MC96F6432
June 22, 2018 Ver. 2.9 245
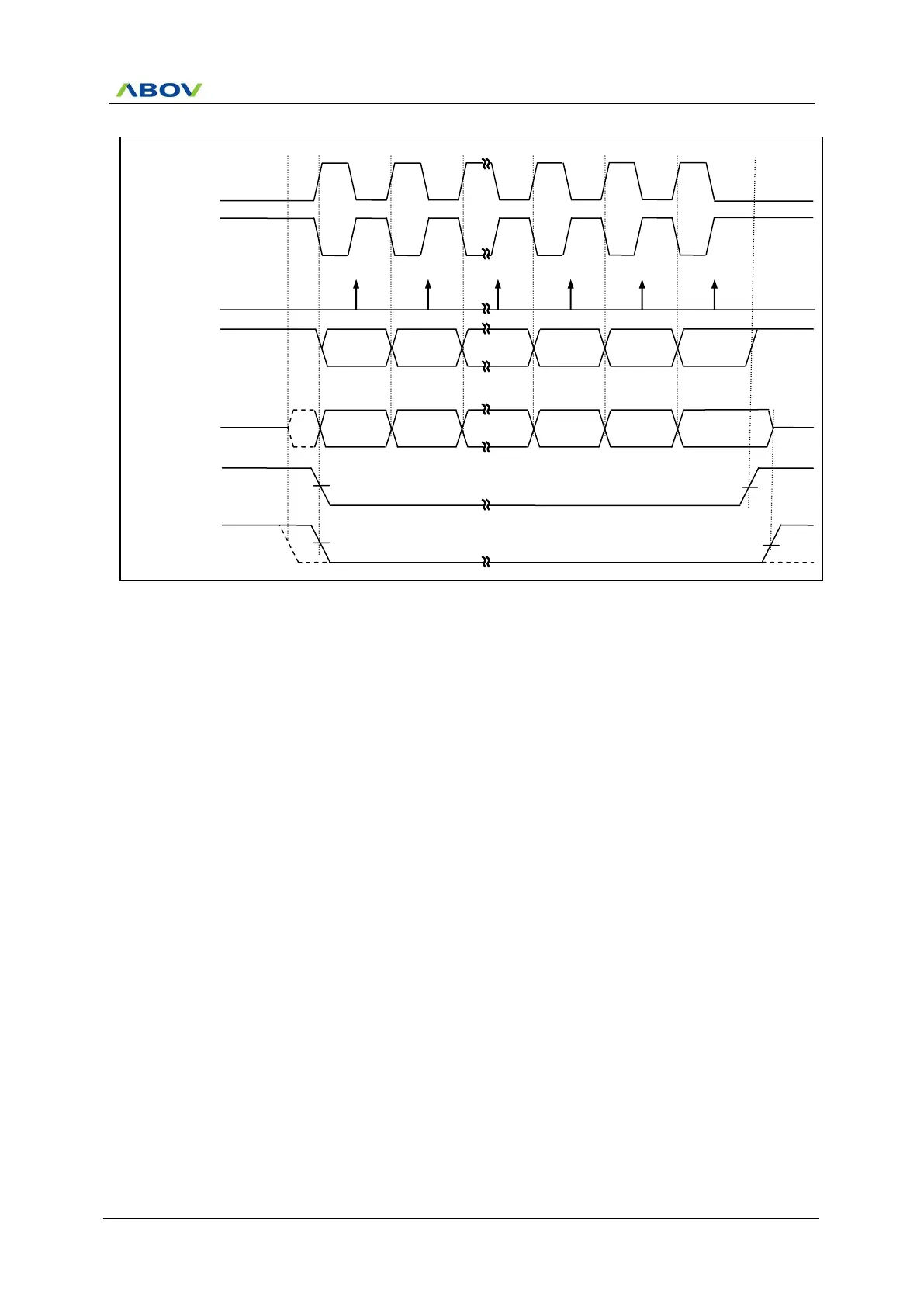
Figure 11.86 USI1 SPI Clock Formats when CPHA1=1
When CPHA1=1, the slave begins to drive its MISO1 output when SS1 goes active low, but the data is not
defined until the first SCK1 edge. The first SCK1 edge shifts the first bit of data from the shifter onto the MOSI1
output of the master and the MISO1 output of the slave. The next SCK1 edge causes both the master and slave
to sample the data bit value on their MISO1 and MOSI1 inputs, respectively. At the third SCK1 edge, the USI1
shifts the second data bit value out to the MOSI1 and MISO1 output of the master and slave respectively. When
CPHA1=1, the slave’s SS1 input is not required to go to its inactive high level between transfers.
Because the SPI logic reuses the USI1 resources, SPI mode of operation is similar to that of synchronous or
asynchronous operation. An SPI transfer is initiated by checking for the USI1 Data Register Empty flag (DRE1=1)
and then writing a byte of data to the USI1DR Register. In master mode of operation, even if transmission is not
enabled (TXE1=0), writing data to the USI1DR register is necessary because the clock SCK1 is generated from
transmitter block.

 Loading...
Loading...