459
3. Instructions
CS/CJ/NSJ Series Instructions Reference Manual (W474)
Special Math Instructions
3
APR
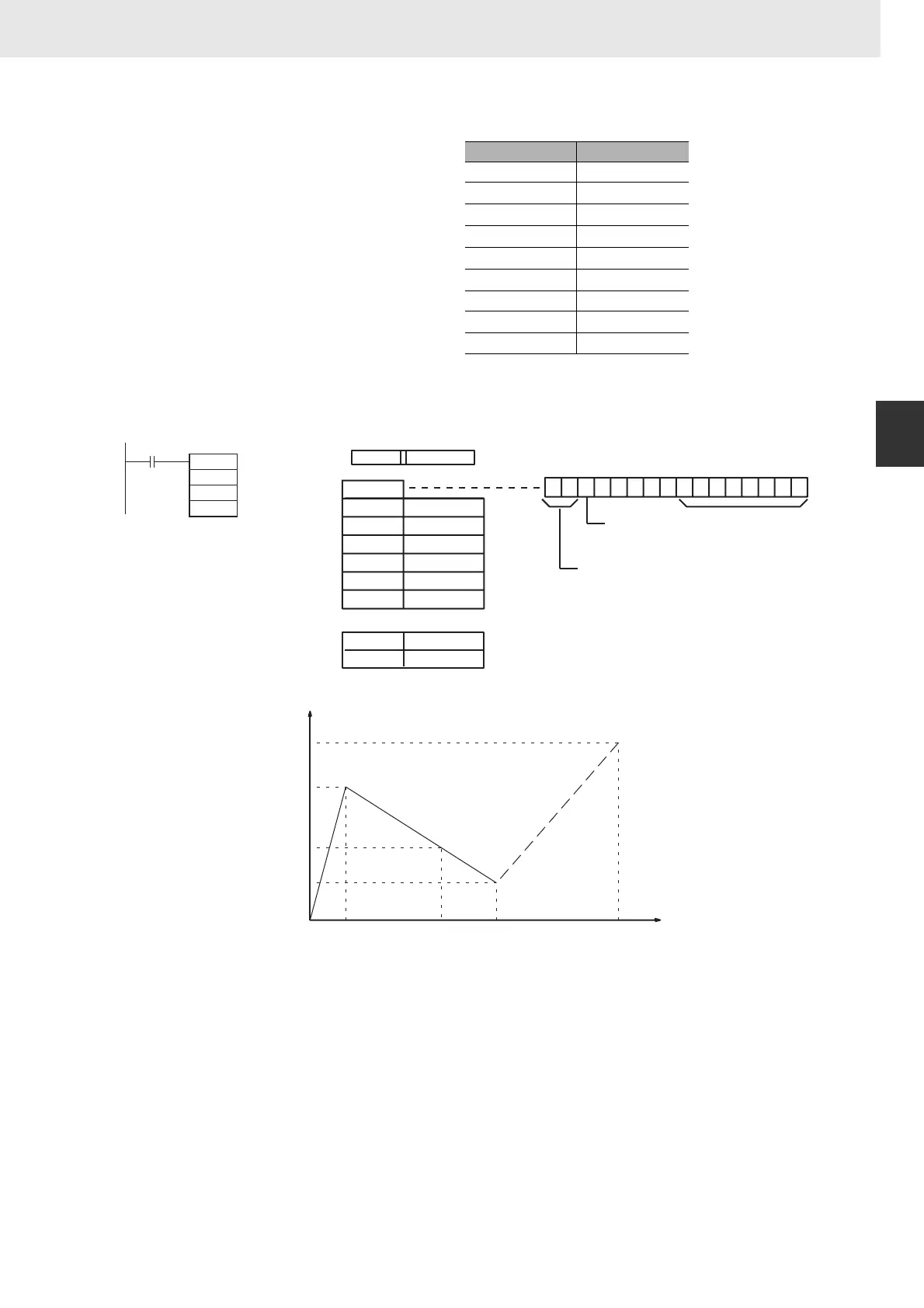
This example shows how to construct a linear extrapolation with 12 coordinates. The block of data is
continuous, as it must be, from D0 to D26 (C to C + (2 × 12 + 2)). The input data is taken from CIO 10,
and the result is output to CIO 11.
In this case, the source word, CIO 0010, contains 0014, and f(0014) = 0726 is output to R, CIO 0011.
The linear-extrapolation calculation is shown below.
•Y
n
= f(X
n
), Y
0
= f(X
0
)
• Be sure that X
n-1
< X
n
in all cases.
• Input all values of (X
n
, Y
n
) as binary data.
Word Coordinate
C+1 Xm (max. X value)
C+2 Y
0
C+3 X
1
C+4 Y
1
C+5 X
2
C+6 Y
2
↓↓
C+(2m+1) X
m
(max. X value)
C+(2m+2) Y
m
D0 000B Hex
D1 05F0 Hex
D2 0000 Hex
D3 0005 Hex
D4 0F00 Hex
D5 001A Hex
D6 0402 Hex
D25 05F0 Hex
D26 1F20 Hex
0000000000001011
15 00
x=S
X
12
Y
0
X
1
Y
1
Y
2
X
2
X
12
Y
12
Bit Bit
Content Coordinate
Output and input
both binary
(m–1 = 11: 12 line
segments)
↓↓ ↓
APR
D0
10
11
0.00
X
Y
$1F20
$0F00
$0726
$0402
(0,0)
$0005 $0014 $001A $05F0
(x,y)
Y0F00
0402 0F00–
001A 0005–
---------------------------------
0014 0015–()×+=
Ω 0726=
Ω 0F00 0086 000F )×(–=
Values are all hexadecimal (Hex).
 Loading...
Loading...











