6-2
Carrier Frequency Selection
Setting the Carrier Frequency
Using the following parameters the carrier frequency setting can be fitted to the applications requirements.
Related Parameters
Carrier Frequency, Current Derating and Overload Capability in Normal Duty 1 and 2
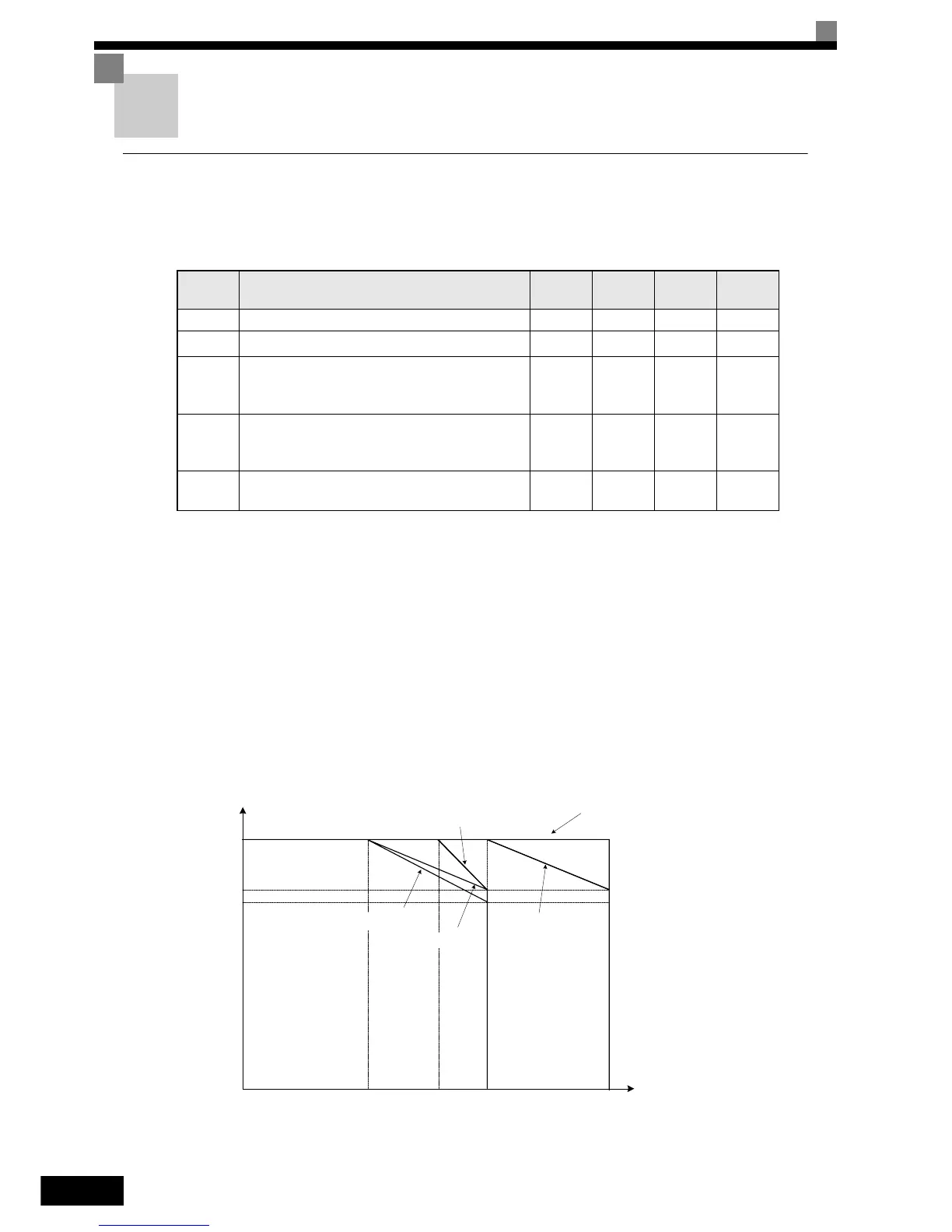
The Inverter overload capability depends among other things on the carrier frequency setting. If the carrier fre-
quency setting is higher than the factory setting, the overload current capability must be reduced.
Further, Normal Duty 2 enables a higher continuous output current before the Inverter overload calculation is
started.
Inverters in Protection Class IP00 and IP20 / NEMA 1 and Normal Duty 1
In Normal Duty 1 the default carrier frequency depends on the Inverter capacity. With the default setting the
overload capability is 120% of the rated output current for 1 minute. If the carrier frequency is set to a higher
value, the overload capability is reduced as shown in Fig 6.1.
Fig 6.1 Overload Capability depending on Carrier Frequency (IP00 and IP20 / NEMA 1) in Normal Duty 1
Parameter
No.
Name
Setting
Range
Factory
Setting
Changes
During
Operation?
Access
Level
C6-01 Normal duty selection 1 or 2 1 No A
C6-02 Carrier frequency selection 0 to F
6
*1
*1. The factory setting depends on the Inverter capacity.
No A
C6-03 Carrier frequency upper limit
2.0 to
15.0
*2
*3
*2. The setting range depends on the Inverter capacity.
*3. This parameter can only be set when C6-02 is set to F.
15.0 kHz
*1
No A
C6-04 Carrier frequency lower limit
0.4 to
15.0
*2*3
15.0 kHz
*1
No A
C6-05 Carrier frequency proportional gain
00 to 99
*3
00 No A
120%
96%
5kHz 10kHz 15kHz
0
Output Current for 1 min.
Carrier Freq.
8kHz
200V Class 37 to 90kW
400V Class 75 to 110kW
400V Class 132kW
200V Class 0.4 to 22kW
400V Class 0.4 to 22kW
90%
200V Class 30kW
400V Class 30 to 55kW
400V Class 160kW

 Loading...
Loading...











