9-39
9 Motion Control Functions
NJ/NX-series CPU Unit Motion Control User’s Manual (W507)
9-5 Common Functions for Single-axis Control
9
9-5-5 Specifying the Operation Direction
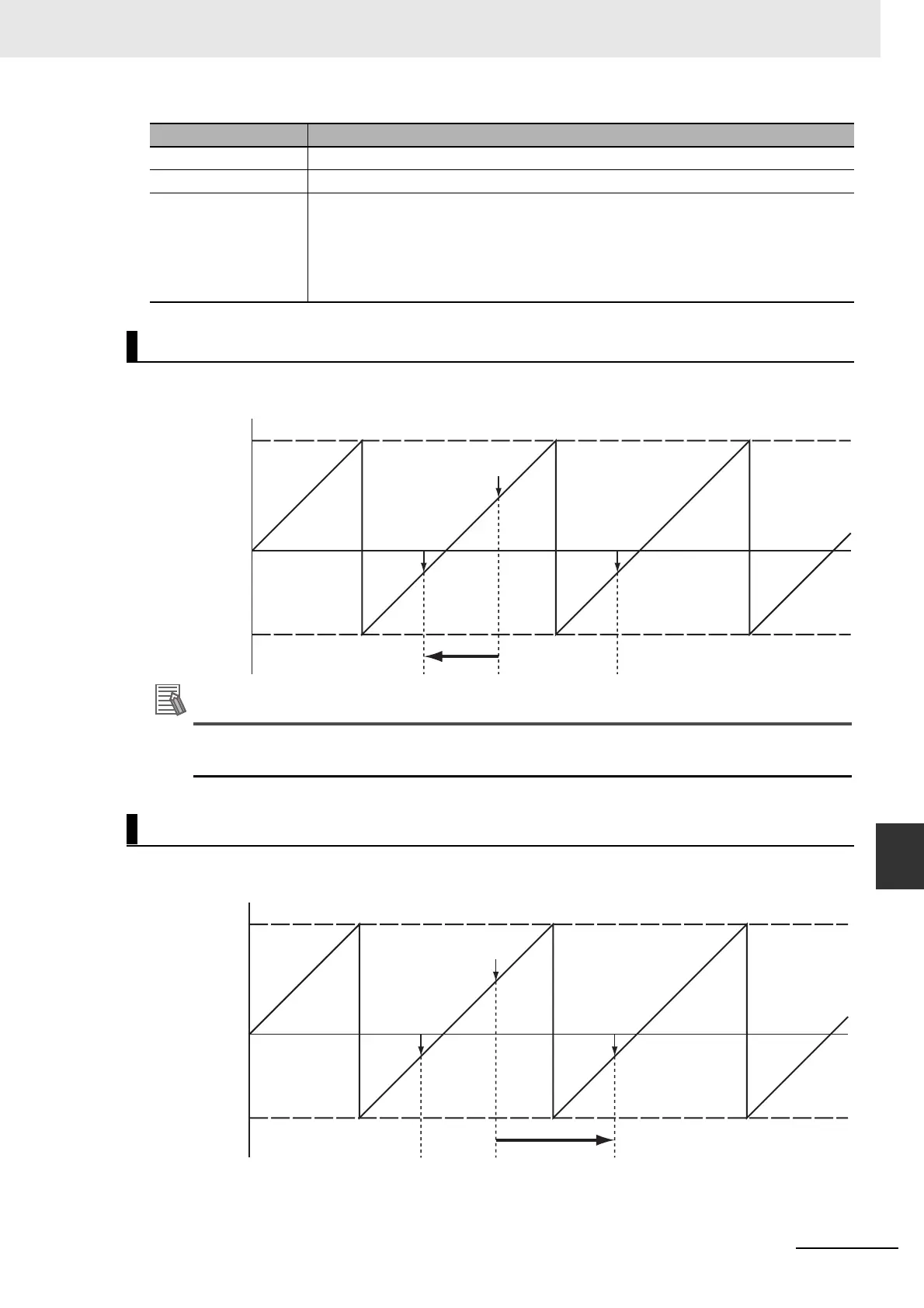
The following example illustrates when positioning is performed towards a target position of −20 when
the command current position is 50.
Moves in the same direction as the Current Direction specification if the travel distance is the
same in the positive and negative directions.
The following example illustrates when positioning is performed towards a target position of −20 when
the command current position is 50.
Negative direction Motion starts in the negative direction.
Current direction Motion starts in the same direction as the previous operation.
No direction specified Motion starts in the direction that does not pass through the upper and lower limits of
the ring counter. With this direction specification, you can specify a target position that
exceeds the upper or lower limits of the ring counter. If that occurs, relative positioning
is performed using the difference between the target position and the command current
position as the target distance. This enables you to perform multi-turn positioning on
the ring counter.
Example for Shortest Way
Example for Positive Direction
Direction Operation
0
Target position:
−20
Moves in negative direction.
Target position:
−20
Command current position:
50
Modulo minimum
position setting
value: −70
Modulo maximum
position setting
value: 100
Moves in positive direction.
Target position:
−20
Target position:
−20
Command current position:
50
Modulo minimum
position setting
value: −70
Modulo maximum
position setting
value: 100
0
 Loading...
Loading...