How a Screed Works
P/N 7010-0341 www.topconpositioning.com
2-9
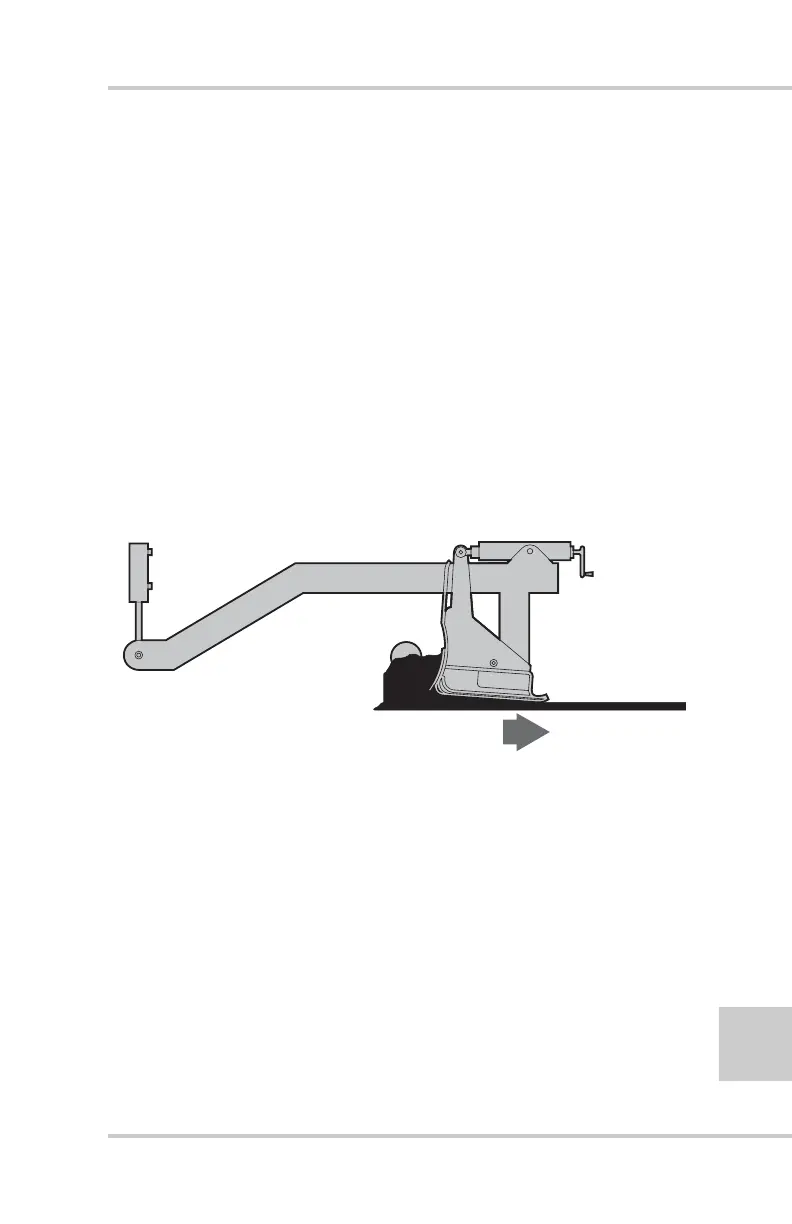
Reaction of Material Under Screed (“R”)
Ideally, every truck load of material delivered to the paver
would be exactly like every other load, with no variation.
However, as a practical matter, changes in mix characteristics
such as mix temperature, density, gradation, A.C. Content,
segregation, etc., will affect the internal stresses developed
within the mix, which in turn affects the resistance of the mix to
flow under the screed (reaction of material under screed, “R”).
The key element to bear in mind is that the screed passing over
the paving material will compact the material to a certain
degree. Variables in the resistance of the material to compactive
forces will cause changes in the screed's angle of attack, which
in turn will affect mat thickness and therefore mat smoothness
(Figure 2-12).
Figure 2-12. Reaction of Material Under Screed
Gradation Mix Characteristics
This aspect of the paving material will vary according to
the intended use of the material as abase course, binder
course or the final wearing surface. Normally, maximum
aggregate size, ratio of aggregates, fines content and most
importantly, asphaltic binder content, is specified by the
contracting agency.
Reaction of Material
Under Screed
(Force "R")
R

 Loading...
Loading...