49
NOTE-MH01-EN rev05
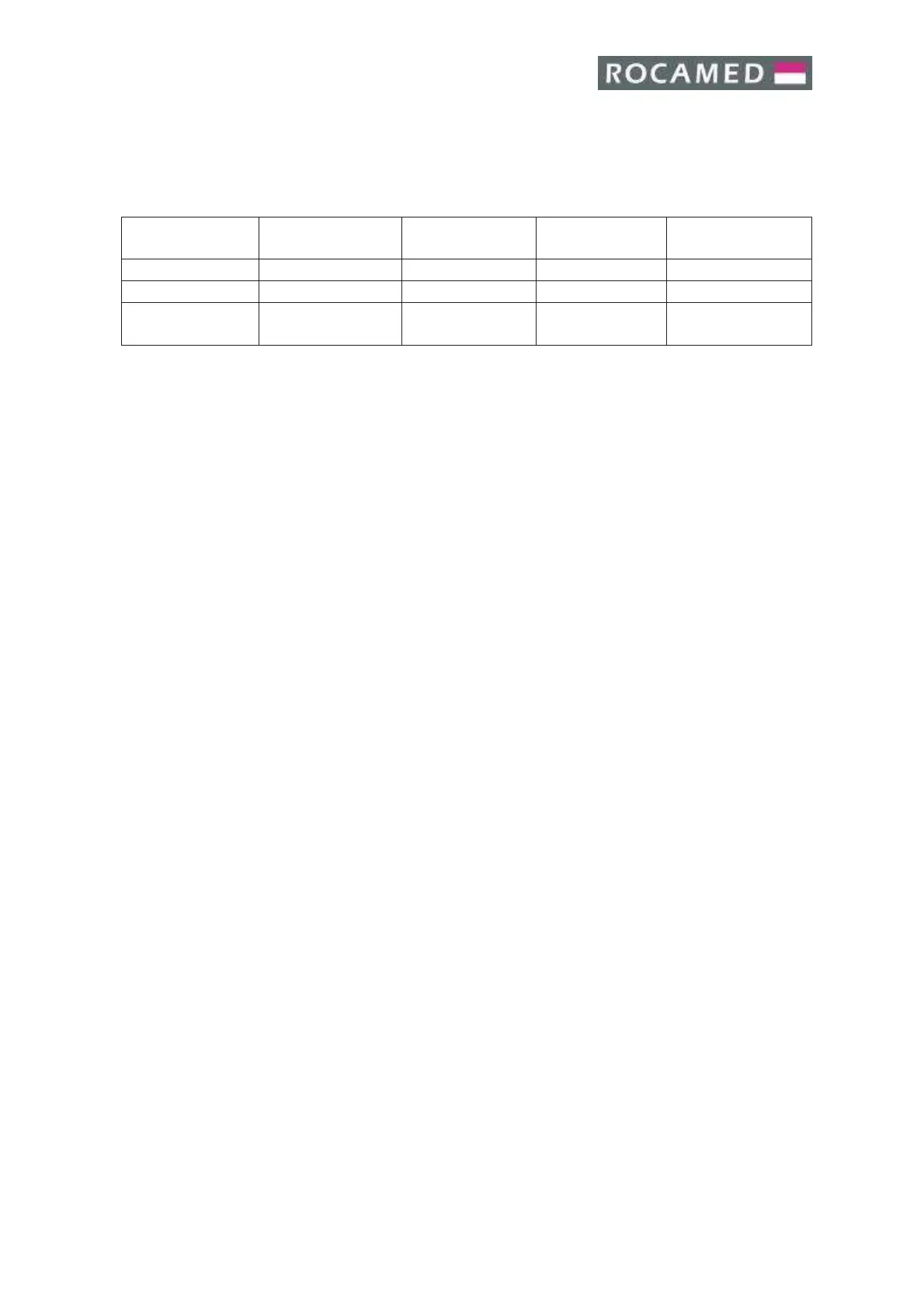
The following table shows the suggested pulse energy, repetition rate, and average power
for endoscopic ablation, vaporization, excision, incision, and coagulation of soft tissue in
urological applications:
Urology – Recommended Treatment Clinical Parameters
0.8 – 3.5 8 – 15 8 – 20 365-800 !m
NOTE!
Laser settings are guidelines only; always start with low settings and increase to achieve the
desired tissue effect. Energy delivered endoscopically in a fluid medium.
6.4 Urinary Lithotripsy Indications
The following applications are indicated for urinary Lithotripsy while using the Ho:YAG
wavelength: Endoscopic fragmentation of urinary (urethral, ureteral, bladder and renal)
calculi, including cystine, calcium oxalate, monohydrate and calcium oxalate dehydrate stones.
6.4.1 Urinary Lithotripsy Contraindications
The Ho:YAG wavelength must not be used in patients with the following conditions:
• Inability to receive endoscopic treatment.
• Intolerance to anaesthesia.
Contraindications for Uretero-renoscopy (URS):
- Acute proneness to bleeding, anticoagulation
- Untreated infections of the urinary passages
- Difficult access to the stone in the case of:
o Narrow ureter
o Adenoma of the prostate
o Urinary diversion (conduit, neo bladder, pouch, urinary diversion through intestinal
segments)
o Implantation of new ureters
o Ureteroceles
o Ureter strictures
Contraindications for Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL):
- Acute proneness to bleeding, anticoagulation
- Untreated infections of the urinary passages
- Tumor in the access area
- Pregnancy
Difficult access to the stone in the case of:
- Skeletal anomalies
- Renal anomalies
- Intestinal interposition
- Pleural interposition

 Loading...
Loading...