TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 77
Q
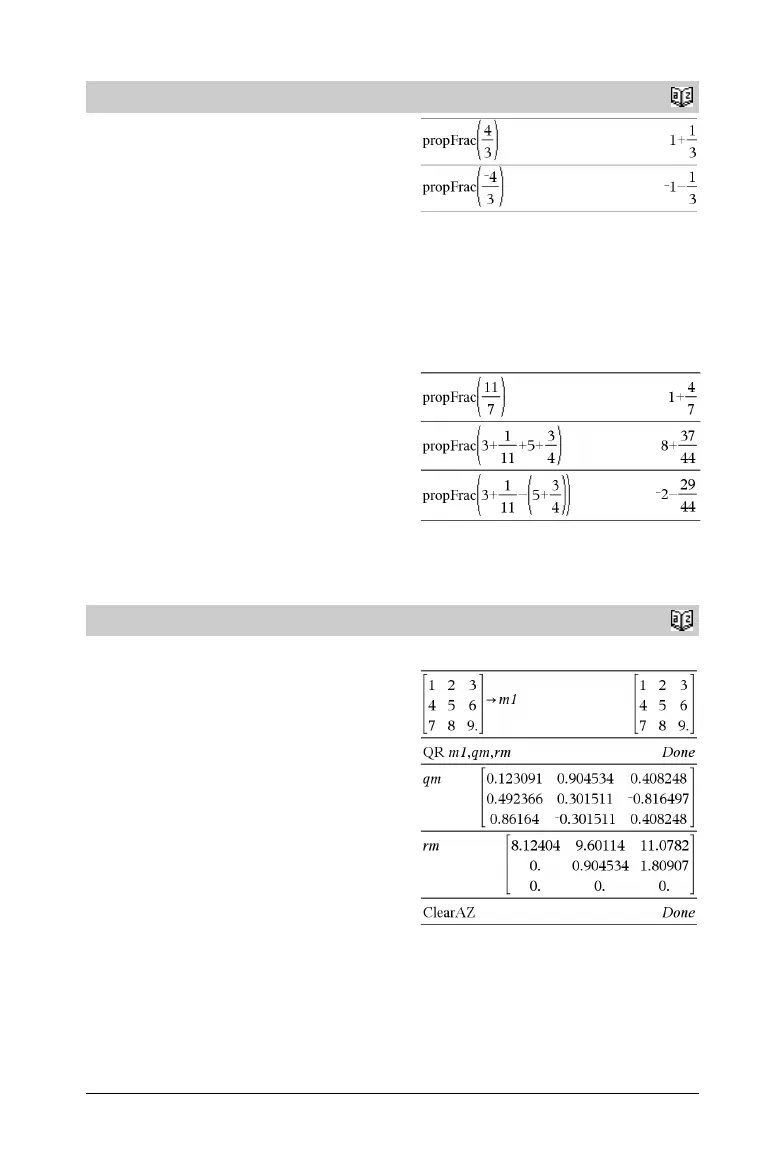
propFrac()
Catalog
>
propFrac(Va lu e1 [, Va r ]) ⇒ value
propFrac(rational_number) returns rational_number as the sum
of an integer and a fraction having the same sign and a greater
denominator magnitude than numerator magnitude.
propFrac(rational_expression,Va r) returns the sum of proper
ratios and a polynomial with respect to Va r . The degree of Va r in the
denominator exceeds the degree of Va r in the numerator in each
proper ratio. Similar powers of Va r are collected. The terms and their
factors are sorted with Va r as the main variable.
If Va r is omitted, a proper fraction expansion is done with respect to
the most main variable. The coefficients of the polynomial part are
then made proper with respect to their most main variable first and so
on.
You can use the propFrac() function to represent mixed fractions
and demonstrate addition and subtraction of mixed fractions.
QR
Catalog
>
QR Matrix, qMatrix, rMatrix[, Tol ]
Calculates the Householder QR factorization of a real or complex
matrix. The resulting Q and R matrices are stored to the specified
Matrix. The Q matrix is unitary. The R matrix is upper triangular.
Optionally, any matrix element is treated as zero if its absolute value
is less than Tol . This tolerance is used only if the matrix has floating-
point entries and does not contain any symbolic variables that have
not been assigned a value. Otherwise, Tol is ignored.
• If you use
/
·
or set the Auto or Approximate
mode to Approximate, computations are done using floating-
point arithmetic.
•If Tol is omitted or not used, the default tolerance is calculated
as:
5EL14 ·max(dim(Matrix)) ·rowNorm(Matrix)
The floating-point number (9.) in m1 causes results to be
calculated in floating-point form.
The QR factorization is computed numerically using Householder
transformations. The symbolic solution is computed using Gram-
Schmidt. The columns in qMatName are the orthonormal basis
vectors that span the space defined by matrix.

 Loading...
Loading...