8. MAINTENANCE OPERATIONS
8-6
8.2 Collecting a Memory Dump
When one of the errors in Table 8-1 occurs, this equipment records the contents of the
system memory in a file (memory dump file). Then a blue screen appears and a STOP error
code is displayed. By analyzing the data in this memory dump file, you can investigate the
cause of the failure.
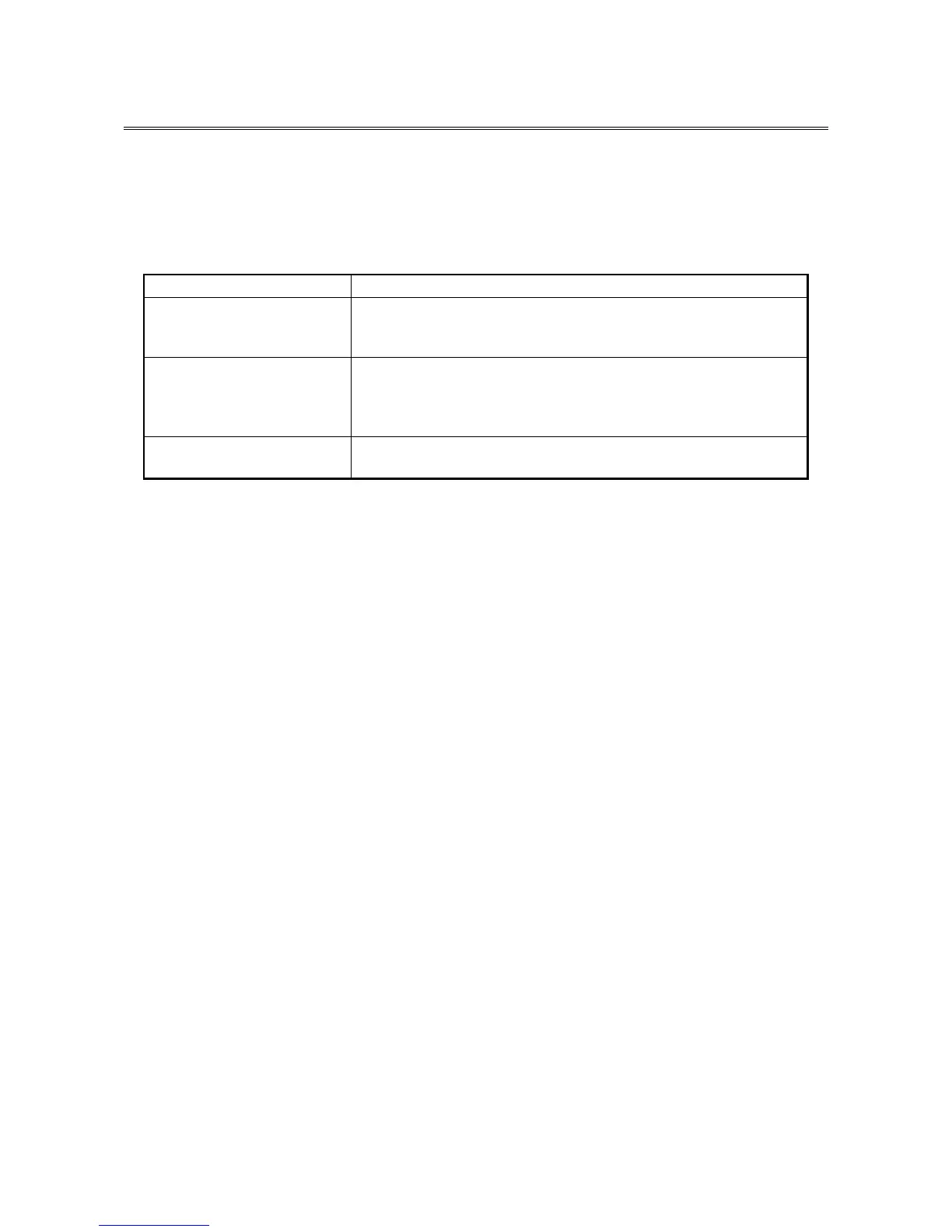
Table 8-1 Error That Trigger a Memory Dump
Cause Description
Forced recovery from OS
hang
When the OS hangs, press the reset switch or input a remote reset
signal to the external contact RMTRESET (*1).
Then a memory dump is collected.
Hardware NMI When a severe failure (such as uncorrectable memory error or a PIC
bus parity check error) occurs in the hardware of this equipment, a
non- maskable interrupt (NMI) is generated and a memory dump is
collected.
Microsoft® Windows®
STOP error
When a fatal error occurs in the Microsoft® Windows® kernel, a
memory dump is collected.
(*1) Do not input a remote reset signal continuously to the RMTRESET external contact.
If you do, this equipment cannot collect a memory dump.
For details about the displayed STOP error code, see “9.3 STOP Error Codes”.
To select the memory dump file type, open System in Control Panel. You can select from the
following five types defined below (In the case of Windows® 7, you can select from the three
types except “Automatic memory dump” and “Active memory dump”). Because the memory
dump file type determines how far you can analyze the failure by using the dump file, we
recommend selecting “Complete memory dump” whenever you can. The factory default is
“Complete memory dump”.
・Complete memory dump : The entire contents of system memory is recorded. The boot
volume (*2) must have enough free space to hold a paging file
equal to the size of the physical memory plus 1 MB.
・Kernel memory dump : The kernel memory is recorded. The boot volume (*2) must have
enough free space to hold a paging file about one third the size
of the physical memory.
・Minimum memory dump : The minimum information necessary for identifying what caused
the equipment to stop is recorded. The boot volume (*2) must
have enough free space to hold a paging file of more than 2 MB.
・Automatic memory dump: Similarly to the kernel memory dump, the kernel memory is
recorded. The difference from the kernel memory dump is that
the Auto memory dump can make the initial paging file small
from the physical memory size.
・Active memory dump :
The contents of the memory assigned to a virtual machine are
filtered, and the contents of the memory used in the Hyper-V
hosts are recorded only. The active memory dump can make the
recorded memory dump file smaller than the complete memory
dump.
(*2) The boot volume is a volume that contains Windows® files and Windows® support files.

 Loading...
Loading...