2 Instruction Descriptions
2-336
NJ-series Instructions Reference Manual (W502)
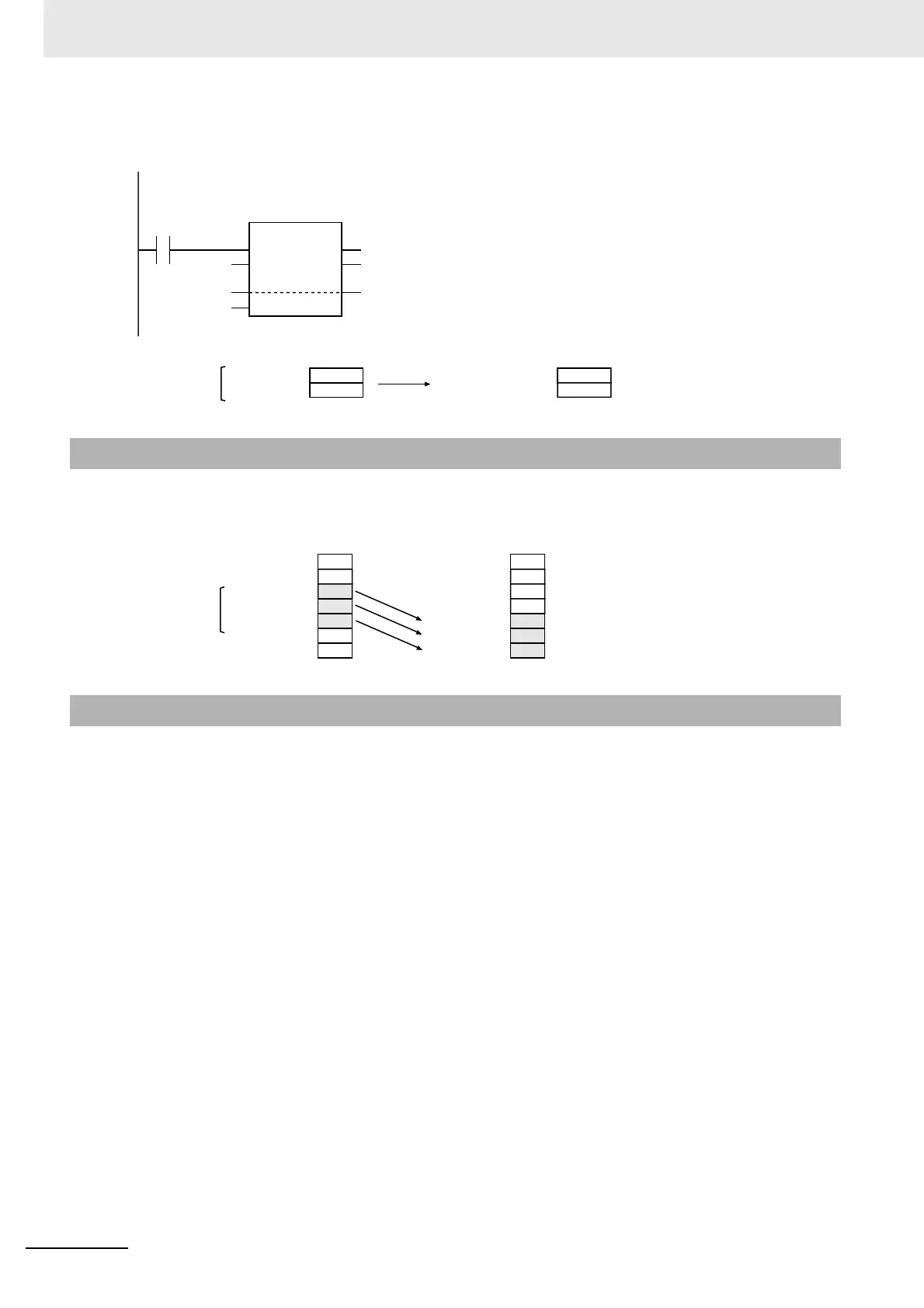
The following example is for when Size is UINT#2.
• If the data types of In[] and AryOut[] are the same, the MemCopy instruction is faster.
• You can specify the same array for In[] and AryOut[]. Also, the move source and destination data can
overlap. The following example is for when In[0] is A[2], AryOut[0] is A[4], and Size is UINT#3.
• The data types of In[] and AryOut[] can be different as long as they are both in one of the following
groups. The valid range of AryOut[] must include the valid range of In[].
• BYTE, WORD, DWORD, and LWORD
• USINT, UINT, UDINT, ULINT, SINT, INT, DINT, LINT, REAL, and LREAL
• If In[] is an array of structures, use the same data types for In[] and AryOut[].
• If the value of Size is 0, the value of Out will be TRUE and AryOut[] will not change.
• Return value Out is not used when the instruction is used in ST.
• An error occurs in the following case. ENO will be FALSE, and AryOut[] will not change.
• The value of Size exceeds the size of In[] or AryOut[].
• In[] and AryOut[] are STRING arrays and one of the elements to move does not end in a NULL
character.
• In[] or AryOut[] is a STRING array and the length of a text string in an element to move exceeds
the size of the element in AryOut[].
Additional Information
Precautions for Correct Use
AryMove(abc[1], def[2], UINT#2);
LD ST
abc[1]
def[2]
UINT#2
def[2]
AryMove
EN ENO
In
AryOut
Size
Moved
In[0]=abc[1]
In[1]=abc[2]
AryOut[0]=def[2]
AryOut[1]=def[3]
Size=UINT#2
A[0]
A[1]
In=A[2]
A[3]
AryOut=A[4]
A[5]
A[6]
A[0]
A[1]
In=A[2]
A[3]
AryOut=A[4]
A[5]
A[6]
1234
2345
3456
4567
5678
6789
7890
1234
2345
3456
4567
3456
4567
5678
Size=UINT#3

 Loading...
Loading...