2-79
2 Instruction Descriptions
NJ-series Instructions Reference Manual (W502)
Sequence Control Instructions
2
FOR and NEXT
• The value of Index after repeat processing is different in a ladder diagram and ST. In a ladder dia-
gram, the value of StepVal is not added to Index at the end of repeat processing. In ST, the value of
StepVal is added to Index at the end of repeat processing. Processing is repeated the same number
of times.
The following example is for when InitVal is 1, EndVal is 100 and StepVal is 1.
Ladder diagram: The value of Index will be 100 after 100 repetitions.
ST: The value of Index will be 101 after 100 repetitions.
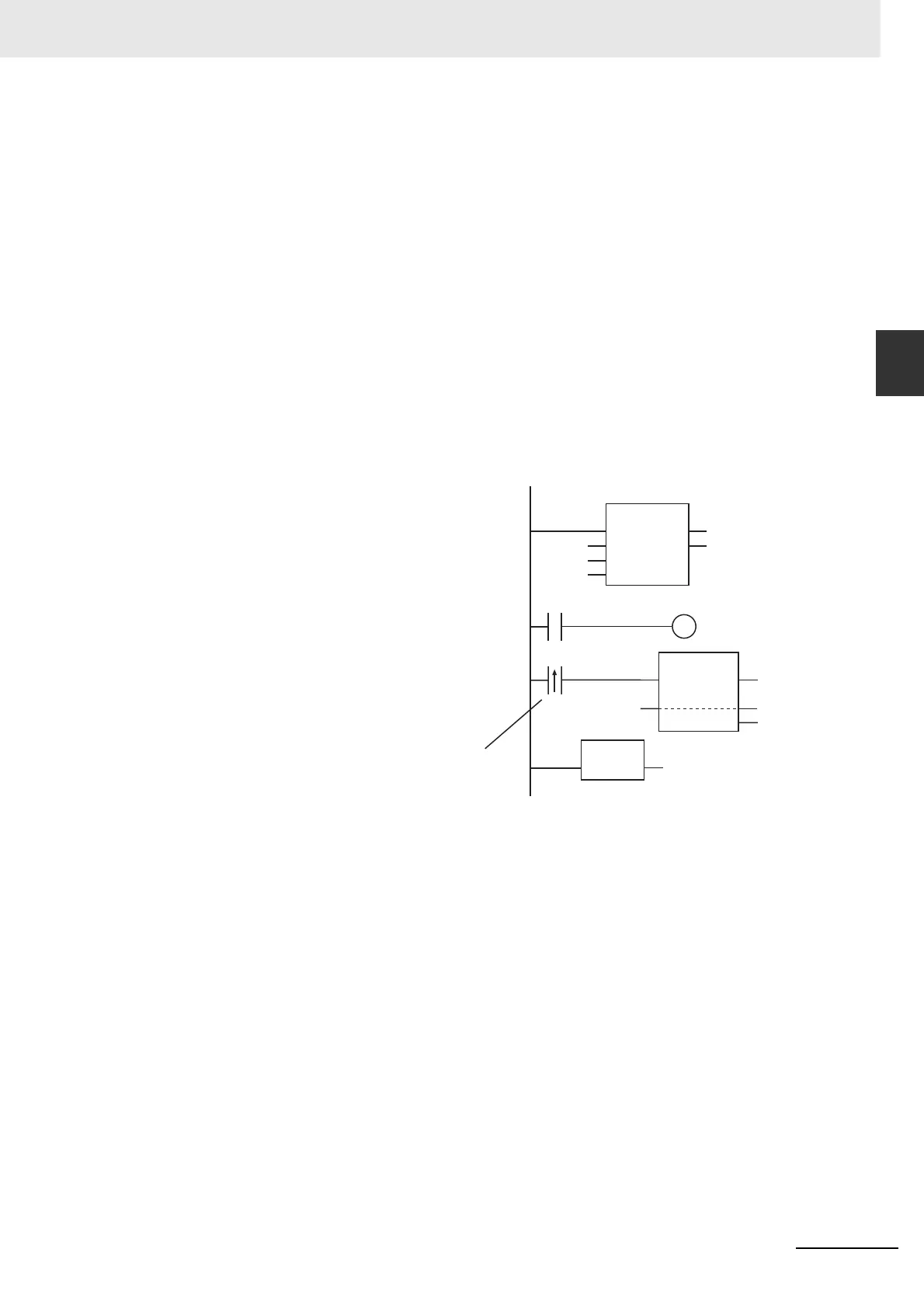
• Caution is required when you specify upward or downward differentiation for a LD, AND, or OR
instruction in a FOR loop in a ladder diagram and an array is used for the LD, AND, or OR instruction.
For upward or downward differentiation, the value of the specified variable at the previous execution
is compared with the value of the specified variable at the current execution to determine upward or
downward differentiation. Normally, the value of the specified variable does not change every time
the instruction is executed. However, if an array is specified in a FOR loop, the array element
changes each time the instruction is executed. Therefore, upward or downward differentiation is
determined by comparing different array elements. In the following programming, the LD instruction
in the third execution of the FOR loop (x = 2) compares the current value x[2] to the value of the
specified variable the last time the LD instruction was executed, x[1], to determine that the value did
not change to TRUE. As a result, Count1[2] is not incremented.
DINT#0
DINT#10
DINT#1
i
FOR
EN ENO
InitVal Index
EndVal
StepVal
NEXT
EN ENO
x[i]
x[i]
Count1[i]
AllSet
Upward differentiation is determined by comparing x[i] to x[i−1].
Inc
EN ENO
InOut

 Loading...
Loading...