Chapter 1 Installation
GC-2014 Service Manual
8
1.4 Gas
1.4.1 Purity
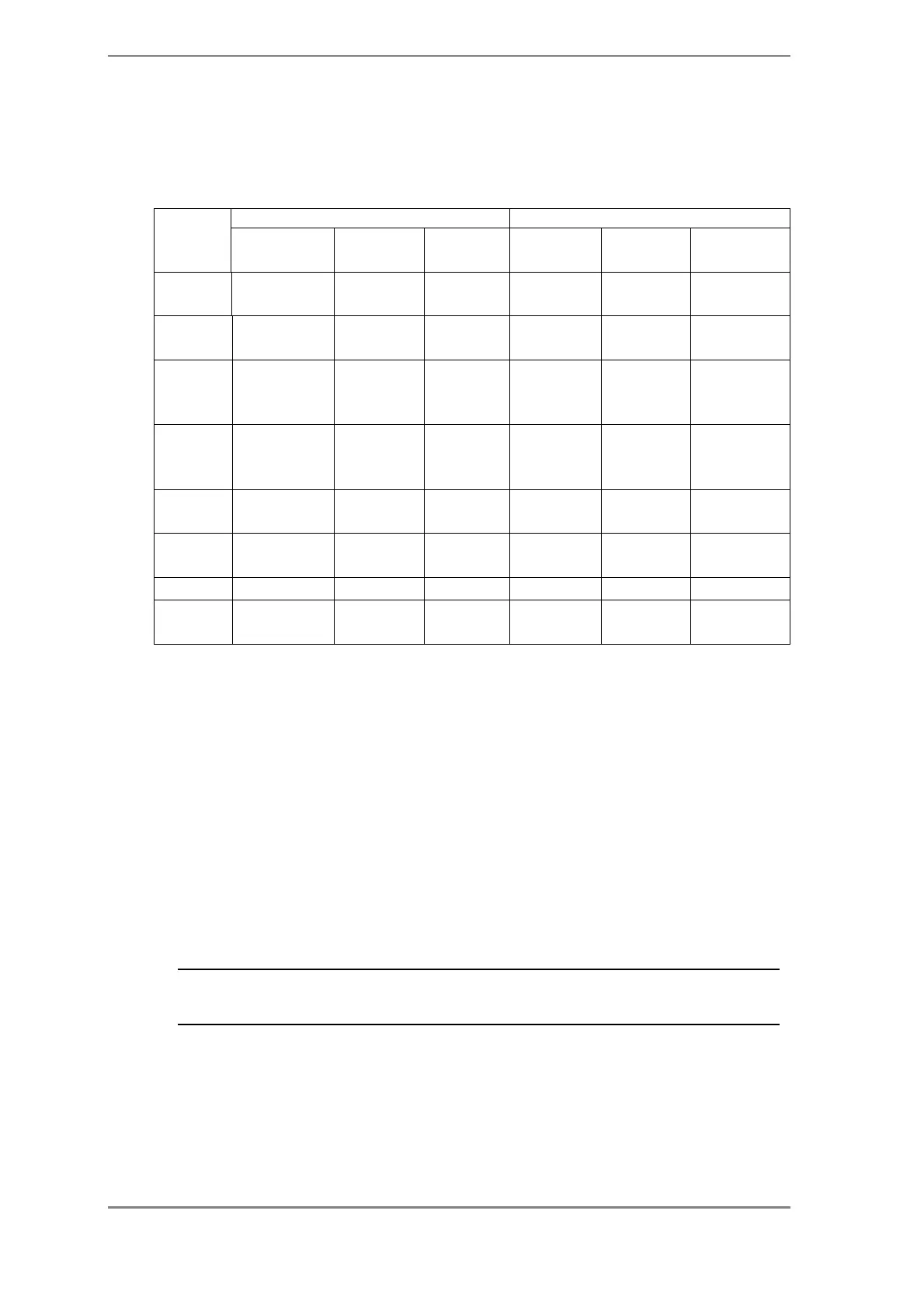
In order to maintain performance specifications, prepare the following gases.
Carrier gas Detector gas
Detector
He
(recommended)
N
2
(usable) Other H
2
Air Make-up
FID 99.995% min. 99.995% min. 99.995% min.
Compressor
air
N
2
, He
99.995% min.
FID, high
sensitivity
99.999% min. 99.999% min. 99.999% min. Cylinder air
N
2
, He
99.999% min.
TCD 99.995% min. 99.995% min.
Ar, etc.
99.995%
min.
He, N
2
, Ar, etc.
99.995% min.
TCD, high
sensitivity
99.999% min. 99.999% min.
Ar, etc.
99.999%
min.
He, N
2
, Ar, etc.
99.999% min.
ECD 99.999% min. 99.999% min.
N
2
99.999% min.
ECD, high
sensitivity
99.9999% min.
99.9999%
min.
N
2
99.9999% min.
FPD 99.999% min. 99.999% min. 99.999% min. Cylinder air
FTD 99.999% min. 99.999% min. Cylinder air
He
99.999% min.
* Use air that has been compressed in an oil-less compressor and then dehumidified.
1.4.2 Supply Pressure
Carrier gas: 300 to 980 kPa
Make-up gas: 300 to 980 kPa
Hydrogen: 300 to 500 kPa
Air: 300 to 500 kPa
Use the following formulas for approximate conversion between kPa and kgf/cm
2
.
1 kPa = 1.02 × 10
-2
kgf/ cm
2
1 kgf/ cm
2
= 98.1 kPa
Use the following formulas for approximate conversion between kPa and psi.
1 kPa = 1.45 × 10
-1
psi
1 psi = 6.89 kPa
NOTE
• For precautions on handling high-pressure gas cylinders and using hydrogen gas,
refer to the instruction manual for the GC-2014 main unit.

 Loading...
Loading...











