36
Introduction
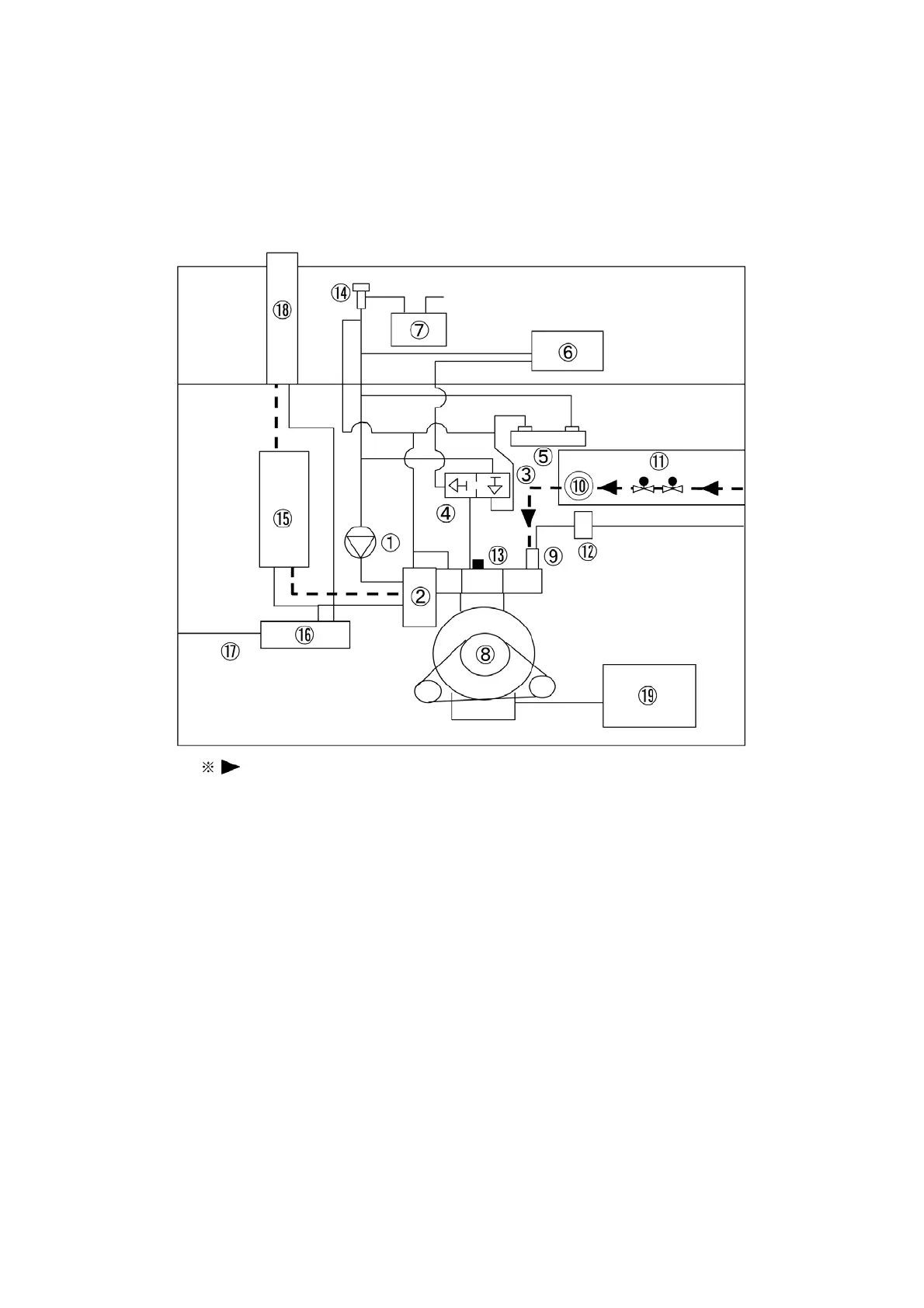
Fuel gas · · · Fuel gas flowing through the series of electromagnetic gas valves ( ⑪ ) is depressurized down to
atmospheric pressure by the gas regulator ( ⑩ ) and supplied to the gas mixer ( ⑨ ).
The high-pressure portion of the fuel system is separated from the engine compartment to assure
safety.
① : Engine coolant pump ⑧ : Engine ⑮ : Exhaust muffler
② : Exhaust air heat exchanger ⑨ : Gas mixer ⑯ : Exhaust water drain filter
③ : Thermostat (140 ℉ (60 ℃ ) ⑩ : Gas regulator ⑰ : Exhaust water drain hose
④ : Thermostat (158 ℉ (70 ℃ ) ⑪ : Electromagnetic gas valve ⑱ : Exhaust water drain trapper
⑤ : Sub heat exchanger ⑫ : Air filter ⑲ : Sub oil reservoir
⑥ : Radiator ⑬ : Engine coolant temperature sensor
⑦ : Engine coolant reserve tank ⑭ : Radiator cap
shows the fuel gas flow direction
 Loading...
Loading...