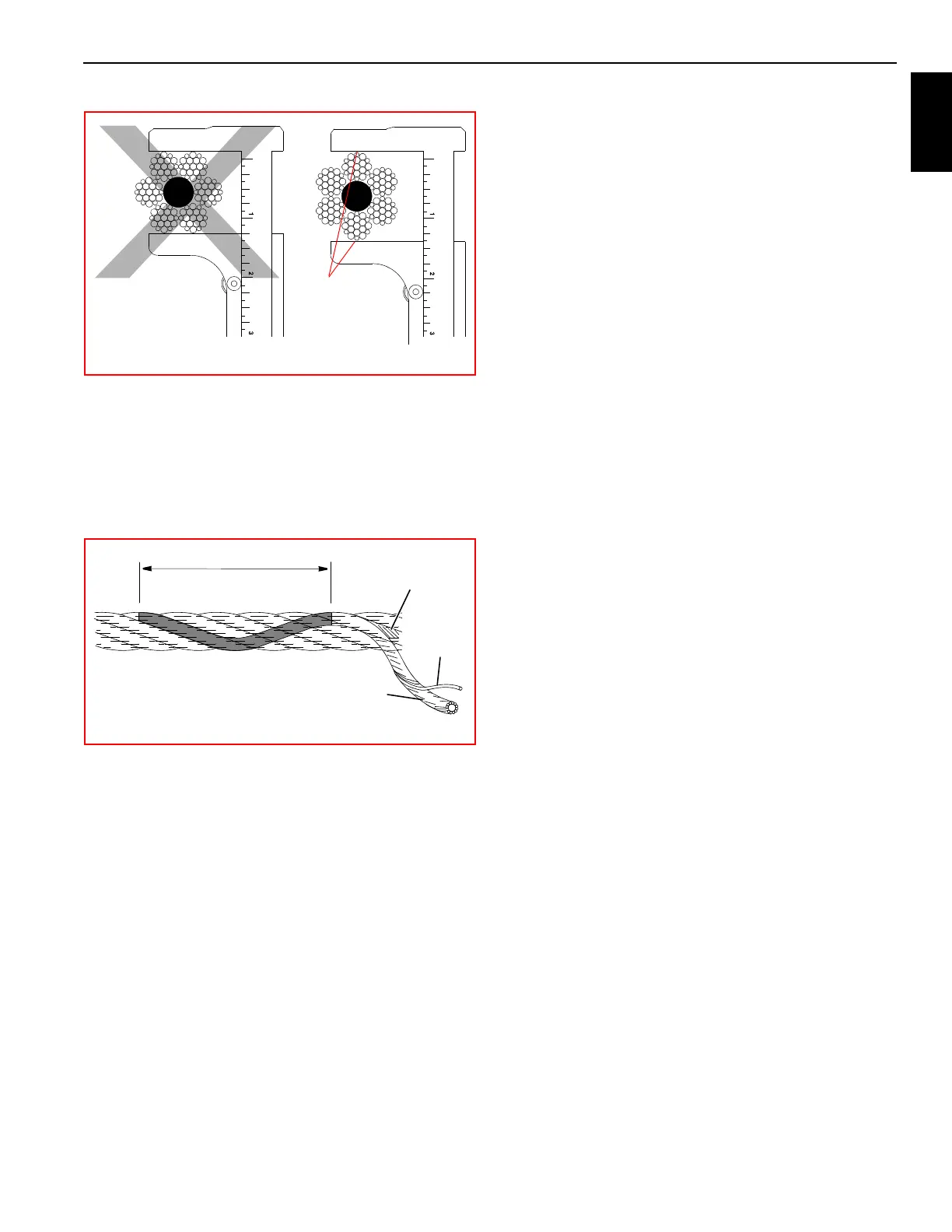
13. When checking for broken wires (5) ((Figure 1-7)) relax
the rope, move it off “pick-up points”, and flex it as much
as possible. Use a sharp awl to pick and probe between
wires and strands, lifting any wire which appears loose
or moves excessively. Defect in the rope is spoke of in
relations to “Lay Length” (2) which is the d
istance
measured along rope in which one strand (3) makes one
complete revolution around core (4).
Wire Rope Inspection (Running Ropes and
Pendant Cables)
Wire rope should be inspected frequently/daily and
periodically/yearly in accordance with the following
information excerpted from a National Consensus Standard
as referenced by Federal Government Agencies.
Recommended inspection intervals may vary from machine
to machine and may vary based on environmental
conditions, frequency of lifts, and exposure to shock loads.
The inspection time intervals may also be predetermined by
state and local regulatory agencies.
NOTE: Wire rope may be purchased through Manitowoc
CraneCARE.
Any deterioration observed in the wire rope should be noted
in the equipment inspection log and an assessment
concerning wire rope replacement should be made by a
qualified person.
Keeping Records
A signed and dated report of the wire rope’s condition at
each periodic inspection must be kept on file at all times. The
report must cover all inspection points listed in this section.
The information in the records can then be used to establish
data which can be used to determine when a wire rope
should be replaced.
It is recommended that the wire rope inspection program
include reports on the examination of wire rope removed
from service. This information can be used to establish a
relationship between visual inspection and the rope’s actual
internal condition at the time of removal from serivce.
Frequent Inspection
A frequent daily visual inspection is recommended for all
running ropes in service. This inspection should be made on
all wire rope which can be expected to be in use during the
day’s operation. This inspection should be used to monitor
progressive degradation and to discover severe damages
necessitating wire rope replacement such as:
1. Distortion, Kinking, Crushing, Un-stranding, Bird caging,
Reduction of diameter, etc.
2. General corrosion.
3. Broken or cut strands.
4. Number, distribution and type of broken wires.
5. Evidence of core failure.
6. End fitting wear/abrasion.
Pay particular attention to areas of the rope where wear and
other damage is likely to occur:
7. Pick-up Points: Sections of wire rope that are
repeatedly stressed during each lift, such as those
sections in contact with sheaves.
8. End Attachments: The point where a fitting is
attached to the wire rope or the point where the wire
rope is attached to the drum.
9. Abuse Points: The point where the wire rope is
subjected to abnormal scuffing and scraping.
Periodic Inspection
Wire rope should be inspected periodically/annually or at a
shorter time interval if necessitated by environmental or
other adverse conditions, and shall cover the entire length of
the wire rope. Only the outer surface of the wire rope need
be inspected, and no attempt should be made to open the
rope. Periodic inspection should include all items listed
under frequent inspection plus the following:

 Loading...
Loading...