227
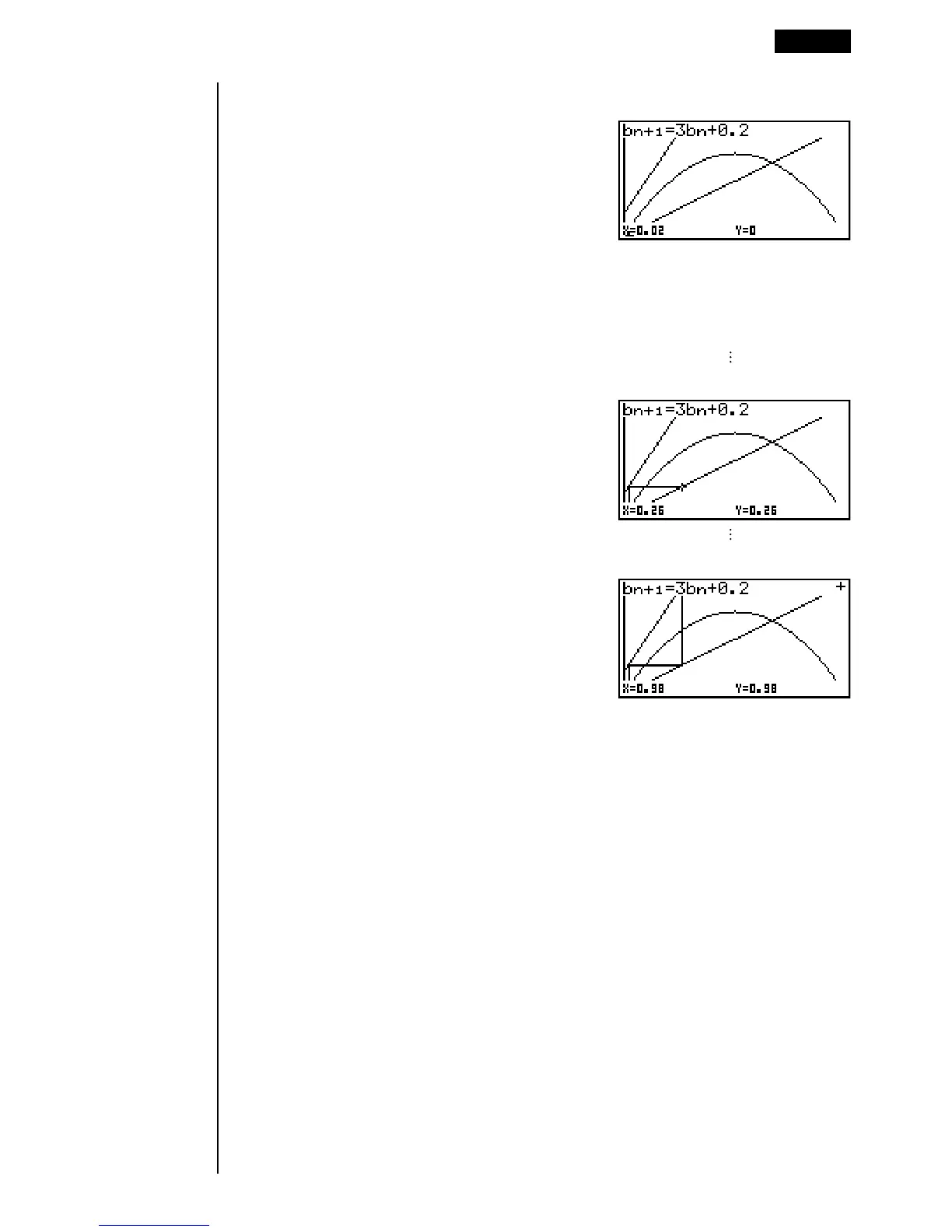
2. Press w and then either f or c to make the pointer appear at the pointer
start point (bnStr = 0.02).
• The Y value for the pointer start point is always 0.
3. Each press of w draws web-like lines on the display.
w
↓
w
↓
This graph indicates that recursion formula bn+1 = 3bn + 0.2 is divergent.
•Inputting bn or n for the expression an+1, or Inputting an or n for the expression
bn+1 for linear recursion between two terms causes an error.
Editing Tables and Drawing Graphs 16 - 3
 Loading...
Loading...