2-
24
LPS-O Line Protection System GE Power Management
2.3 PROTECTION SETTINGS 2 CALCULATION OF SETTINGS
2
2.3.14 OS BLOCKING
Out-of-step blocking (OSB) is offered as a standard feature in the LPS-O system. Refer to Section 1.4.4: OUT-
OF-STEP BLOCKING on page 1–10 for a complete description of the OSB logic. The OSB function is imple-
mented through the phase distance functions in the LPS-O system as shown in Figure 2–11: OSB FUNCTION
CHARACTERISTIC below. For an out-of-step condition, the apparent impedance seen by the relay will follow a
typical swing line. The LPS-O system recognizes an out-of-step condition by sensing that the MOB function
operates first, and that the coordinating function (Zone 2 or 3) operates a short time later. The
MOBZONE
set-
ting is used to select which of the zones (Zone 2 or 3) is used as the coordinating zone.
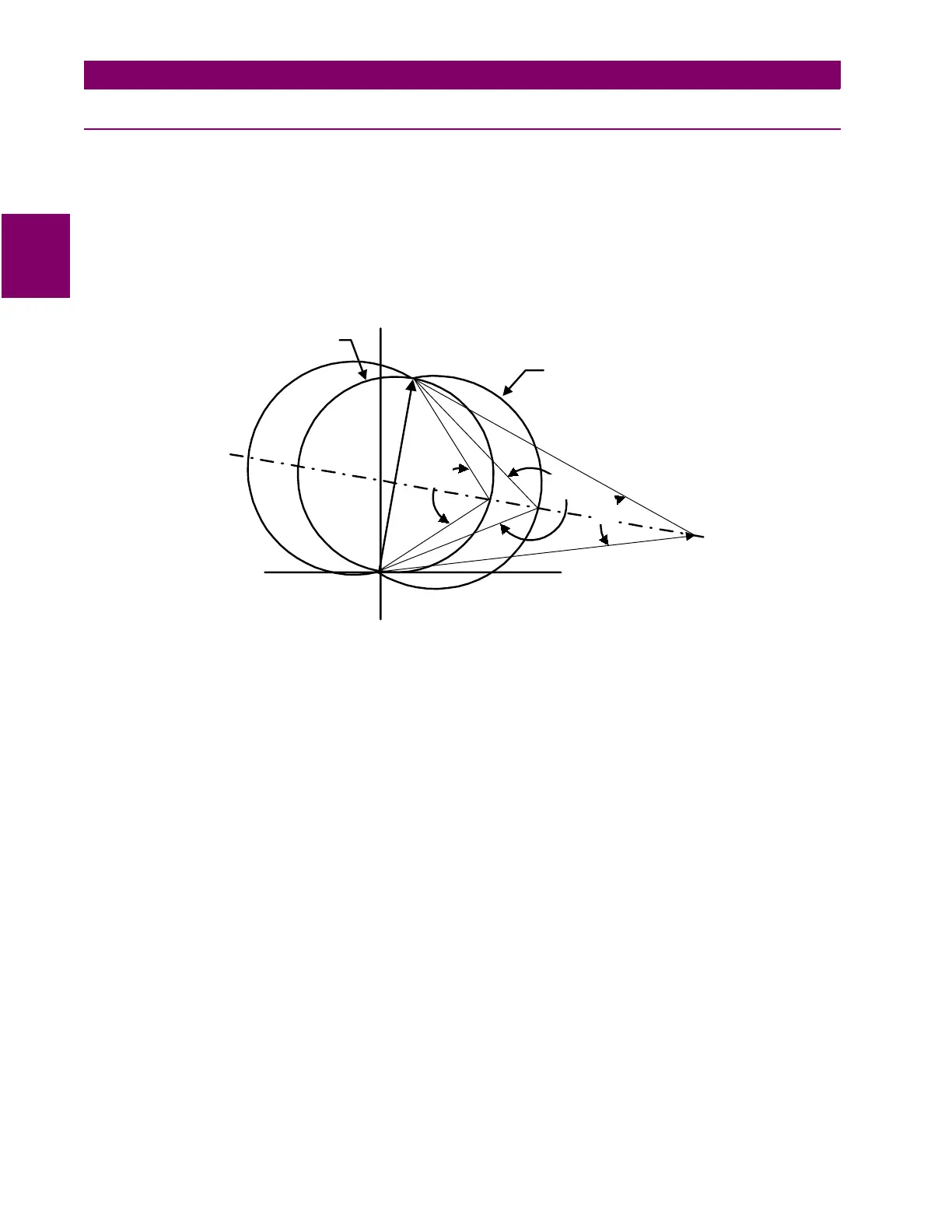
Figure 2–11: OSB FUNCTION CHARACTERISTIC
The angles A, B and C are determined as a function of the reach (Zc) of the coordinating zone, the maximum
load flow (minimum Zload) and the fastest swing (first slip cycle). Angle A is selected via the
ZxPCHARANG
(
x
= 2, 3 or 4) and determines the shape of the coordinating zone characteristic. Angle B is selected via the
MOB-
CHARANG
setting and determines the shape of the MOB characteristic. Angle B should be set so that the time
for the fastest swing to traverse from angle B to angle A is not less than 30 milliseconds. In addition, the A and
B angle settings must be selected so that the difference between angle B and angle C is never less than 20°.
Note that angle C is determined as a function of the minimum load impedance (Zload) and the reach (Zc) of the
coordinating zone. Load flow and stability studies may have to be run to determine the settings necessary to
establish out-of-step blocking.
1301: MOBZONE - Coordinating Zone
Set
MOBZONE
to select a coordinating zone per the criteria described above.
1302: MOBCHARANG - MOB Characteristic Angle
Use the criteria described above to select an appropriate
MOBCHARANG
setting.
1303: BLOCKWHAT - Functions to Block during Out-of-Step Tripping
BLOCKWHAT
is used to select which of the following are to be blocked during an out-of-step condition:
1. BLKALL: Block all tripping regardless of what operated to initiate the trip.
2. BLKDIST: Block tripping for operation of any of the distance functions.
Swing Line
R
X
MOB
Zone 2, 3 or 4
Zload
A
B
C
Zc
Zone 2 or 3
 Loading...
Loading...