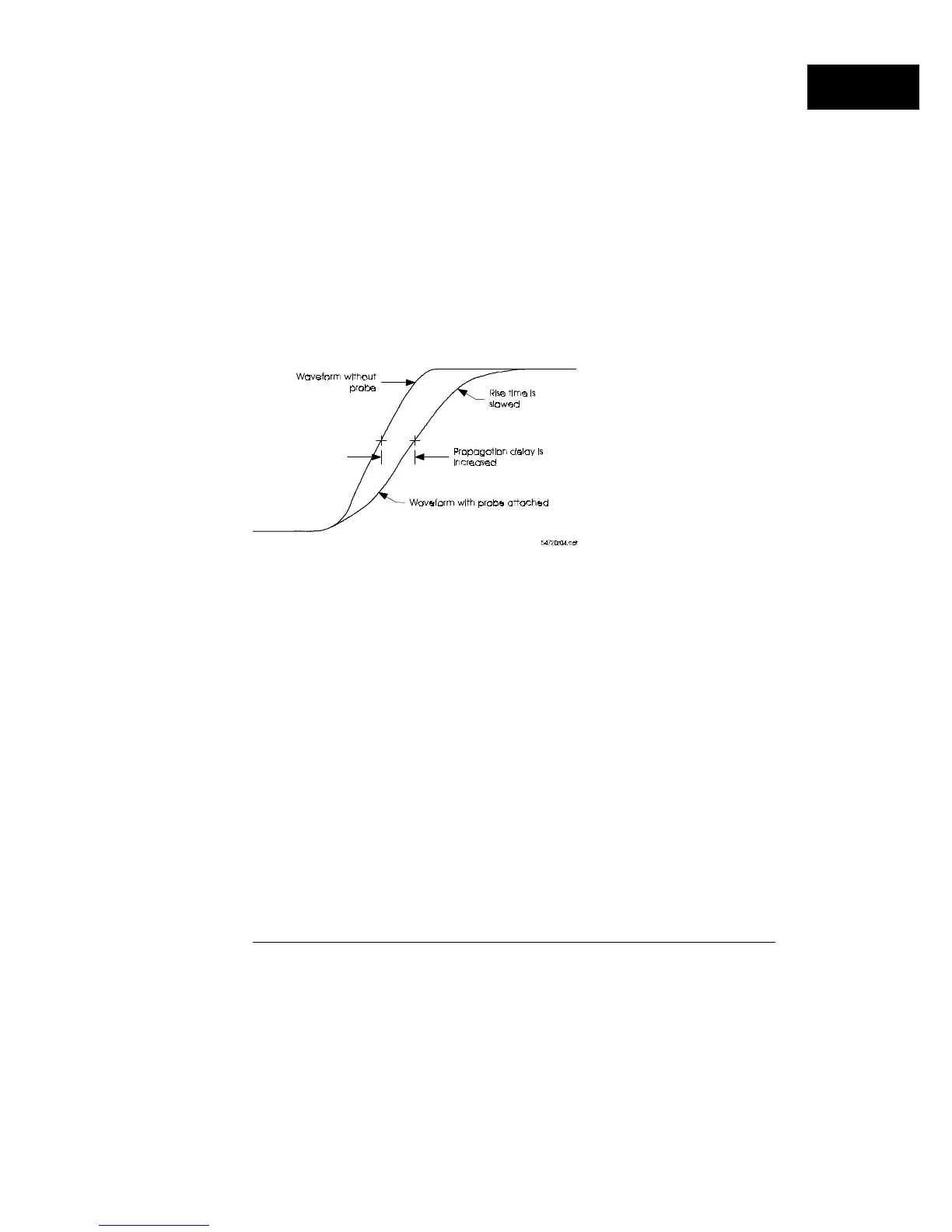
The capacitance of the probe tip to ground forms an RC circuit with the
output resistance of the circuit under test. The time constant of this RC
circuit slows the rise time of any transitions, increases the slew rate, and
introduces delay in the actual time of transitions. The approximate rise time
of a simple RC circuit is 2.2 RC. Thus, for an output resistance of 100
Ω
and
a probe tip capacitance of 8 pF, the real rise time at the node under test
cannot be faster than approximately 1.8 ns. Although, it might be faster
without the probe.
If the output of the circuit under test is current-limited (as is often the case
for CMOS), the slew rate is limited by the relationship dV/dT = I/C. See
figure 1-10.
Effects of probe capacitance
Figure 1-10
How the Oscilloscope Works
Choosing Probes
1–23
 Loading...
Loading...