In the function, W [0] =D0, W [1] =D1…
If D0=D32, then W [0] =D32, W [1] =D33…
If S2=HD32, then W [0] =HD32, W [1] =HD33…
In the function, B [0] = M0, B [1] =M1…
If S2=M32, then B [0] = M32, B [1] =M33…
If S2=HM32, then B [0] = HM32, B [1] =HM33…
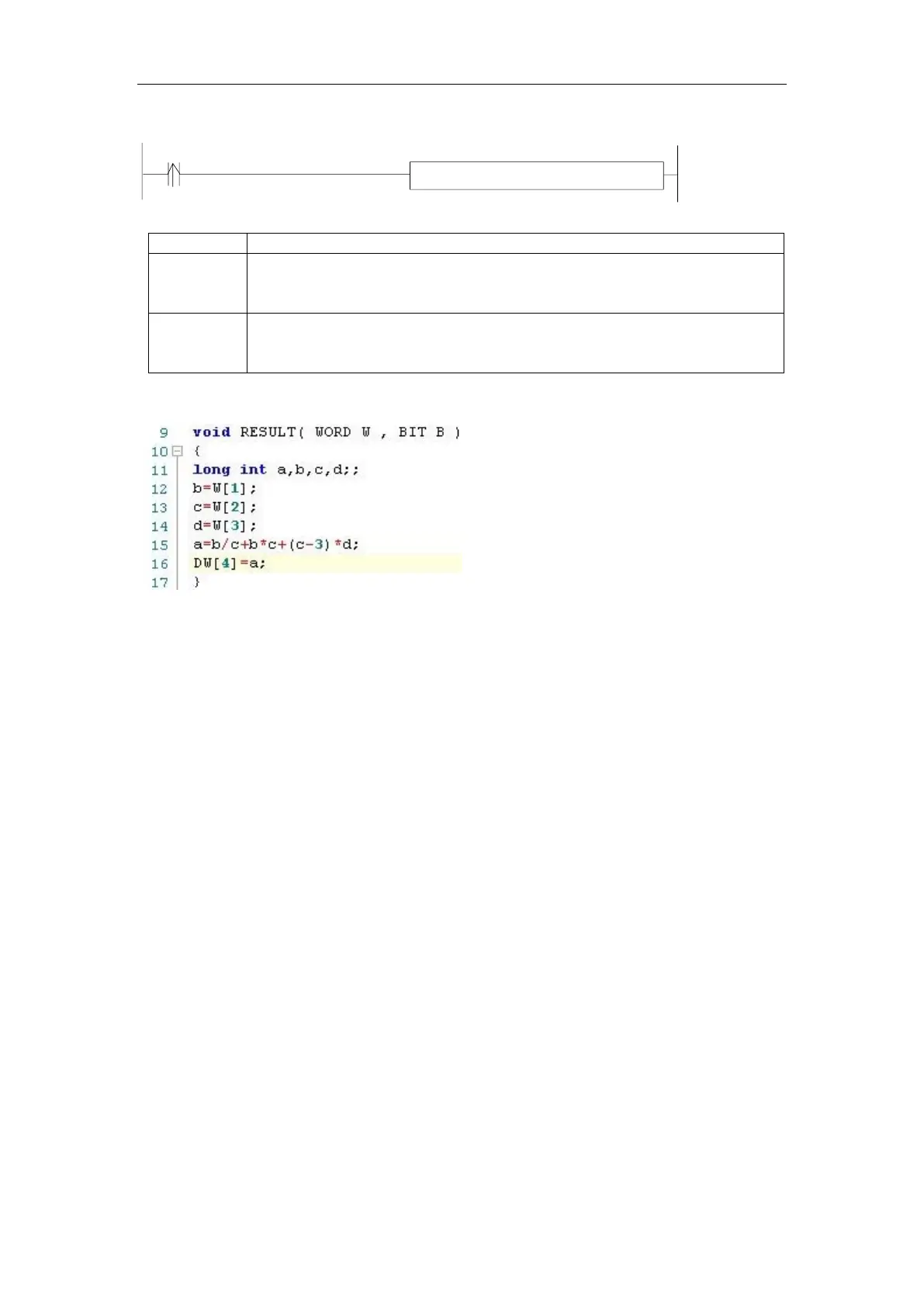
C program
Method 2 can simplify the program.
The above C language function is similar to ladder chart of method 1, whose precision is not
high. If it needs to get the high precision, please use float calculation.
Example 2: Calculate CRC parity value via Func Block
CRC calculation rules:
(1)Set 16-bit register (CRC register) = FFFF H
(2)XOR (Exclusive OR) the first 8-bit byte message and the low 16-bit CRC register.
(3)Right shift 1 bit of CRC register, fill 0 into the highest bit.
(4)Check the right shifted value, if it is 0, save the new value from step3 into CRC
register; if it is not 0, XOR the CRC register value with A001 H and then save the result into
the CRC register.
(5)Repeat step3&4 until all the 8-bit have been calculated.
(6) Repeat step(2)~(5), then calculate the next 8-bit message. Until all the messages
have been calculated, the result will be the CRC parity code in CRC register.
Edit C language Function Block program, see graph below:

 Loading...
Loading...