Working with t he notebook
The operating system d etects all hard disks in a disk array as a single physical
hard disk. The individual disk drives in a disk array are called "members". Member
configuration information is recorded in the reserved sector of the hard disk. With th is
information the hard disk can be identified as a membe r.
There are usually a few methods by which hard disks can be combined. These metho ds
are referred to as different RAID levels. The different RAID levels represent different
performance and security levels as well as implementation costs.
Depending on the size of the hard disk, the process for combining tw o
hard drives to create a RAID group can take several h ours. During this
time period, your screen will turn black.
For further information about how to con figure your RAID system, r efer to the
Help function of the RAID Manager so ftware on your device.
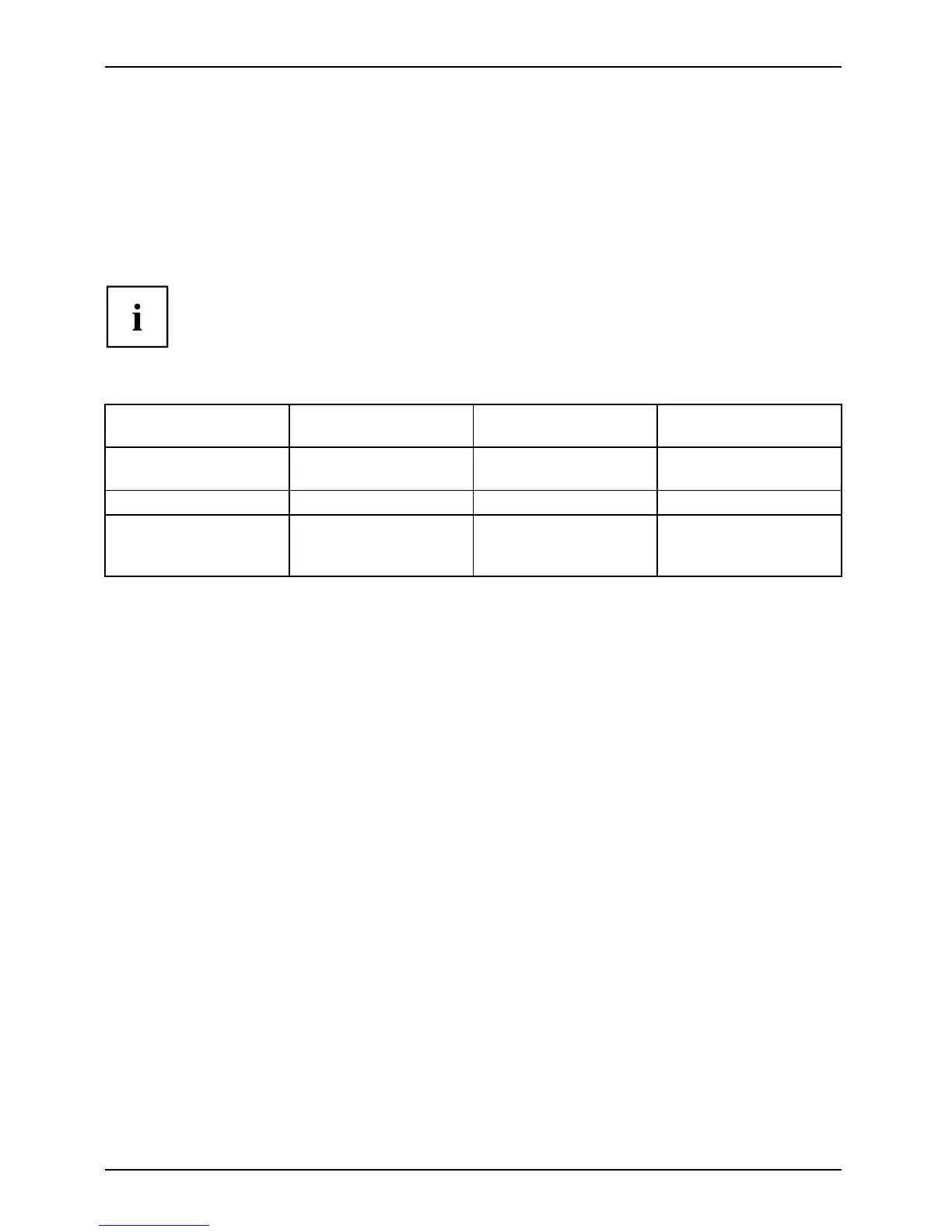
RAID level
Number of hard disk
drives Capacity Benefits
RAID 0 (Striping)
2
Number of hard drives
x smallest size
Highest performance
without data protection
RAID 1 (Mirroring)
2
Smallest size
Data protection
SPAN (JBOD)
2
Up to 4, total of all hard
disk drives
No performance
advantages, no data
protection
RAID 0 (Striping)
Reads and w rites sectors of data interleaved between multiple drives.
RAID 0 does not support fault tolerance. If one hard drive fails, the en tire
disk array is affected by the data loss.
RAID 0 is designed to deliver optimum performan ce. The disk arra y data capacity is
equal to the number of hard disks times the smallest hard disk capacity. T he block
size can be set to be bet ween 4 KB and 128 KB.
RAID 1 ( Mirroring)
Writing identical data on both hard disk drives (redundancy, mirroring) and parallel reading mode.
If one of the mirrored hard disks fails or no longer reacts due to a mecha nical fault, the remaining
hard disk assumes the function. This protects the data from being lost.
Due to this redundancy, the data c apacity of the d isk array is equivalent to
the capacity of the smallest hard disk.
40 AMILO Notebook operating manual, edition 3
 Loading...
Loading...