Preparing for Automation
216 FTB-1v2 and FTB-1v2 Pro
The choice of a technology depends on your particular needs.
For more information on programming aspects, see the section on using
your product in an automated test environment.
Communication Characteristics
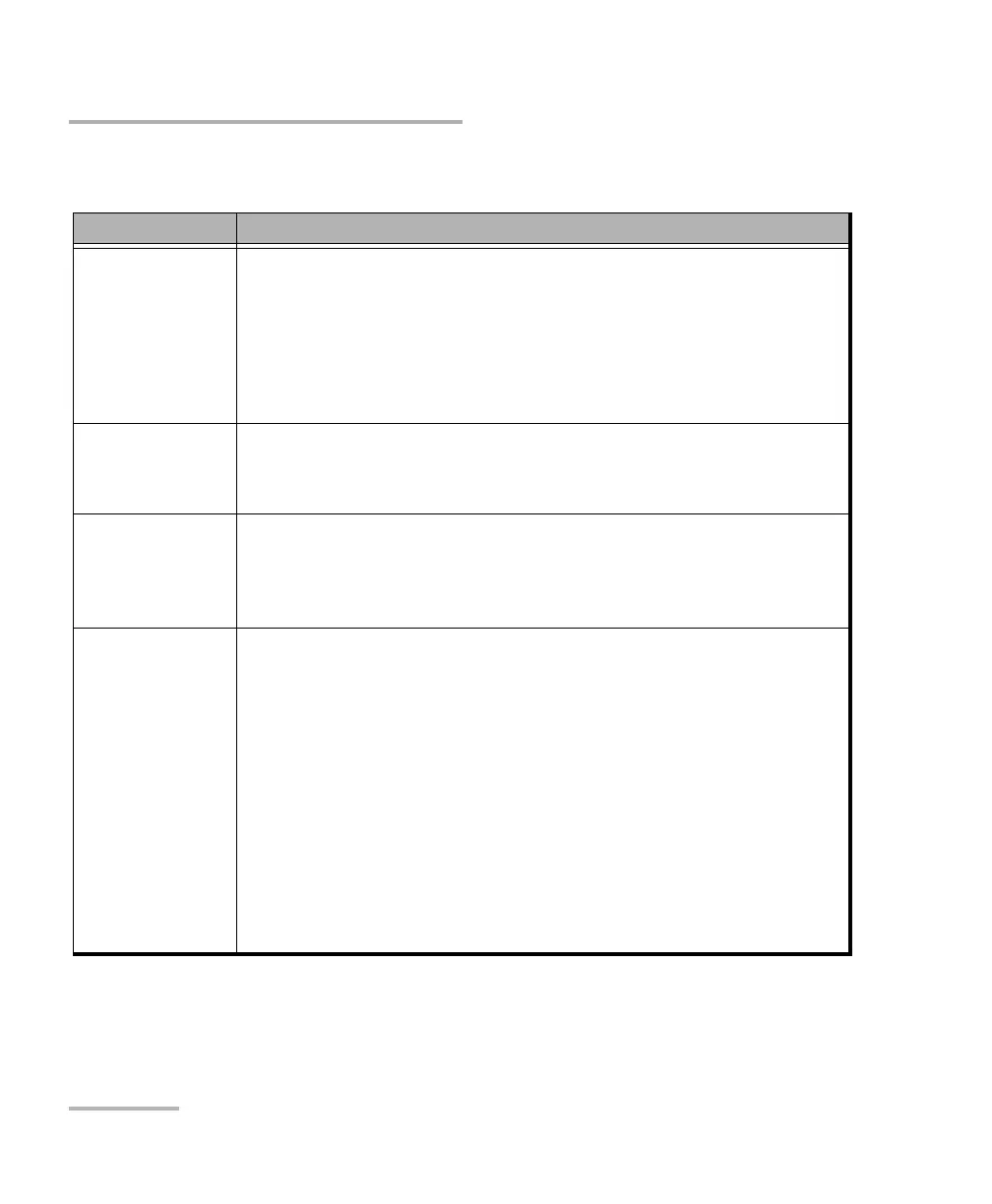
ActiveX (COM) Allows you to develop an application that will run locally on your
unit within Windows.
Best approach when speed is your top priority (no physical
connection that slows down the process).
Supported by most development software.
Lower cost.
ActiveX (DCOM)
(Ethernet,
TCP/IP)
Allows the sharing of network resources.
Allows you to develop computer-based applications to directly
communicate with your unit.
RS-232
Null-modem cable or USB to RS-232 adapter required to
establish connection between the computer and your unit.
For increased speed and performance, run the application
locally on your unit through ActiveX instead of using RS-232.
Telnet and
Socket (Ethernet,
TCP/IP)
Your unit can be directly connected to a Local Area Network
(LAN) or Wide Area Network (WAN) via its 10/100/1000 Base-T
interface.
Allows the sharing of network resources.
Allows you to develop computer-based applications very easily
to directly communicate with your unit.
Telnet allows you to send SCPI commands over the Telnet
service.
Socket allows you to send the same SCPI commands as you
would in Telnet, but without any formatting (raw
communication). The socket communication is similar to a
communication by RS-232, but over a LAN connection.
 Loading...
Loading...