SMARTRG INC. PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT © 2016 19
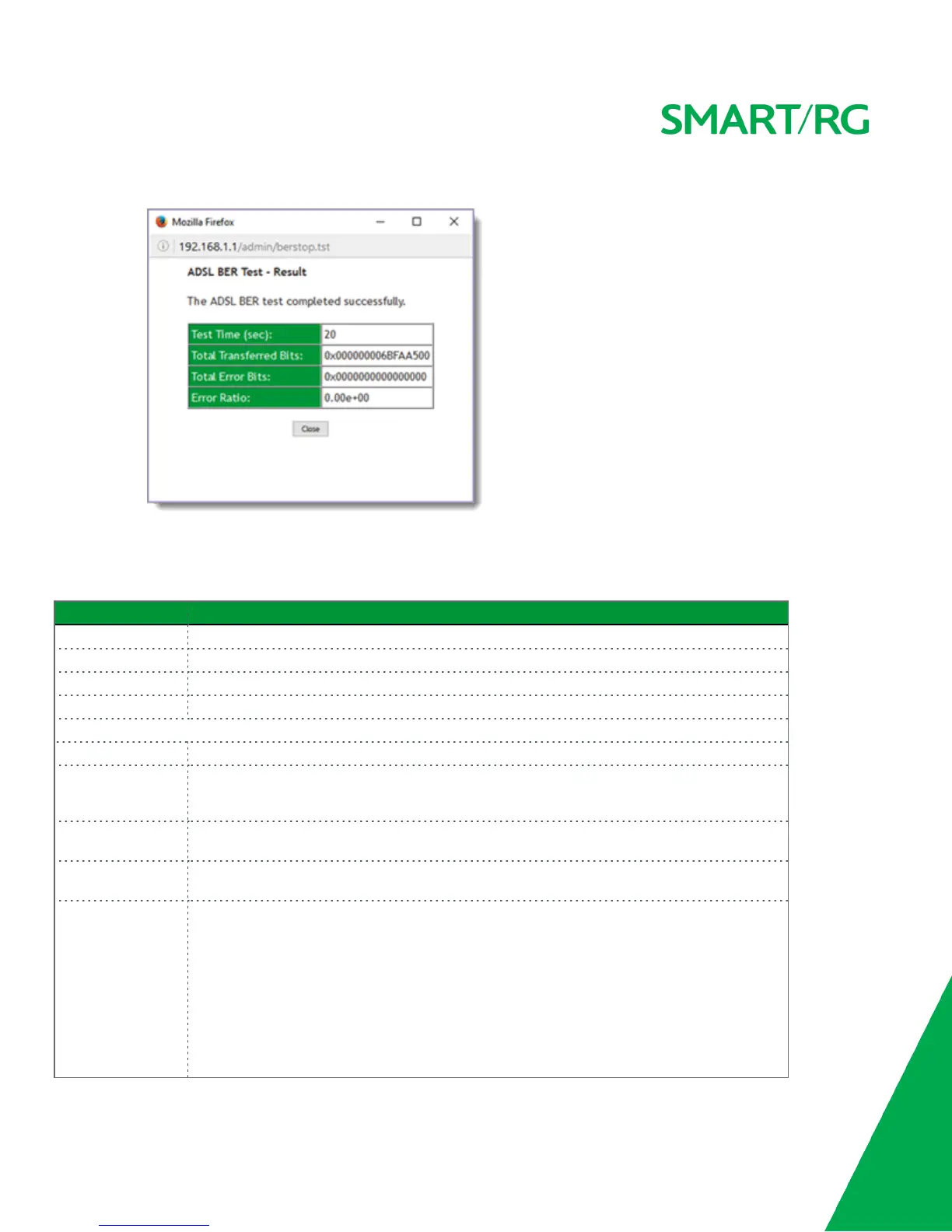
Comparison errors are tabulated and displayed in the dialog box.
3. To reset the counters, click Reset Statistics at the bottom of the page.
The fields on this page are explained in the following table.
Field Name Description
Mode xDSL mode that the modem has trained under, such as ADSL2+, G.DMT, etc.
Traffic Type Connection type. Options are:
ATM
and
PTM
.
Status Status of the connection. Options are:
Up
,
Disabled
,
NoSignal
, and
Initializing
.
Link Power State Current link power management state (e.g., L0, L2, L3).
Downstream
and
Upstream
columns
Line Coding (Trellis) State of theTrellis Coded Modulation. Options are
On
and
Off
.
SNR Margin (dB) The signal-to-noise ration margin (SNRM) is the maximum increase (in dB) of the received
noise power, such that the modem can still meet all of the target BERs over all the frame
bearers. [2]
Attenuation (dB)
The signal attenuation is defined as the difference in dB between the power received at the
near-end and that transmitted from the far-end. [2]
Output Power
(dBm)
Transmission power from the gateway to the DSL loop relative to one Milliwat (dBm).
Attainable Rate
(Kbps)
The typically obtainable sync rate, i.e., the attainable net data rate that the receive PMS-TC
and PMD functions are designed to support under the following conditions:
l Single frame bearer and single latency operation
l Signal-to-Noise Ratio Margin (SNRM) to be equal or above the SNR Target Margin
l BER not to exceed the highest BER configured for one (or more) latency paths
l Latency not to exceed the highest latency configured for one (or more) latency paths
l Accounting for all coding gains available (e.g., trellis coding, RS FEC) with latency
bound
 Loading...
Loading...