2-38 ALPS Advanced Line Protection System
GE Power Management
2.3 PROTECTION SETTINGS 2 CALCULATION OF SETTINGS
2
2.3.18 OS BLOCKING
Out-of-step blocking (OSB) is offered as a standard feature in the ALPS. Refer to Section 1.4.4: OUT-OF-STEP BLOCK-
ING on page 1–14 for a complete description of the OSB logic. The OSB function is implemented through the distance
functions in the ALPS system as shown in Figure 2–13: TL5PICKUP / TL6PICKUP REPRESENTATION on page 2–35. For
an out-of-step condition, the apparent impedance seen by the relay will follow a typical swing line as shown below. The
ALPS recognizes an out-of-step condition by sensing that the MOB function operates first, and that the coordinating func-
tion (Zone 2, 3 or 4) operates a short time later. The MOBZONE setting is used to select which of the zones (Zone 2, 3 or
4) is used as the coordinating zone. Note that Zone 4 can only be used as the coordinating zone when it is set to look in the
forward direction (Z4DIRECTN = FORWRD).
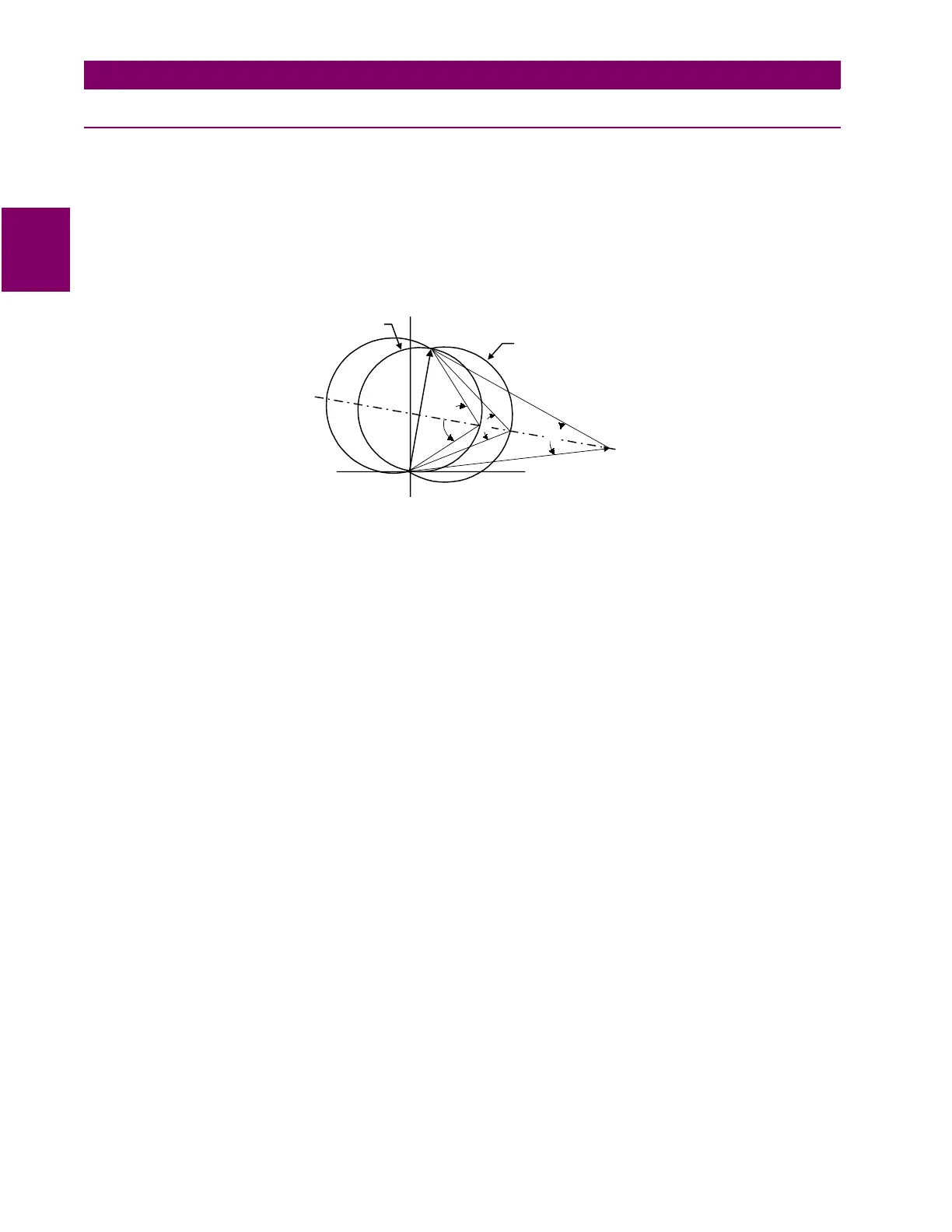
Figure 2–14: OSB FUNCTION CHARACTERISTIC
Angles A, B and C are determined as a function of the reach (Zc) of the coordinating zone, the maximum load flow (mini-
mum Zload) and the fastest swing (first slip cycle). The angle A in the figure is selected via ZxPHARANG (x = 2, 3 or 4) and
determines the shape of the coordinating zone characteristic. Angle B is selected via the MOBCHARANG setting and
determines the shape of the MOB characteristic. Angle B should be set so the time for the fastest swing to traverse from
angle B to angle A is not less than 30 milliseconds. In addition, the A and B angle settings must be selected so that the dif-
ference between angles B and C is never less than 20°. Note that angle C is determined as a function of the minimum load
impedance (Zload) and the reach (Zc) of the coordinating zone. Load flow and stability studies may have to be run to deter-
mine the settings necessary to establish out-of-step blocking.
1601: MOBZONE - Coordinating Zone
Set MOBZONE to select a coordinating zone per the criteria described above.
1602: MOBCHARANG - MOB Characteristic Angle
Use the criteria described earlier to select an appropriate MOBCHARANG setting.
1603: BLOCKWHAT - Functions to Block during Out-of-Step Tripping
BLOCKWHAT is used to select which of the following are to be blocked during an out-of-step condition:
1. BLKALL - Block all tripping regardless of what operated to initiate the trip.
2. BLKDIST - Block tripping for operation of any of the distance functions.
3. BLKPHAS - Block tripping by any of the phase distance functions.
4. BLKNONE - allow tripping for any trip condition.
1604: BLOCKZ1 - Block All Zone 1 Functions
Set BLOCKZ1 = YES to block tripping by any of the Zone 1 distance functions, otherwise set BLOCKZ1 = NO.
1605: BLOCKZ2 - Block All Zone 2 Functions
Set BLOCKZ2 = YES to block tripping by any of the Zone 2 distance functions, otherwise set BLOCKZ2 = NO.
Swing Line
R
X
MOB
Zone 2, 3 or 4
Zload
A
C
Zc
B
 Loading...
Loading...