Detailed Description
2.7 Structure and functions of the basic program
PLC Basic Program Solution Line (P3 sl)
2-38 Function Manual, 08/2005 Edition, 6FC5397-0BP10-0BA0
Control/status signals
A shared feature of the control and status signals is that they are bit fields. The basic
program updates them at the start of OB1.
The signals can be subdivided into the following groups:
• General signals
• Mode-group-specific signals such as operating modes
• Channel-specific signals such as program and feed modifications
• Axis- and spindle-specific signals such as feed disable
Auxiliary and G functions
The auxiliary and G functions have the following characteristics:
• Transfer to the PLC is block-synchronous (referred to a parts program block)
• Transfer is acknowledge-driven.
• The acknowledgment times have an immediate effect on the execution time of NC blocks
containing auxiliary functions requiring acknowledgment.
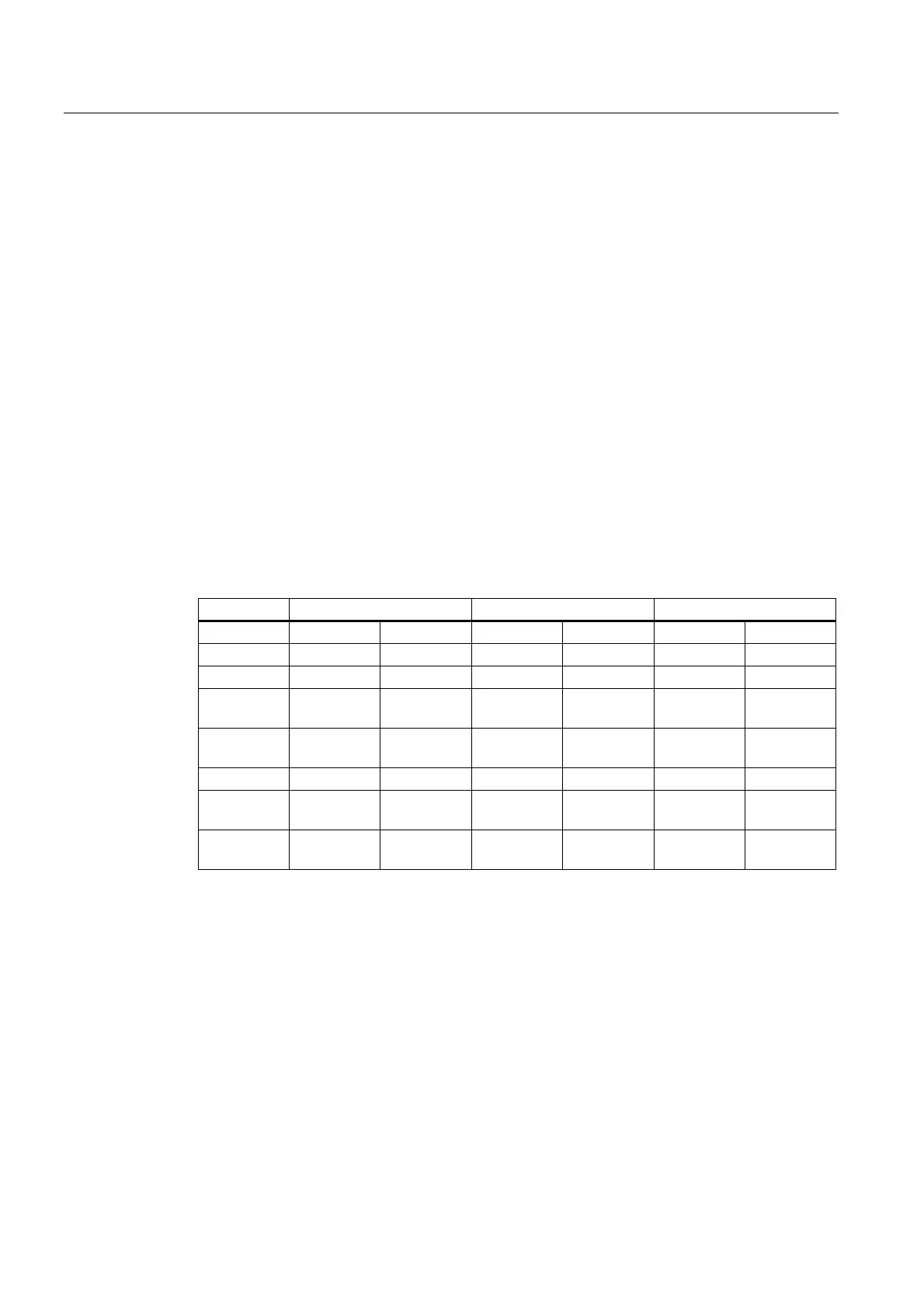
The value range is presented in the table below:
Function Structure Value range Data type
1. Value 2. Value 1. Value 2. Value 1. Value 2. Value
G function G function 255
1)
Byte
M word M group M word 99 99,999,999 Word DWord
S word Spindle no. S word 6 Floating
point
2)
Word DWord
T word Magazine
no.
T word 99 65535 Word Word
D word - D word 99 255 Byte Byte
H word H group H word 99 Floating
point
Word DWord
F word Axis No. F word 18 Floating
point
Word DWord
1)
relative number, transferred for each G group
2)
corresponding STEP7 format (24-bit mantissa, 8-bit exponent)
The M, S, T, H, D and F values sent by the NCK are output together with the accompanying
change signals to the CHANNEL DB interface via the auxiliary/G functions (see
documentation "Lists of SINUMERIK 840D sl"). The function value and the extended
address are transferred to the appropriate data word. The accompanying modification signal
is activated to 1 for one PLC cycle. When the modification signal is reset, the
acknowledgment is passed to the NCK. The acknowledgment of high-speed auxiliary
functions is given by the basic program immediately the basic program detects the auxiliary
function.
In addition to distribution of the auxiliary and G functions, selected signals are processed as
described below.

 Loading...
Loading...



















