Publication 1734-UM011A-EN-P - February 2004
Configure the 1734-AENT Adapter for Your EtherNet/IP Network 3-3
You can distinguish the class of the IP address from the first integer in its
dotted-decimal IP address as follows:
Each node on the same physical network must have an IP address of the same
class and must have the same net ID. Each node on the same network must
have a different Host ID thus giving it a unique IP address.
IP addresses are written as four decimal integers (0-255) separated by periods
where each integer gives the value of one byte of the IP address.
For example, the 32-bit IP address:
10000000 00000001 00000000 00000001 is written as 128.1.0.1.
Gateway Address
This section applies to multi-network systems. If you have a single network
system, please skip to the next section.
The Gateway Address is the default address of a network. It provides a single
domain name and point of entry to the site. Gateways connect individual
physical networks into a system of networks. When a node needs to
communicate with a node on another network, a gateway transfers the data
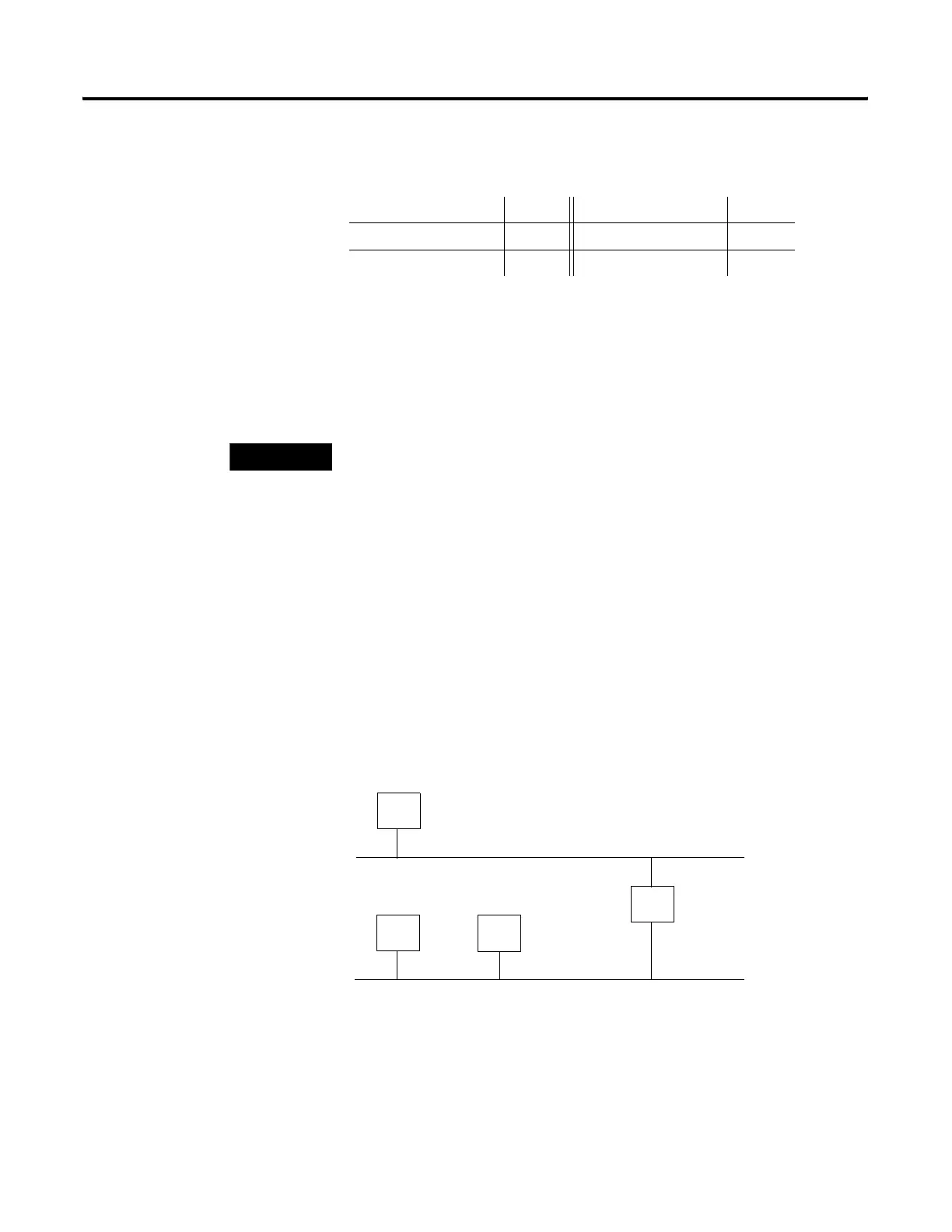
between the two networks. The following figure shows gateway G connecting
Network 1 with Network 2.
When host B with IP address 128.2.0.1 communicates with host C, it knows
from C’s IP address that C is on the same network. In an Ethernet
environment, B can then resolve C’s IP address into a hardware address (MAC
address) and communicate with C directly.
Range of first integer Class Range of first integer Class
0 -127 A 192 - 223 C
128 -191 B 224 - 255 other
EXAMPLE
128.1.0.1
128.2.0.1 128.2.0.2
128.2.0.3
128.1.0.2
A
B
C
G
Network 1
Network 2

 Loading...
Loading...