Aprisa LTE User Manual 2.1
LTE Architecture Overview
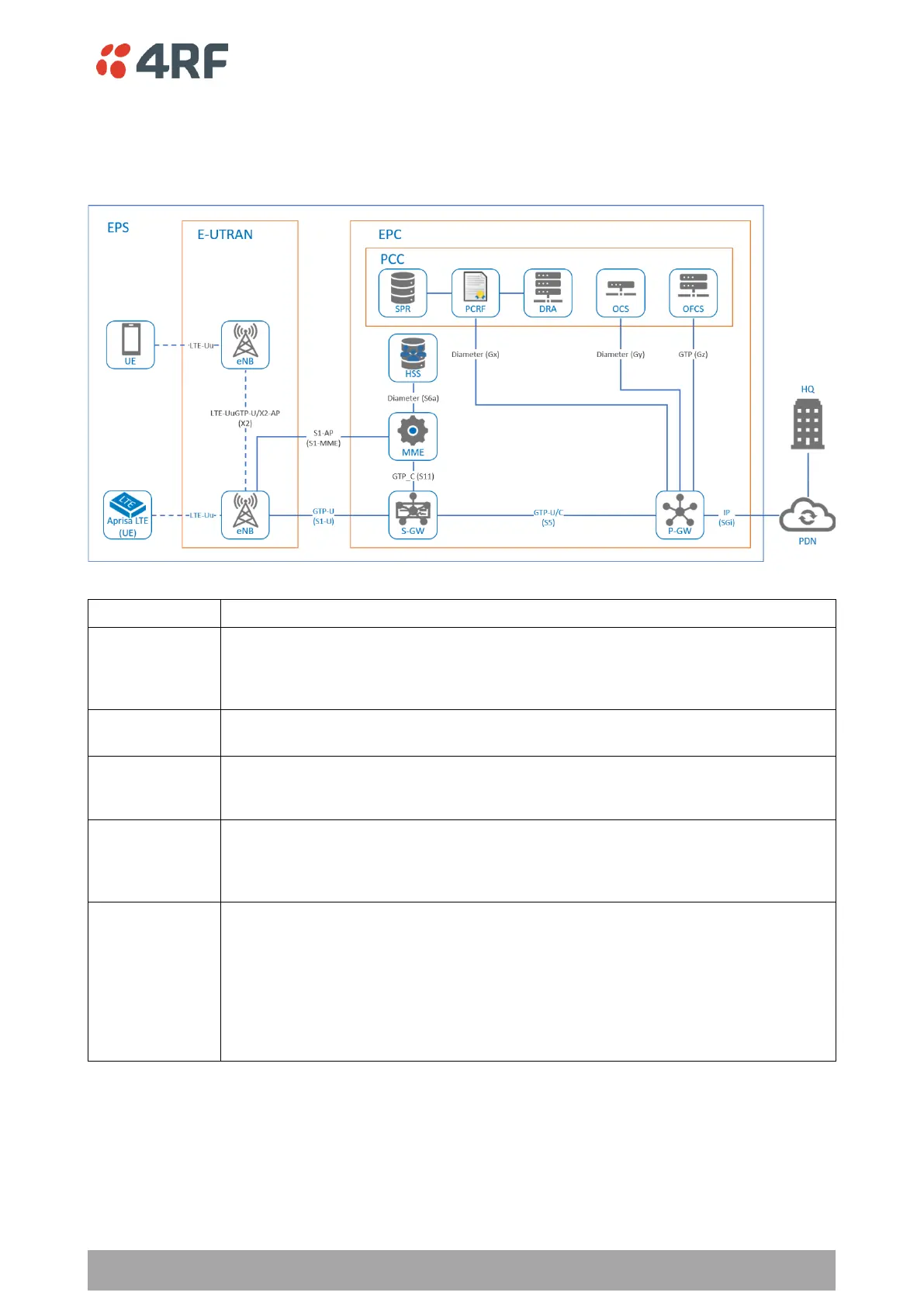
The following describes the LTE Architecture and its components. Figure 1 shows an LTE network reference
model, consisting of LTE/E-UTRAN entities and EPC entities connected to PDN network.
Figure 1 Network Reference Model
The LTE network called EPS (Evolved Packet System) is an end-to-end (E2E) all IP
network; EPS is divided into two main parts E-UTRAN and EPC. An E2E all IP network
means that all traffic flows from a UE all the way to a PDN which connects to a
service entity are transferred based on IP protocol within EPS.
The E-UTRAN (Evolved-Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network) is the LTE part
which deals with the technology related to a radio access network
The EPC (Evolved Packet Core) deals with the technology related to a core network.
The EPC is based on IP as the transport technology for data and control plane
(including for instance voice service).
The PCC (Policy and Charging Control) framework allows operators to control the
service a customer receives over the network and its billing services (based on time
or data volume or event occurring) based on the network state and SDF (Service Data
Flow) IP flow QoS enforcement, i.e. the way traffic flows.
A PDN (Packet Data Network) is a generic term for the network that LTE subscriber
would connect for mobile/fix data services. i.e. an internal or external IP domain of
the operator and provides the UE with services such as the Internet, data services or
IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS).
APN (Access Point Name) identifies a PDN Gateway (P-GW). It includes an APN
network identifier which defines the PDN to which the UE requests connectivity and
may also include an APN operator identifier which defines in which Public Land
Mobile Network (PLMN) the P-GW is located.
 Loading...
Loading...