45
Capacities and Selection Data
4. Capacities and Selection Data
4.1 Procedure for Selection of the System
This section explains the procedure to select the most suitable outdoor unit , with the values to be taken into account and the
necessary steps to be carried out.
This procedure allows to select the unit with the best characteristics to provide the greatest level of eciency and comfort,
considering the building layout, the specications of the indoor units to be installed and the distribution of air and refrigerant
ows.
The ease of access for installation and maintenance work must be taken into account when selecting the location for
installation of the outdoor unit.
4.1.1 Unique features of the system
The system boasts some unique features that must be taken into account before selecting the outdoor unit.
Possibility of installing a reduced total unit capacity
The system allows the connection of a total combined indoor capacity as low as 50% and as high as 150%, of the nominal
capacity of the outdoor unit. In comparison with other air conditioning systems requiring the indoor and outdoor nominal
capacities to be equal, the system allows the installation of an outdoor unit with a nominal capacity up to 50% smaller than
the total combined indoor capacity. This possibility is explained in the following example:
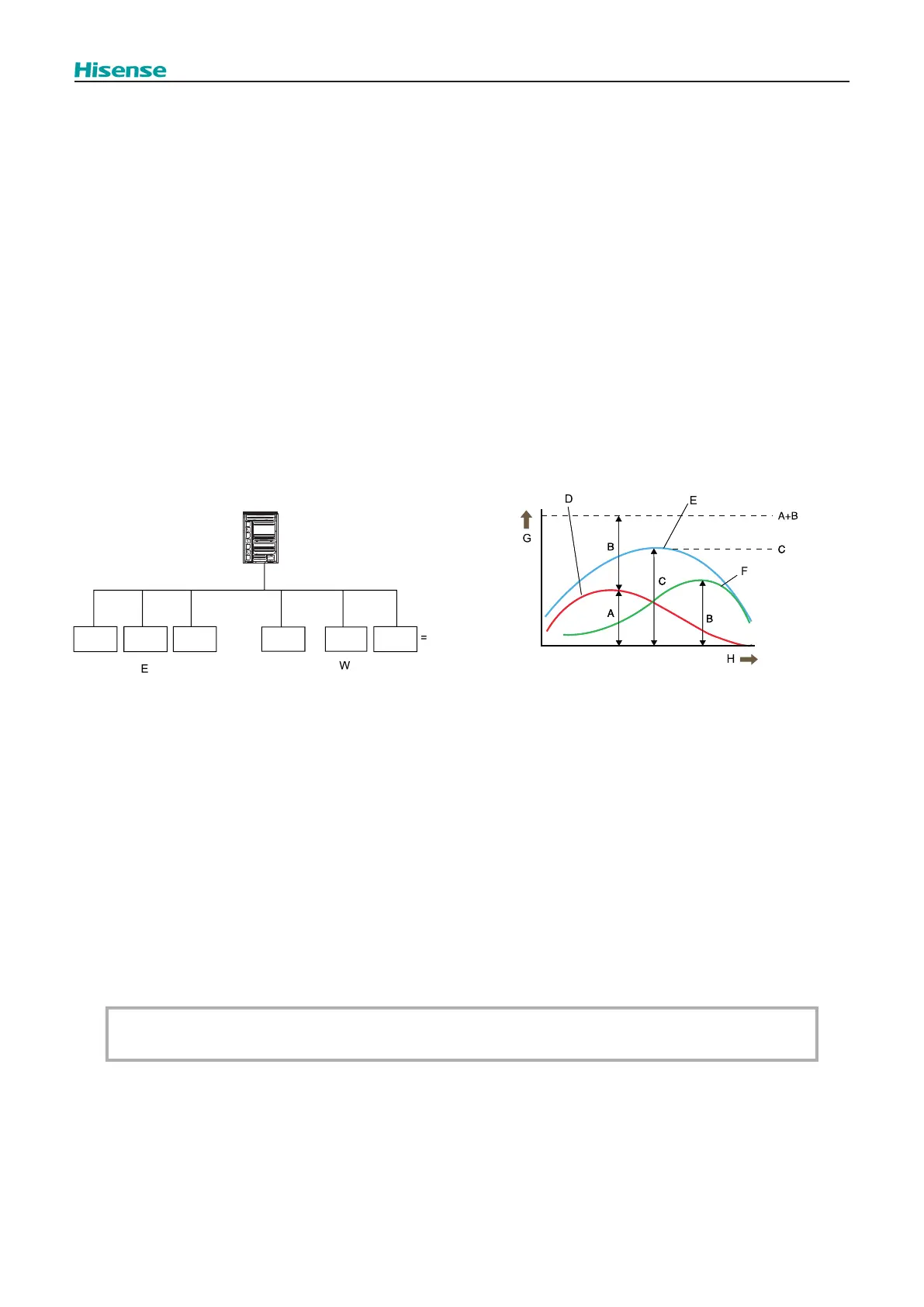
The diagram shows a typical building with a morning peak heat load on the east zone equivalent to a 57,300 Btu/h unit. In the
afternoon, a peak equivalent to a 64,400 Btu/h unit occurs on the west zone.
In this case, a conventional system would require the installation of a 121,700 Btu/h outdoor unit, matching the total installed
indoor capacity (57,300 Btu/h + 64,400 Btu/h). However, the maximum simultaneous load in the whole building occurs at
noon, and is equal to 92,000 Btu/h of unit capacity. Therefore, a 92,000 Btu/h outdoor unit could be selected, directing its
capacity to either the east or the west zone as dictated by the system controls.
NOTE
:
● The maximum required loads of east and west zone must not be simultaneous.
● In systems in which all the indoor units are operated simultaneously, the total indoor capacity must not exceed the
nominal capacity of the outdoor unit. Otherwise, poor performance or a narrowing of the operation range in overload
conditions may occur.
The ratio of total combined capacity is calculated with the following formula:
Ratio of total combined capacity= (Total capacity of the indoor units / Capacity of the outdoor unit)
x 100% = (121,700 Btu/h / 92,000 Btu/h) x 100% ≈132%
Indoor unit capacity
E: East zone (57,300Btu/h)
W: West zone (64,400Btu/h)
A: morning peak heat load in the eastern area
B: evening peak heat load in the western area
C: maximum simultaneous load for the entire building
D: eastern area load
E: total load
F: western area load
G: load
H: time
92,000Btu/h
121,700Btu/h
19,100
Btu/h
19,100
Btu/h
19,100
Btu/h
27,400
Btu/h
27,400
Btu/h
9,600
Btu/h
+

 Loading...
Loading...











