122
1.
Router B and Router C multicast DF election messages to all PIM routers—224.0.0.13. The election
messages carry the RP’s address, and the priority and metric of the unicast route, MBGP route, or
multicast static route to the RP.
2. The router with a route of the highest priority becomes the DF.
3. If a tie occurs in the priority, the router with the route with the lowest metric wins the DF election.
4. If a tie occurs in the metric, the router with the highest IP address wins.
Bidirectional RPT building
A bidirectional RPT comprises receiver-side RPT and source-side RPT. The receiver-side RPT is rooted at
the RP and takes the routers directly connected with the receivers as leaves. The source-side RPT is also
rooted at the RP but takes the routers directly connected with the sources as leaves. The processes for
building these two parts are different.
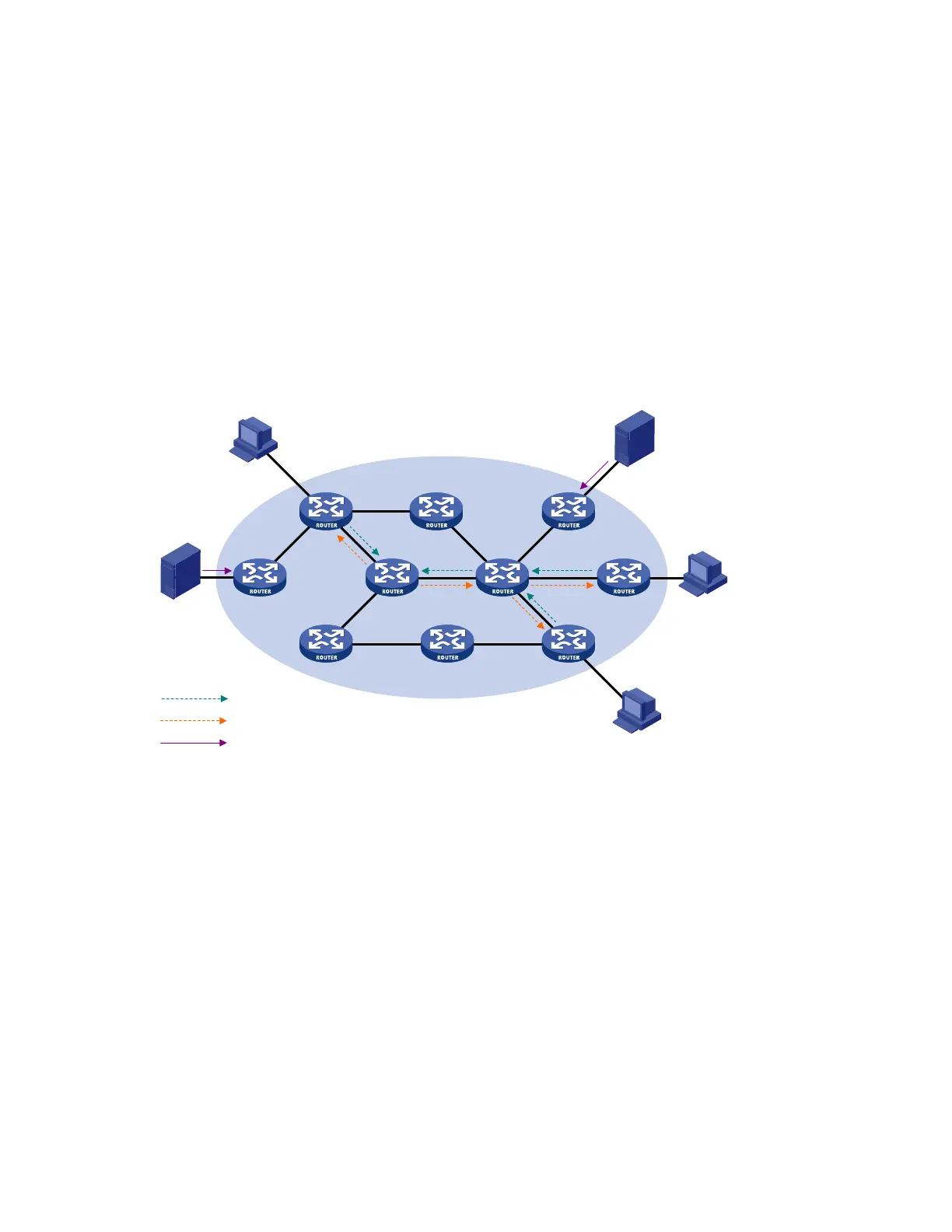
Figure 43 RPT building at the receiver side
Source
Server A
Server B
Host B
Host C
Receiver
Receiver
Multicast packets
Receiver-side RPT
Join message
RP
Source
Host A
Receiver
As shown in Figure 43, the process for building a receiver-side RPT is similar to that for building an RPT
in PIM-SM:
1. When a receiver joins multicast group G, it uses an IGMP message to inform the directly connected
router.
2. Upon getting the receiver information, the router sends a join message, which is forwarded hop by
hop to the RP of the multicast group.
3. The routers along the path from the receiver’s directly connected router to the RP form an RPT
branch, and each router on this branch adds a (*, G) entry to its forwarding table. The * means
any multicast source.
When a receiver is no longer interested in the multicast data addressed to multicast group G, the directly
connected router sends a prune message, which goes hop by hop along the reverse direction of the RPT
to the RP. Upon receiving the prune message, each upstream node deletes the interface connected with
the downstream node from the outgoing interface list and checks whether it has receivers in that
multicast group. If not, the router continues to forward the prune message to its upstream router.

 Loading...
Loading...











