3. Instructions
458
CS/CJ/NSJ Series Instructions Reference Manual (W474)
Example Programming
z Sine Function (C: #0000)
The following example shows APR(069) used to calculate the sine of 30°.
(SIN(30) = 0.5000)
z Cosine Function (C: #0001)
The following example shows APR(069) used to calculate the cosine of 30°.
(COS(30) = 0.8660)
z Floating-point Data (CJ2, CS1-H,
CJ1-H, CJ1M, and CS1D Only)
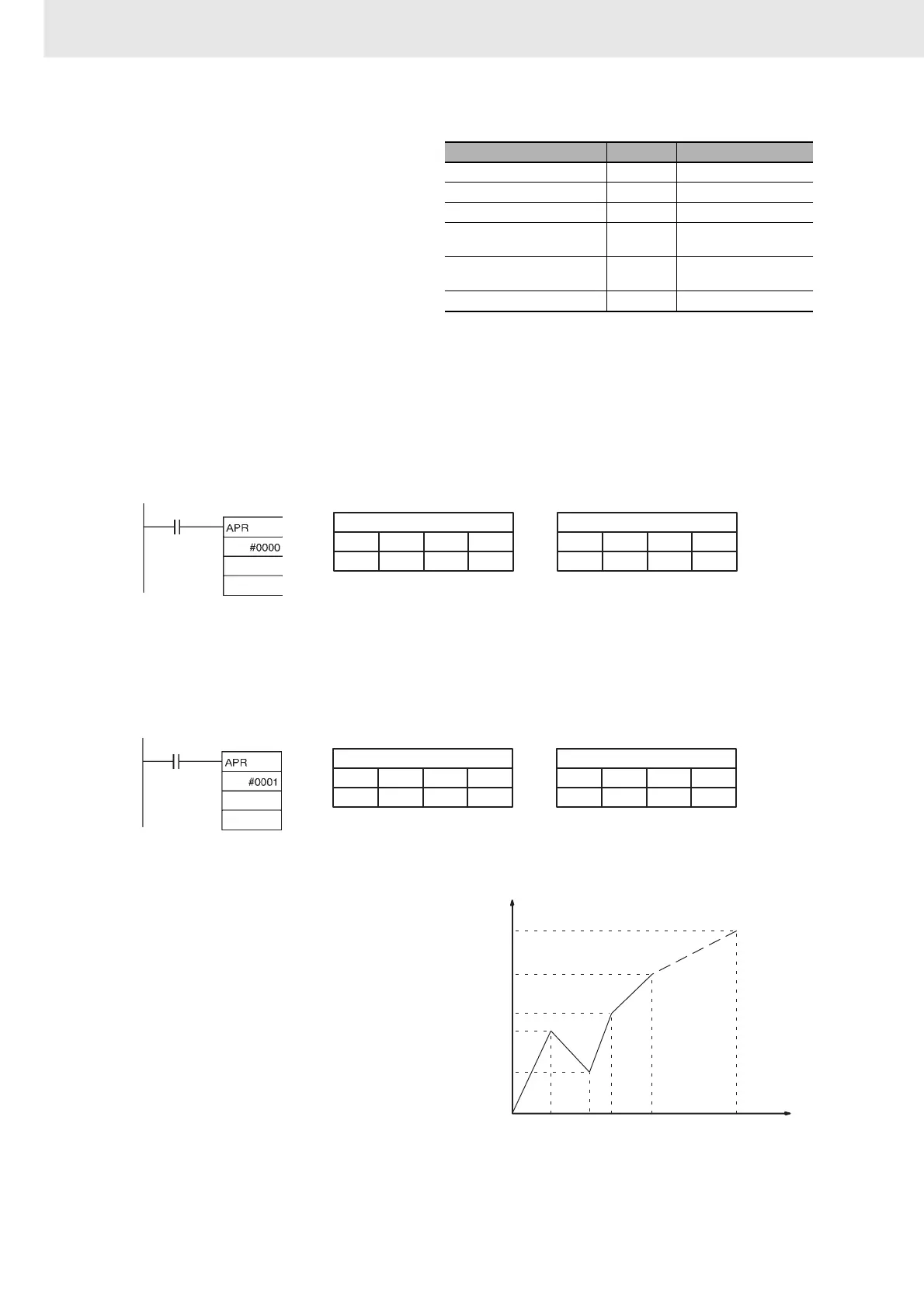
z Linear Extrapolation (C: Word Address)
• Using 16-bit Unsigned BCD or Binary Data
APR(069) processes the input data
specified in S based on the control data in C
and the line-segment data specified in the
table beginning at C+1. The result is output
to D.
Note If the “Floating-point specification” in bit 09 of C is set to 1, a constant
cannot be input for S.
Setting name Bit in C Setting
Input data (S) format 15 0
Output data (D) format 14 0
Source data form 13 0
Signed data specification for S
and D
11
0
Data length specification for S
and D
10
0
Floating-point specification 09 1: Floating-point data
S: D0 R: D100
0 ×10
1
×10
0
×10
–1
×10
–1
×10
–2
×10
–3
×10
–4
0 3 0 0 5 0 0 0
0.00
D000
D100
Source data Result
Set the source data in ×10
–1
degrees.
(0000 to 0900, BCD)
Result data has four significant digits,
fifth and higher digits are ignored.
(0000 to 9999, BCD)
Source data Result
Set the source data in ×10
–1
degrees.
(0000 to 0900, BCD)
Result data has four significant digits,
fifth and higher digits are ignored.
(0000 to 9999, BCD)
S: D10 R: D200
0 ×10
1
×10
0
×10
–1
×10
–1
×10
–2
×10
–3
×10
–4
0 3 0 0 8 6 6 0
0.00
D010
D200
Y
0
Y
2
Y
1
Y
3
Y
4
Y
m
X
0
X
1
X
2
X
3
X
4
X
m
X
Y
 Loading...
Loading...











