Detailed Description
2.7 Structure and functions of the basic program
PLC Basic Program Solution Line (P3 sl)
2-58 Function Manual, 08/2005 Edition, 6FC5397-0BP10-0BA0
03,'3
'3
++8
1&.
(WKHUQHW
0&3
0&3
'
3
5
3URILEXVFRQI
IRU0&3++8
&3
'VO
LQW3/&
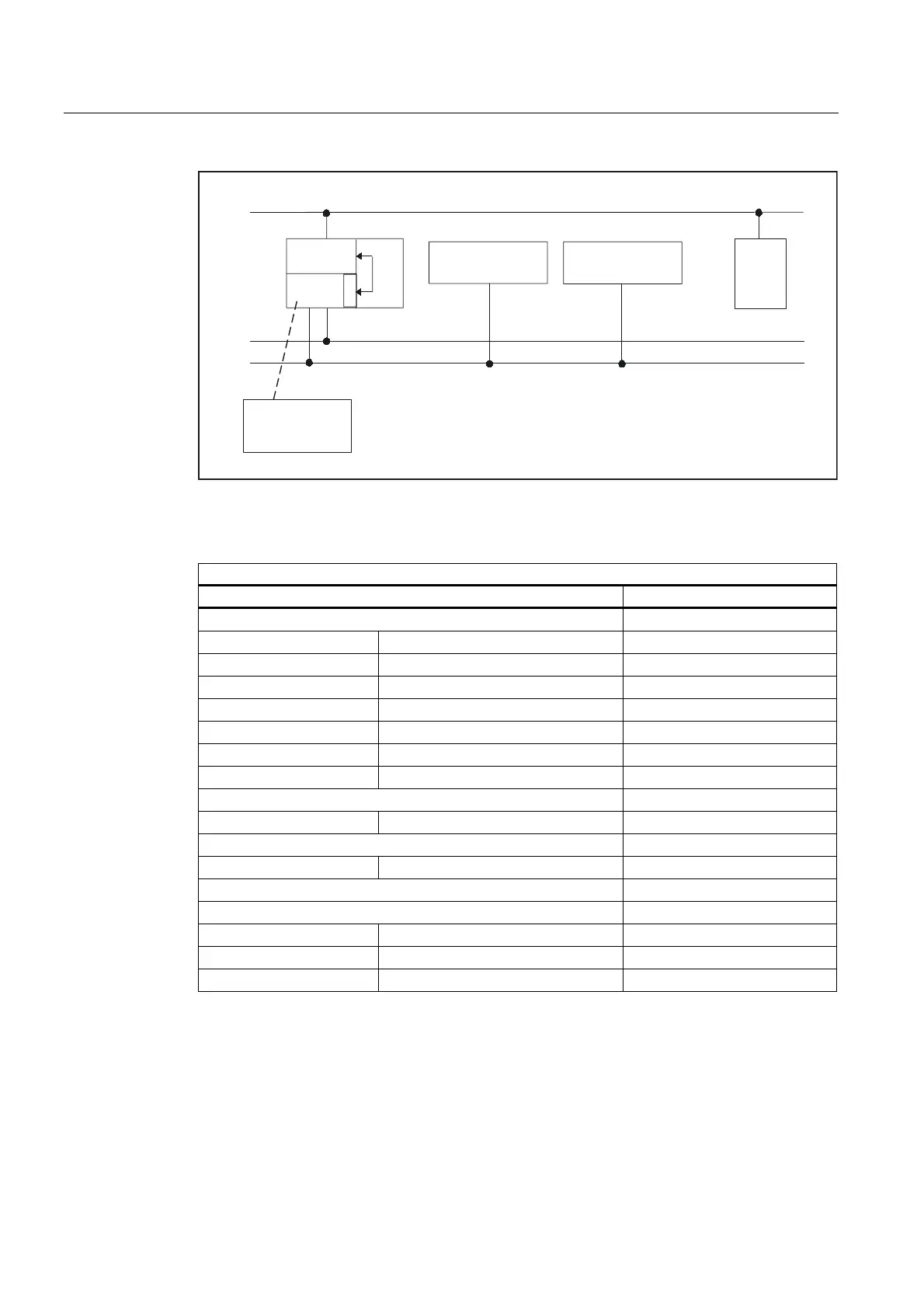
Fig. 2-17 PROFIBUS connection
Relevant parameters (FB1)
MCP HHU
MCPNum = 1 or 2 (number of MCPs) HHU = 5 (via CP 840D sl)
MCP1In MCP2In BHGIn
MCP1Out MCP2Out BHGOut
MCP1StatSend (n.r.) MCP2StatSend (n.r.) BHGStatSend
MCP1StatRec MCP2StatRec BHGStatRec
MCP1BusAdr MCP2BusAdr BHGInLen
MCP1Timeout MCP2Timeout BHGOutLen
MCP1Cycl (n.r.) MCP2Cycl BHGTimeout
MCPMPI = FALSE BHGCycl
MCP1Stop MCP2Stop BHGRecGDNo
MCPBusType = b#16#33 BHGRecGBZNo (n.r.)
BHGRecObjNo (n.r.)
MCPSDB210= FALSE BHGSendGDNo (n.r.)
MCPCopyDB77 = FALSE BHGSendGBZNo (n.r.)
BHGSendObjNo (n.r.)
BHGMPI = FALSE
BHGStop
MCP failure switches the PLC to the STOP state. If this is undesirable, OB 82, OB 86 can be
used to avoid a stop. Setting MCPxStop := True deactivates the MCP as a slave via SFC 12.
If the PLC does not switch to the stop state following the failure of or a fault on the MCP, an
interrupt message will be generated via the basic program. The interrupt is deleted when the
station recovers.

 Loading...
Loading...



















