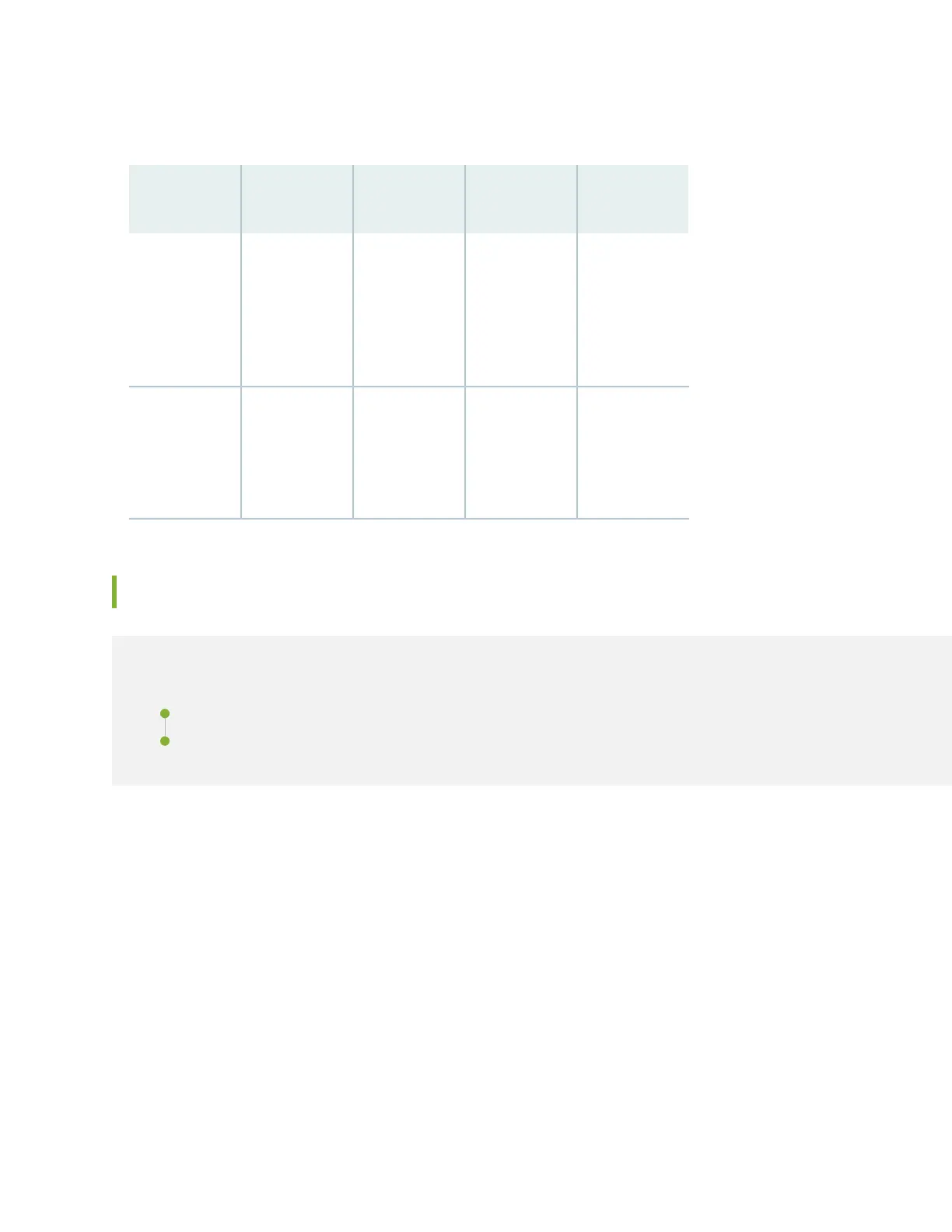
Table 23: Cable and Wire Specifications for Routing Engine and RCB Management and Alarm
Interfaces (continued)
Router
Receptacle
Maximum
Length
Cable/Wire
Supplied
Cable
SpecificationPort
RJ-45
autosensing
100 mOne 4.57-m
length with
RJ-45/RJ-45
connectors
Category 5
cable or
equivalent
suitable for
100Base-T
operation
Routing Engine
Ethernet
interface
—NoneNoWire with
gauge between
28-AWG and
14-AWG (0.08
and 2.08 mm
2
)
Alarm relay
contacts
Understanding Fiber-Optic Cable Signal Loss, Attenuation, and Dispersion
IN THIS SECTION
Signal Loss in Multimode and Single-Mode Fiber-Optic Cable | 66
Attenuation and Dispersion in Fiber-Optic Cable | 67
This topic describes signal loss, attenuation, and dispersion in fiber-optic cable.
Signal Loss in Multimode and Single-Mode Fiber-Optic Cable
Multimode fiber is large enough in diameter to allow rays of light to reflect internally (bounce off the walls
of the fiber). Interfaces with multimode optics typically use LEDs as light sources. However, LEDs are not
coherent sources. They spray varying wavelengths of light into the multimode fiber, which reflects the
light at different angles. Light rays travel in jagged lines through a multimode fiber, causing signal dispersion.
When light traveling in the fiber core radiates into the fiber cladding, higher-order mode loss results.
Together these factors limit the transmission distance of multimode fiber compared with single-mode
fiber.
66

 Loading...
Loading...