FP3 MEWNET-TR
Chapter8-6. Page.138
134
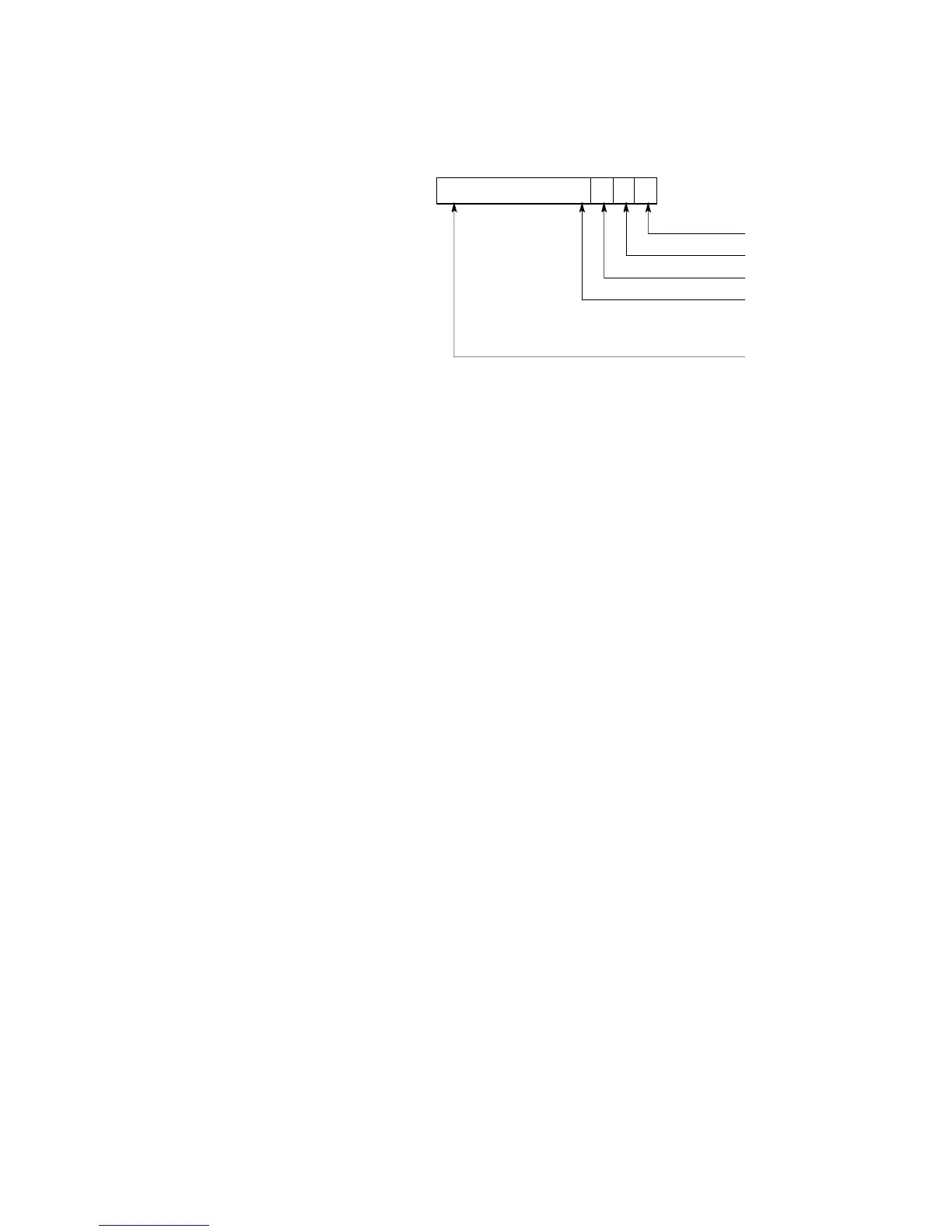
binary number system:
A number system that uses two symbols, “0” and “1”. Each digit position has a
weighted value of 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and so on begining with the least significant
(right-most) digit.
n
S
10
Bit position
Z0
×
2
0
=N0
23
SSSS
Zn
S
Z1 Z0Z2Z3
SSSS
Base = 2
Z1
×
2
1
=N1
Z2
×
2
2
=N2
Z3
×
2
3
=N3
Zn
×
2
n
=Nn
S
S
S
The sum of N0 through Nn is the decimal equivalent of the number in base “2”.
Block Check Code (BCC):
Thiscode isused to detecterrors in message transmissions.It is createdbyExclusive
ORing allof thecodes from the headerthough the lasttext character, thentranslating
the result (8-bit) data into two ASCII characters.
buffer:
A group of registers used for temporary data storage. This is used for data
transmission and works effectively when there are transmission rate differences
between sending and receiving devices.
bug:
Software errors which will cause unexpected actions.
bus:
Power distribution conductors.
Central Processing Unit:
The Central Processing Unit is usually referred to as the CPU.
The CPU controls system activities of the programmable controller.
character:
A symbol such as a letter of the alphabet or decimal number. An ASCII character is
most commonly used to express characters using binary.
complement:
A logicaloperation that inverts a signal or bit. The complement of “1” is “0”, and the
complement of “0” is “1”.
computer link:
One of the communication methods between a computer and programmable
controllers. In a computer link, the computer is the host, and it can control
programmablecontrollers usinga protocol.For FPseriesprogrammablecontrollers,
communication between a computer and programmable controllers is performed
using the MEWTOCOL-COM communication protocol. From the computer, you
can read, write, or monitor data stored in the memory of a programmable controller.
CPU:
See Central Processing Unit.
CRT:
Abbreviation for cathode-ray tube.
8-6. Terminology
 Loading...
Loading...











