X-Stream Operator’s Manual
WM-OM-E Rev I 221
Note: Enhanced resolution can only improve the resolution of a trace; it cannot improve the accuracy or linearity of the
original quantization. The pass-band will cause signal attenuation for signals near the cut-off frequency. The highest
frequencies passed may be slightly attenuated. Perform the filtering on finite record lengths. Data will be lost at the start and
end of the waveform: the trace will be slightly shorter after filtering. The number of samples lost is exactly equal to the length
of the impulse response of the filter used: between 2 and 117 samples. Normally this loss (just 0.2 % of a 50,000 point trace)
is not noticed. However, you might filter a record so short there would be no data output. In that case, however, the
instrument would not allow you to use the ERES feature.
To Set Up Enhanced Resolution (ERES)
1. In the menu bar, touch Math, then Math Setup... in the drop-down menu.
2. Touch a function tab F1 through Fx. (The number of math traces available depends on the
software options loaded on your scope. See Specifications.)
3. Touch inside the Operator1 data entry field.
4. Select ERES from the All Functions or Filter group of Math functions.
5. Touch the Trace On checkbox.
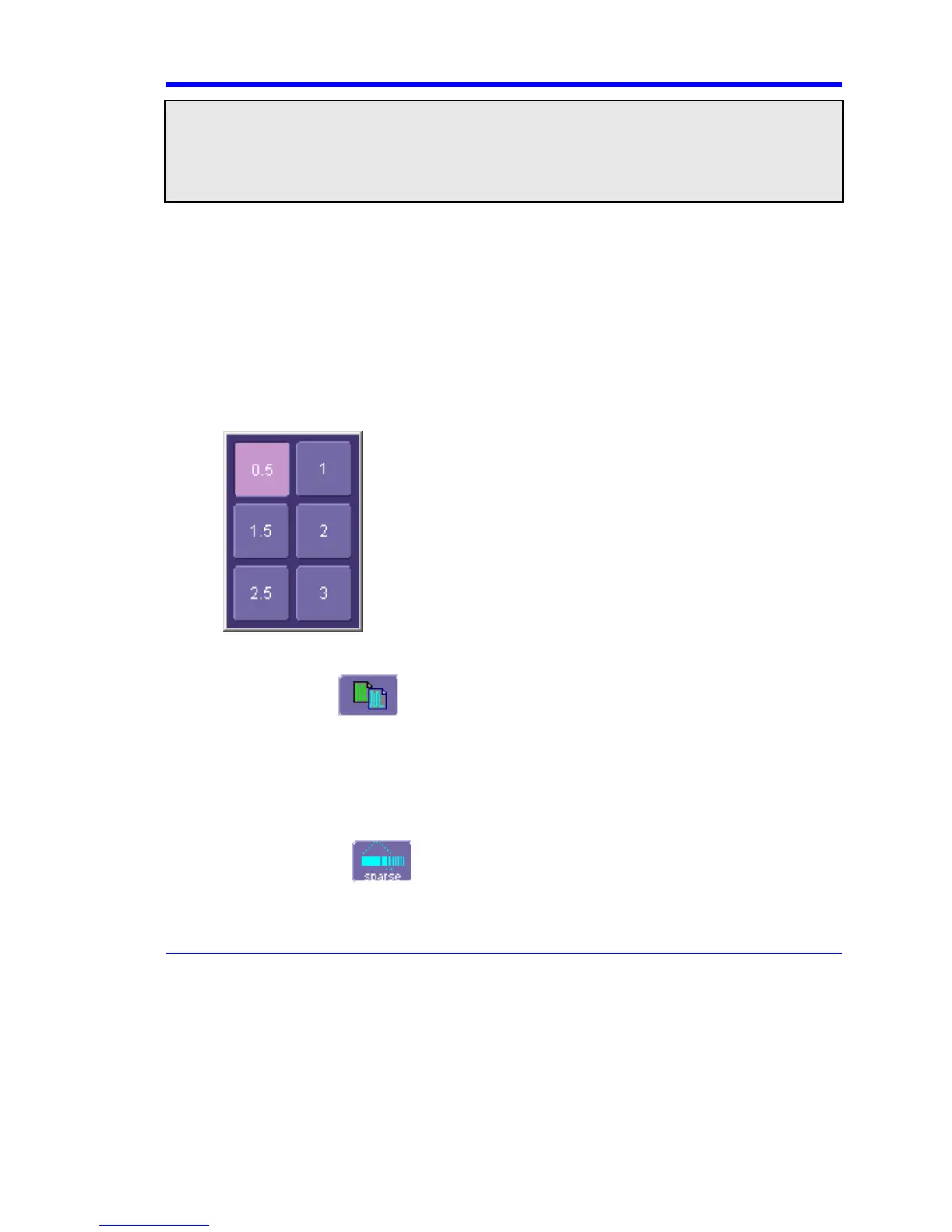
6. Touch the "ERES" tab in the right-hand dialog, then touch inside the bits field and make an
"Enhance by" selection from the pop-up menu:
.
Waveform Copy
The Copy math function makes a copy of your present waveform in its unprocessed state.
While processing may continue on the original waveform, the copy enables faster throughput in
some cases by preserving the original data. That is, no calculations need to be undone on the copy
before additional math can be calculated.
This benefit of faster throughput, however, comes at the expense of memory usage.
Waveform Sparser
The Sparse math function allows you to thin out an incoming waveform by skipping
points at regular intervals, and by starting acquisition at a particular "offset" (point). The Sparsing
factor specifies the number of sample points to reduce the input waveform by. A sparsing factor of
4, for example, tells the scope to retain only one out of every 4 samples. A Sparsing offset of 3, on
 Loading...
Loading...