300004969171/B Page 141 of 148
Accuracy Analysis
Tissue Classification Algorithm Development:
Regions of Interest (ROIs) that represent four basic homogeneous tissue types (i.e., fibrous tissue,
fibro-fatty, necrotic core, and dense calcium) were identified on the histology slides, and their
location was recorded on the digitized histology images. A total of 290 homogenous ROIs were
selected from the 93 lesion sections. See Table 1 for the corresponding distribution of the ROIs
by tissue type.
Table 1. The number of regions-of-interest (ROIs) of each tissue type that were used for
training the Volcano system Eagle Eye VH algorithm.
Tissue Type Number of Training ROIs
Fibrous Tissue 114
A classification algorithm was trained based on these ROIs that included the plaque type of each
ROI and corresponding backscatter spectral properties that were determined from the IVUS data.
VH Algorithm Evaluation:
The algorithm developed above from the set of homogenous ROIs was used to create VH IVUS
images for multiple lesion sections. For accuracy analysis, a randomized set of heterogeneous
ROIs were identified on the histology slides, and their location was recorded on the digitized
histology image. The corresponding regions on the final VH IVUS images were also identified
and compared to the digitized histology images. From separate data collection of 51 LADs (94
sections), 889 heterogeneous ROIs were further selected representing the following distribution
of tissue types:
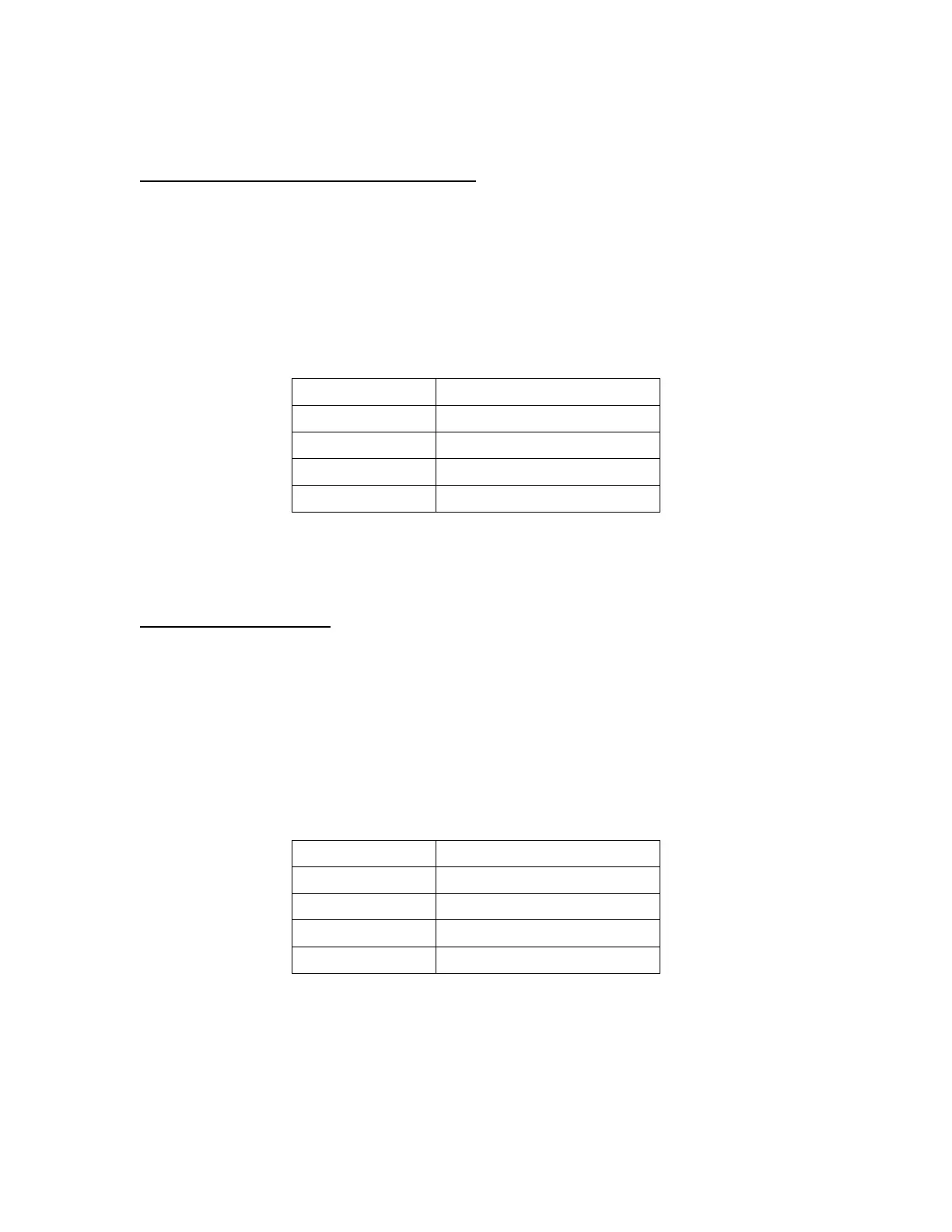
Table 2. The number of regions-of-interest (ROIs) of each lesion type that were used for
evaluation of the accuracy the Eagle Eye VH algorithm.
Number of Evaluation ROIs
Fibro-Fatty 130
Necrotic Core 132
Dense Calcium 156
Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive accuracy were calculated using standard formulae.
 Loading...
Loading...