Chapter 4 Maintenance 69
Ehave Series Full Digital IGBT CO
2
/MAG/MMA Multifunctional Inverter Welder User Manual
4.3.3 Rectifying Welder Faults and Welding Process Issues
When the welder is faulty or fails to perform self-identification, perform the checks specified in
Table 4-6.
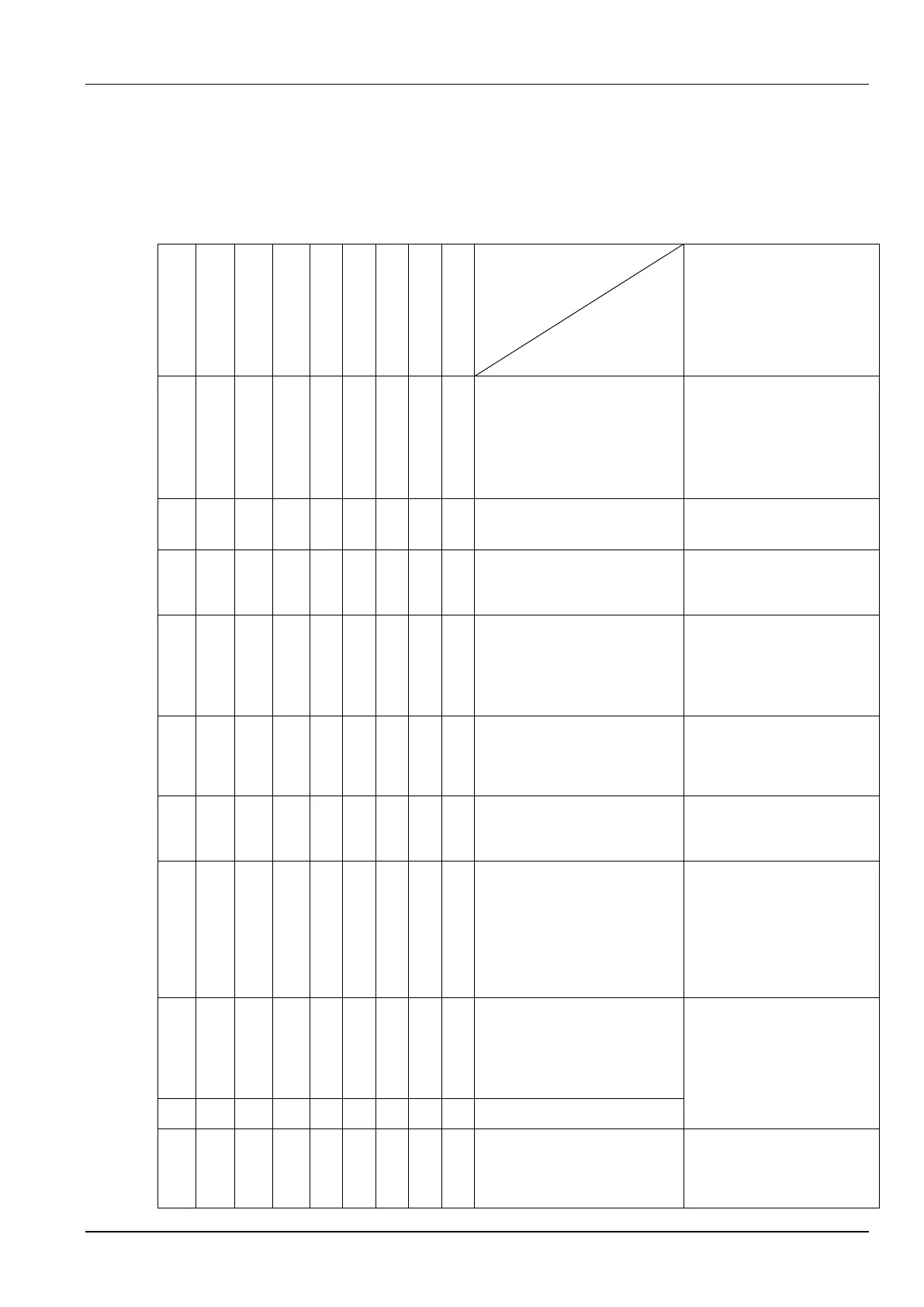
Table 4-6 Welder fault symptoms
Starting arc
generation failure
Sticking between
wire and workpiece
Sticking between
wire and tip
Fault Symptom
Check Content
Related Component or
Environment
The switch is not turned on or is
tripped.
The fuse is blown.
Phase loss occurs on the
three-phase power supply.
The connection is loose.
The cable is disconnected.
The connection is loose.
The switch is not turned on or is
tripped.
The fuse is blown.
The main valve of the gas cylinder is
not opened.
The gas volume is insufficient.
The gas purity does not meet the
requirement.
The gas flow control by the regulator
is inappropriate.
The connection to the gas tube or
gas cylinder is loose.
Electrically-heated CO
2
regulator
The gas tube is broken.
The connection to the regulator or
wire feeder is loose.
The wire inching roll and wire liner
do not match the wire diameter.
The wire inching roll is broken or the
groove is blocked.
The force imposed by the strut bar
of the wire inching roll is insufficient.
The inlet of the wire liner is blocked.
The welder power cable or welding
torch power cable is broken.
The connection to the wire feeder is
loose.
The cables are damaged.
Welder power cable and welding
torch power cable
Excessive roll-up or bending occurs.
The tip and wire liner do not match
the welding wire.
The tip or wire liner is worn out,
blocked, or deformed.
 Loading...
Loading...