Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-RM003N-EN-P - October 2011 679
Structured Text Programming Appendix C
Instructions
Structured text statements can also be instructions. See the Locator Table
on page 29
for a list of the instructions available in structured text. A structured
text instruction executes each time it is scanned. A structured text instruction
within a construct executes every time the conditions of the construct are true. If
the conditions of the construct are false, the statements within the construct are
not scanned. There is no rung-condition or state transition that triggers
execution.
This differs from function block instructions that use EnableIn to trigger
execution. Structured text instructions execute as if EnableIn is always set.
This also differs from relay ladder instructions that use rung-condition-in to
trigger execution. Some relay ladder instructions only execute when rung-
condition-in toggles from false to true. These are transitional relay ladder
instructions. In structured text, instructions will execute each time they are
scanned unless you pre-condition the execution of the structured text instruction.
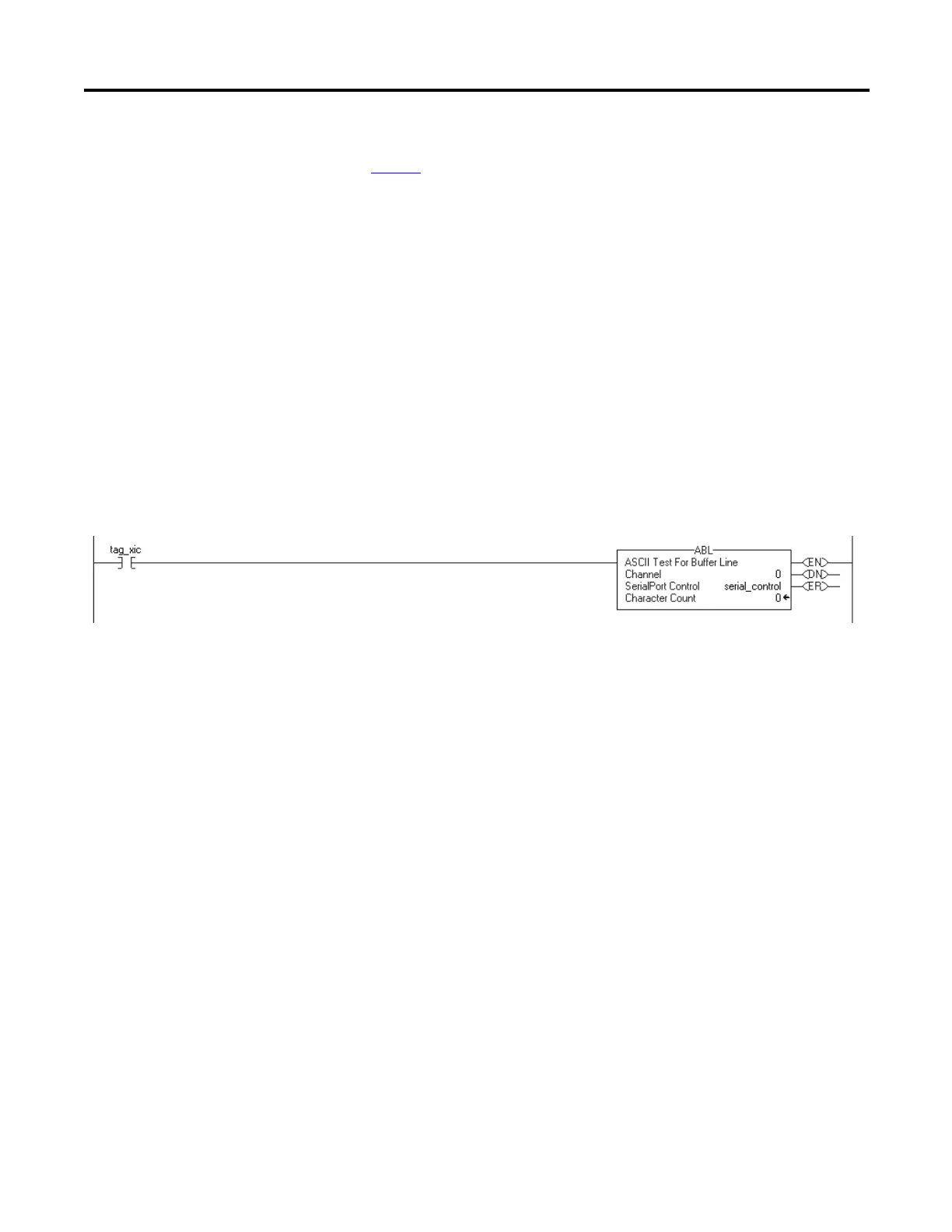
For example, the ABL instruction is a transitional instruction in relay ladder. In
this example, the ABL instruction only executes on a scan when tag_xic
transitions from cleared to set. The ABL instruction does not execute when
tag_xic stays set or when tag_xic is cleared.
In structured text, if you write this example as:
IF tag_xic THEN ABL(0,serial_control);
END_IF;
The ABL instruction will execute every scan that tag_xic is set, not just when
tag_xic transitions from cleared to set.
If you want the ABL instruction to execute only when tag_xic transitions from
cleared to set, you have to condition the structured text instruction. Use a
one shot to trigger execution.
osri_1.InputBit := tag_xic;
OSRI(osri_1);
IF (osri_1.OutputBit) THEN
ABL(0,serial_control);
END_IF;
 Loading...
Loading...











