Communications services
3.6 Secure Communication
Communication
38 Function Manual, 11/2019, A5E03735815-AH
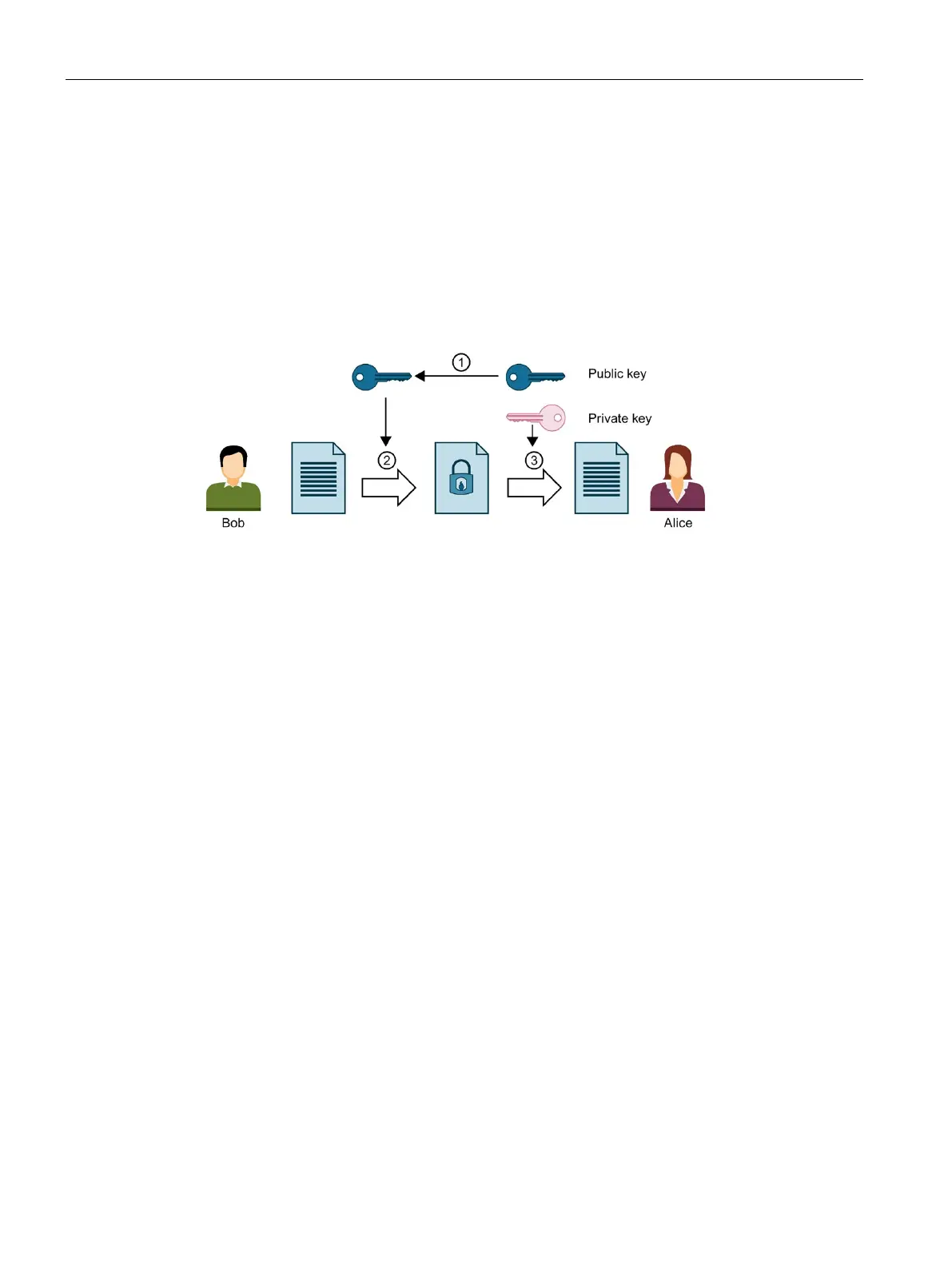
Asymmetric encryption
Asymmetric encryption works with a pair of keys consisting of one public key and one private
key. Used with a PKI, it is also known as Public Key cryptography or simply PKI
cryptography. A communication partner, Alice in the figure below, has a private key and a
public key. The public key is provided to the public, in other words any potential
communication partner. Anyone with the public key can encrypt messages for Alice. In the
figure below, this is Bob.
Alice's private key, which she must not disclose, is used by Alice to decrypt an encrypted
message addressed to her.
Alice provides Bob with her public key. No precautionary measures are required to this pur-
pose: Anyone can use the public key for messages to Alice if they are sure that it is actually
Bob encrypts his message with Alice's public key.
Alice decrypts the encrypted message from Bob with her private key. As only Alice has the
private key and never discloses it, only she can decrypt the message. With her private key, she
can decrypt any message encrypted with her public key - not only messages from Bob.
Figure 3-8 Asymmetric encryption
The system can be compared to a mailbox into which anyone can put a message, but from
which only the person with the key can remove messages.
● Advantages: A message encrypted with a public key can only be decrypted by the owner
of the private key. As another (private) key is required for decryption, it is also much
harder to work out the decryption key on the basis of large numbers of encrypted
messages. This means that the public key does not have to be kept strictly confidential,
unlike with symmetric keys.
Another advantage is easier distribution of public keys. No specially secured channel is
required in asymmetric cryptography to transfer the public key from the recipient to the
sender encrypting the messages. Less work is thus required in managing the keys than
would be the case in symmetric encryption procedures.
● Disadvantages: Complex algorithm (e.g. RSA, named after the three mathematicians
Rivest, Shamir and Adleman), and therefore poorer performance than with symmetric
encryption.

 Loading...
Loading...