GE Power Management
ALPS Advanced Line Protection System 6-11
6 FUNCTIONAL TESTS (USER SETTINGS) 6.5 ZONE REACH TESTS
6
(305), Z3GRDREACH = [________] (Zone 3)
(406), Z4GRDREACH = [________] (Zone 4)
(111), Z1GCHARANG = [________] (Fixed at 90° for Zone1 on single-phase tripping models)
(207), Z2GCHARANG = [________] (Zone 2)
(306), Z3GCHARANG = [________] (Zone 3)
(406), Z4GCHARANG = [________] (Zone 4)
(108), Z1GROUNDK0 = [________] (Zone 1 only)
(1404), ZEROSEQK0 = [________] (Zones 2-4)
2. Determine the test current,
I
T
, for Zone 1, Zone 2, Zone 3, and Zone 4 from Table 6–1: TEST CURRENT RANGES
FOR PHASE-TO-GROUND REACH below.
I
T
(Z1GR) = [________] Amps rms
I
T
(Z2GR) = [________] Amps rms
I
T
(Z3GR) = [________] Amps rms
I
T
(Z4GR) = [________] Amps rms
3. Calculate the impedance,
Z
, for each zone, where
Z
equals the magnitude of the expression:
The real and imaginary components of
Z
are given by
The magnitude is then given by:
The settings are:
Z
1
= [________] (Zone magnitude)
Z
n
= [________] (magnitude of Zones 2, 3, and 4)
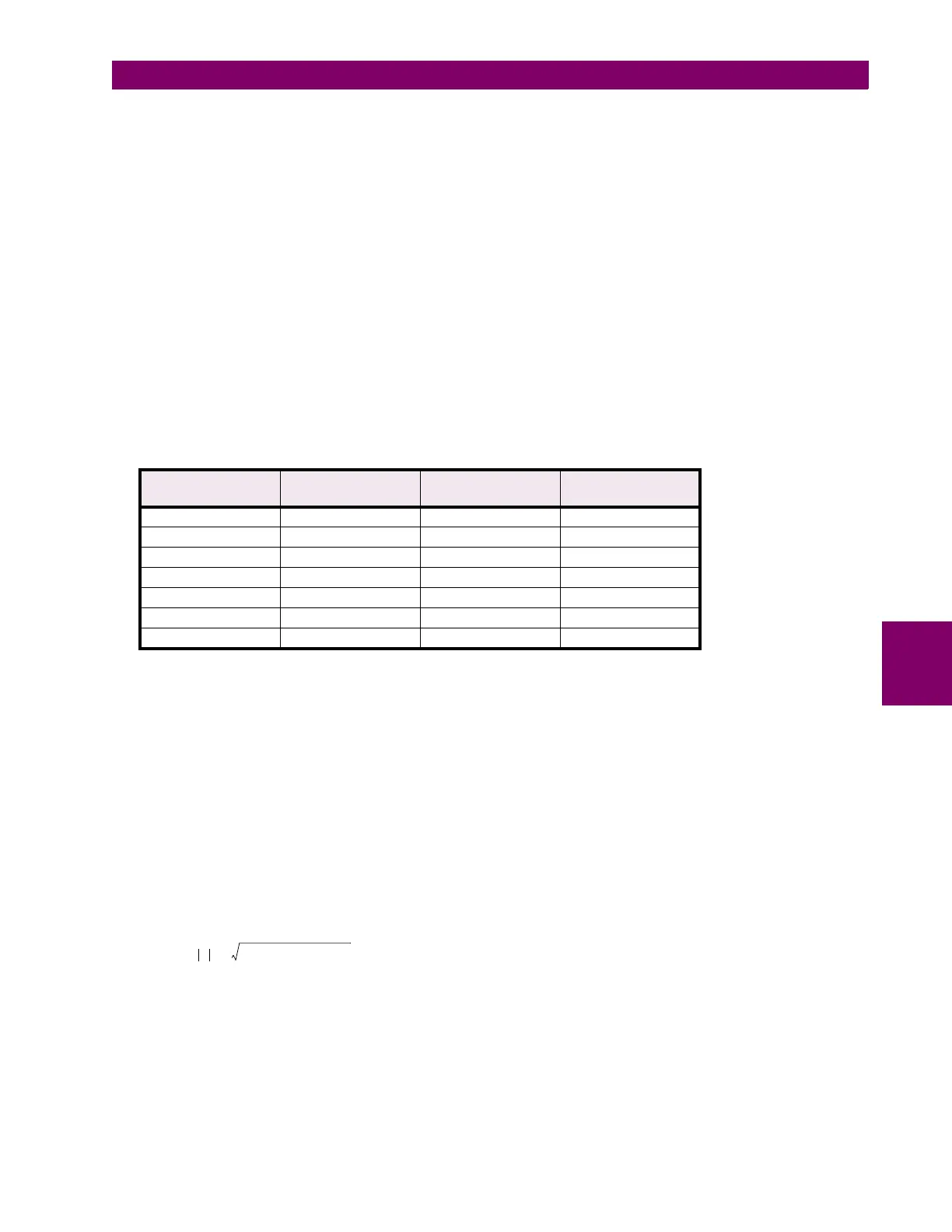
Table 6–1: TEST CURRENT RANGES FOR PHASE-TO-GROUND REACH
Z
R
REACH
(
I
N
= 5 A)
I
T
(A)
Z
R
REACH
(
I
N
= 1 A)
I
T
(A)
0.1 to 2.5 10 0.5 to 12.5 2
2.5 to 6.0 7 12.5 to 30.0 1.4
6.0 to 12.0 3.5 30.0 to 60.0 0.7
12.0 to 20.0 2.1 60.0 to 100.0 0.4
20.0 to 30.0 1.4 100.0 to 150.0 0.3
30.0 to 40.0 0.8 150.0 to 200.0 0.2
40.0 to 50.0 1.0 200.0 to 250.0 0.2
2
3
---
POSSEQANG
∠
K
0
3
------
ZERSEQANG
∠
+
Z
()
real
2
3
---
POSSEQANG
()
cos
K
0
3
------
ZERSEQANG
()
(eq. 6–21)cos
+=
Z
()
imag
2
3
---
POSSEQANG
()
sin
K
0
3
------
ZERSEQANG
()
(eq. 6–22)sin
+=
ZZ
()
2
real
Z
()
2
imag
+
(eq. 6–23)
=
 Loading...
Loading...