Chapter 29
| IP Routing Commands
Border Gateway Protocol (BGPv4)
– 917 –
2. Use the bgp confederation peer command to add an internal peer autonomous
system to a confederation.
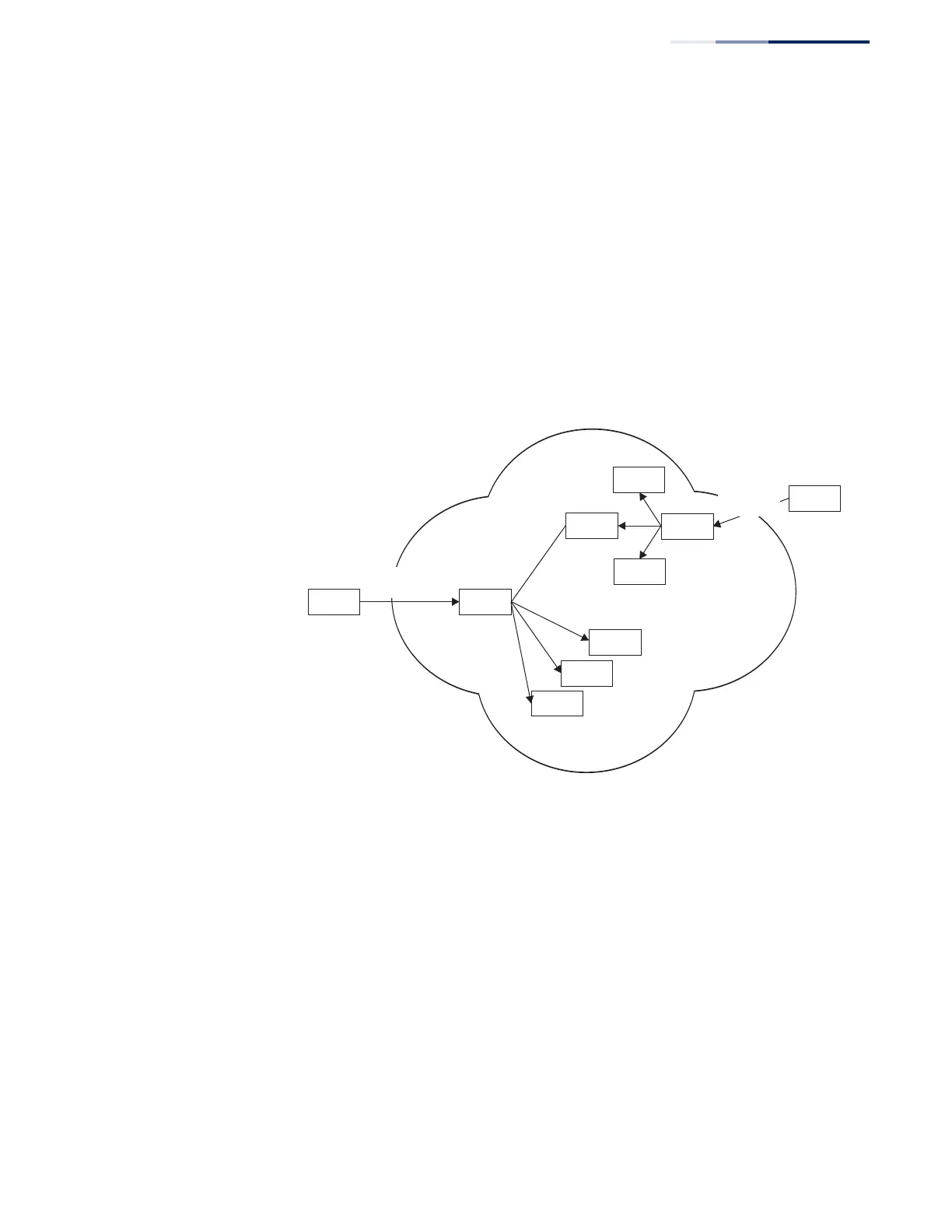
Route Servers
Route Servers are used to relay routes received from remote ASes to client routers,
as well as to relay routes between client routers. Clients maintain BGP sessions only
with the assigned route servers. Sessions with more than one server can be used to
provide redundancy and load sharing. All routes received from a client router are
propagated to other clients through the Route Server. Since all external routes and
their attributes are relayed unmodified between client routers, they acquire the
same routing information as they would via direct peering in a full mesh
configuration.
Figure 10: Connections for Route Server
Configuration Guidelines
Use the neighbor route-server-client command to configure this router as a route
server and the specified neighbor as its client.
Route Flap
Dampening
An update message is sent from a BGP speaker to a neighboring speaker whenever
any change to a route occurs. A speaker announcing such a route is also
responsible for any changes, including withdrawal, change in AS-Path or Next-Hop,
to the same neighbor, irrespective of where the change was learned. In practice this
may cause a BGP speaker to announce a new route, and then almost immediately
withdraw or update the route a few seconds later, repeatedly. Since routing
information is propagated to other downstream speakers, there is a ripple effect
that creates a cascading storm of updates through the ASes. This causes instability
in the routing tables, as well as the computational overhead required to compute
the best path, and an increase in convergence time.
Router
Router
Router
Router
Route
Server
Router
eBGP
Speaker
Router
Router
Advertised
Routes
Router
Router
Router
eBGP
Speaker
Advertised
Routes
Route
Server
 Loading...
Loading...











