Though the coil assembly is rigid and durable, sudden jolts or bangs can cause
random signals and inaccurate target IDs, as well as excessive wear and tear. Careful
sweeping will ensure the coil performs to an optimum level at all times.
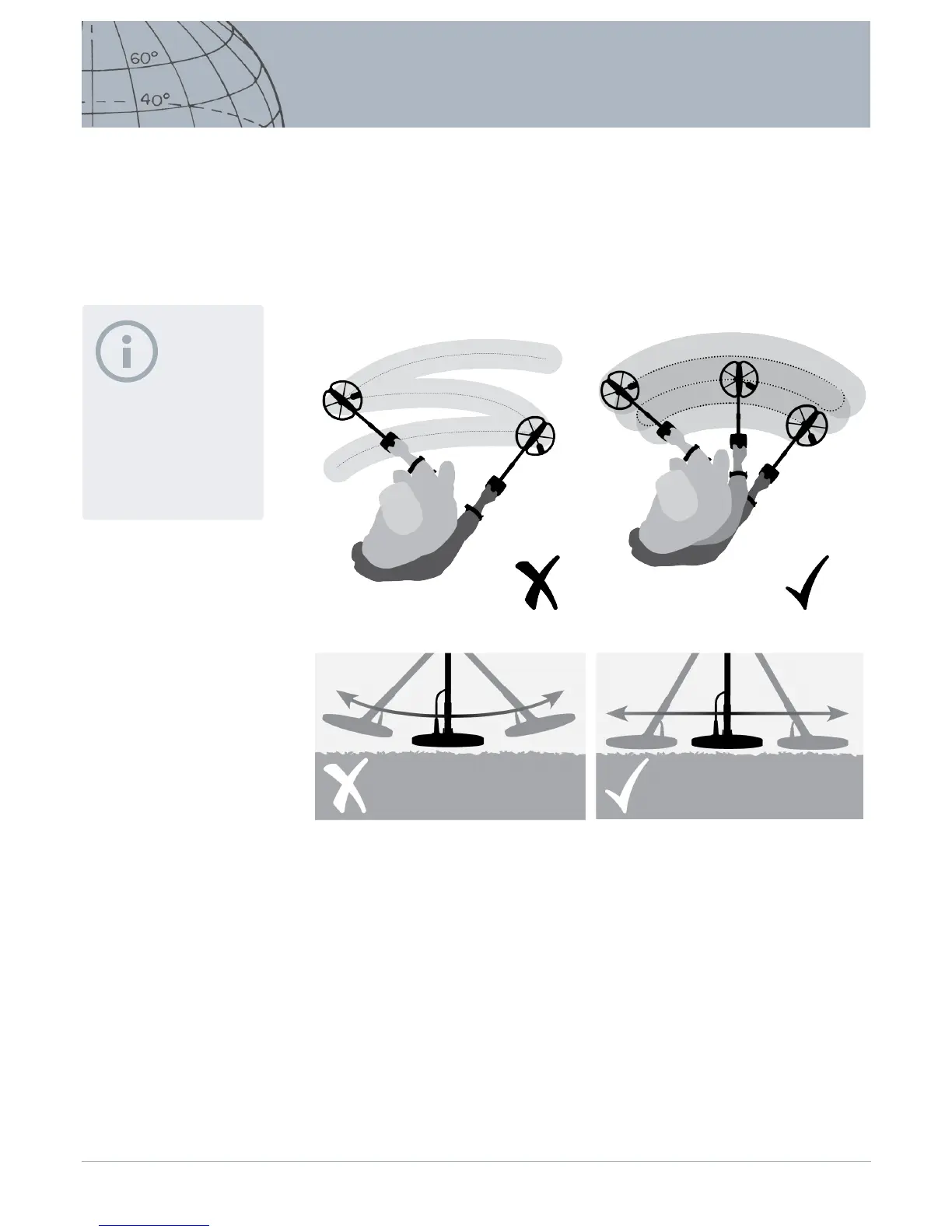
Practice sweeping the coil over the ground in a side-to-side motion while slowly
walking forward at the end of each sweep. Slightly overlap the previous sweep to
ensure full ground coverage. An average sweep speed is four seconds from left to
right to left.
Figure 42 – Sweeping the coil
Targets
Metal objects are referred to as targets. Targets are comprised of ferrous and
nonferrous metals. Ferrous metals are those containing iron; such as steel, nails and
some types of coins. Nonferrous metals are those which are not magnetic, such as
gold, silver, copper, bronze and aluminum.
You may wish to nd a range of both ferrous and nonferrous targets.
Examples of common targets:
• Desired high ferrous target – war relic
• Undesired high ferrous target – iron nail
• Desired nonferrous target – gold coin
• Undesired nonferrous target – pull-tab
NOTE
If you are getting signals from
a visibly clear patch of ground,
there could be buried metal
objects. Try nding another area
to practice.
 Loading...
Loading...











