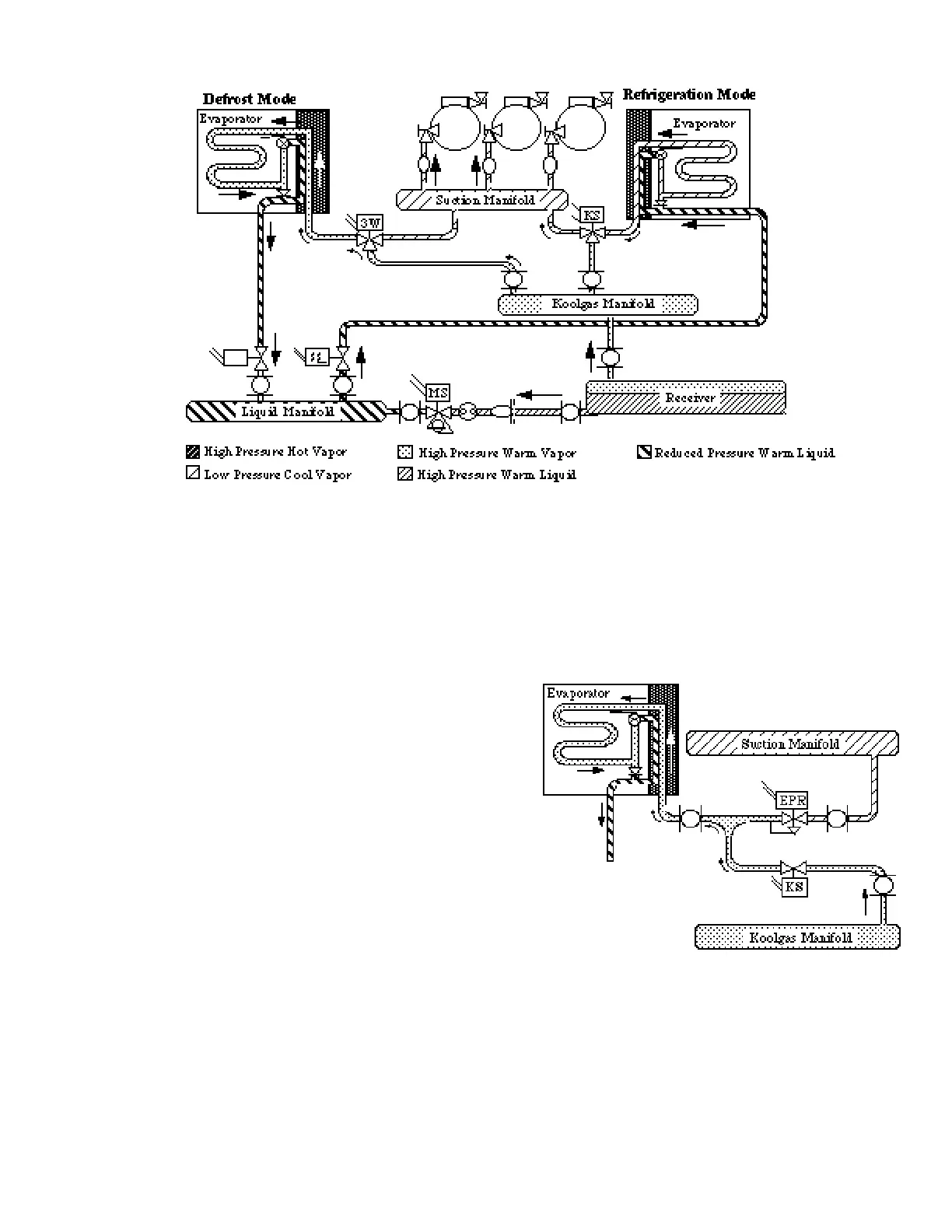
KOOLGAS DEFROST CYCLE
Beginning with the Receiver the Koolgas Cycle
splits in two directions—Receiver Vapor and
Receiver Liquid. The high pressure liquid
flowing from the Receiver is throttled by the
Main Liquid Line Solenoid Va l v e causing a
pressure reduction in the Liquid Manifold.
The Branch Liquid Line Solenoid Va l v e i s
designed to allow backflow into the reduced
pressure Liquid Manifold. When a branch of
refrigeration cases enters the defrost cycle its
Branch Va l v e allows refrigerant to flow into the
Liquid Manifold. The valve solenoid is energ i z e d
both for refrigeration and for defrost.
The Receiver Vapor flows directly into the
Koolgas Manifold. This Koolgas Va p o r
maintains the same high pressure as the
Receiver. A 3-Way Valve closes the suction line
to the Suction Manifold and opens the Koolgas
line to the E v a p o r a t o r. Koolgas Vapor flows
backward through the Evaporator, giving up
heat to the Evaporator for defrost.
The Koolgas Vapor condenses and flows into the
reduced pressure liquid line through a B y p a s s
Check Va l v e around the TEV. From there it is
returned to the Liquid Line Manifold.
If a Suction Stop EPR Valve is used to control
Evaporator temperature, the 3-Way Valve is not
used. When defrost is called for, the suction line
control valve closes and a two-way K o o l g a s
Valve opens the line from the Koolgas Manifold
to the Evaporator.
Revised August 1, 1996 P/N 340272A
2 - 7
HUSSMANN CORPORATION • BRIDGETON, MO 63044-2483 • Printed in USA
 Loading...
Loading...