Chapter 6 CVS-842/852/843
Using the Menu Operation Manual
have a longer wavelength produce small amount of echoes from small fish.
The image-mixing mode is an image processing function that enables weak fish like young sardines to
be better defined by comparing or subtracting the images from both the HIGH and LOW frequencies.
When echoes are detected by the HIGH frequency wave, the sounder displays these echoes in a
pre-selected color to indicate small fish targets. The MIX function has three modes as, A (Comparison),
B (Subtraction) and C (Selection).
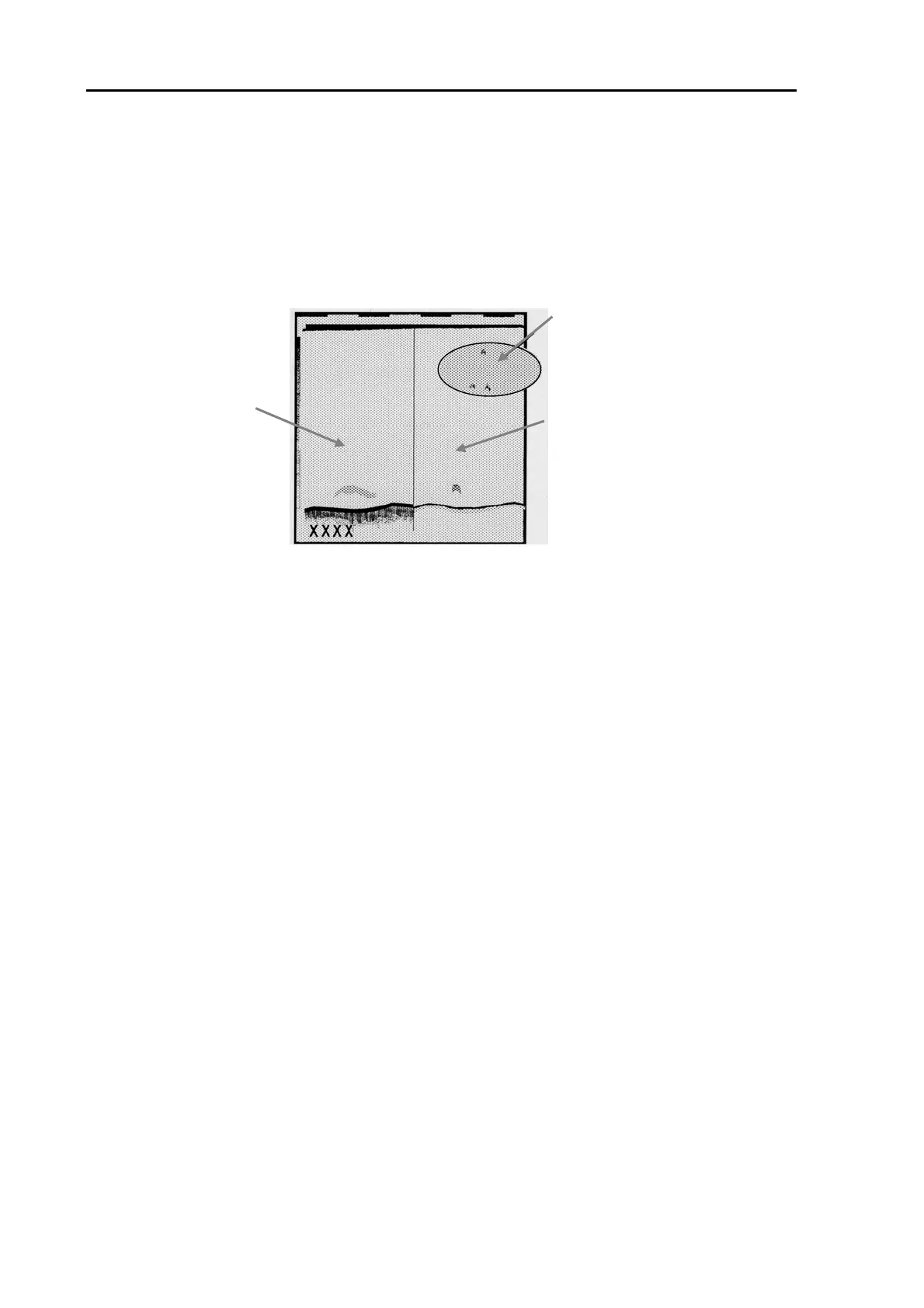
Image detected only by high
frequency, which is painted in a
pre-selected color.
Mixed image
Normal image
(High or Low
Frequency)
Figure 6.8 Mixed image
A (COMPARISON) mode:
This mode displays the result of the comparison between the HIGH and LOW frequency echoes. If
those echoes of the same signal level are overlapped at the same depth, the resultant colors are
displayed in mixed colors (gray). However, if the HIGH frequency echo is stronger than that of LOW
frequency, the HIGH frequency echo can be distinguished against the gray background echo
displayed in a dominant color like red or orange. This result clearly indicates where the echoes, which
is sensitive to the HIGH frequency, are located.
B (SUBTRACTION) mode:
This mode displays the resultant image by subtracting the HIGH frequency echoes from those of LOW
frequency. Using this method, you can discern a fish school by size. For instance, if the resultant
echoes are displayed in similar colors as the HIGH frequency echoes, this result suggests the majority
of the fish species is sensitive to the HIGH frequency transmission, i.e. the detected fish school could
be small fish like young sardine. If the resultant echoes are shown in different colors from the HIGH
frequency transmission, it indicates the fish school is sensitive to LOW frequency, therefore a larger
size of fish species.
C (SELECTION) mode:
This method is similar to A mode in principle, however, the process in determining display color is
different. If the High Frequency echo is predominant against those of Low Frequency, the resultant
color is displayed in colors shown in High Frequency image. If the Low Frequency echoes are
predominant against High Frequency in color presentation, no echo will be shown. This indicates there
is few school of small fish.
6-8 0093132692-05
 Loading...
Loading...