148 IBM System Storage N series Hardware Guide
10.1 Background
In this chapter, the term volume, when used alone, is defined to mean both traditional
volumes and aggregates. Data ONTAP volumes have the following distinct versions:
Traditional volumes
Virtual volumes, which are called
FlexVols
FlexVols offer flexible and unparalleled functionality that is housed in a construct that is known
as an
aggregate. For more information about FlexVol and thin provisioning, see N series Thin
Provisioning, REDP-47470, which is available at this website:
http://www.redbooks.ibm.com/abstracts/redp4747.html?Open
Traditional single-parity RAID technology offers protection from a single disk drive failure. If a
secondary event occurs during reconstruction, the RAID array might experience data
corruption or a volume being lost. The single-parity RAID solution can improve performance,
but presents greater risk of data loss. Select the solution carefully so that it complies with your
organization’s policies and application-specific requirements.
Although disk drive technology increased capacities and reduced seek time performances, it
did not reduce the amount of contrast between decreased reliability. It addition, the
technology increased bit error rates. The result is an increase of potential uncorrectable bit
errors and reduced reliability of traditional single parity RAID adequately protecting data.
Today, traditional RAID is stretching past its limitations.
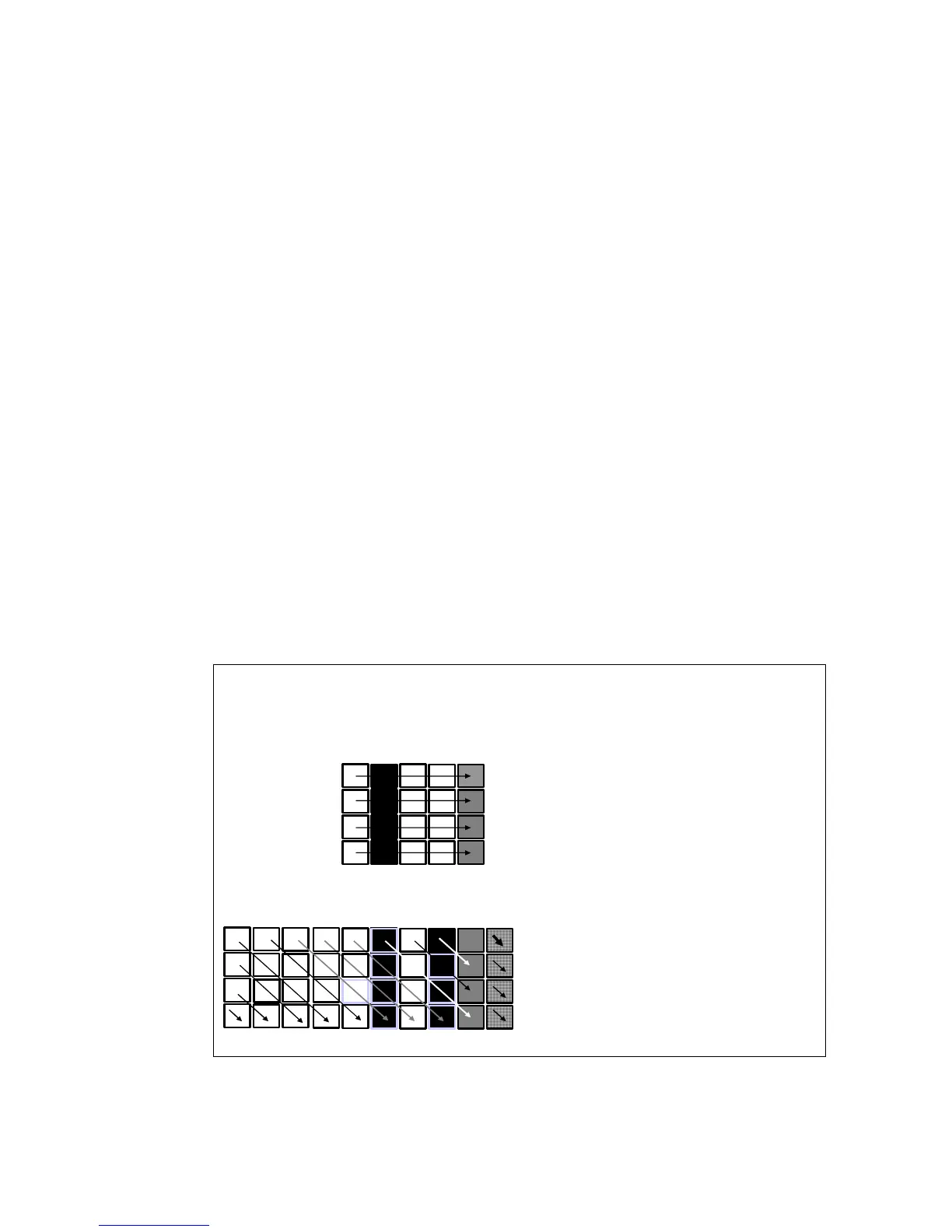
By increasing the data fault tolerance of various disk failures and infusing block-level striping,
double parity distributions presents RAID data protection called RAID Double Parity. This
protection is also called RAID-DP, and is shown in Figure 10-1. RAID-DP is available on the
entire IBM System Storage N series data storage product line.
Figure 10-1 RAID-DP
© 2005 IBM Corporation
35
Address the challenge with RAID Double Parity (RAID-DP)
Survives any 2-disk-failure
scenario
Compared to single-parity RAID,
RAID-DP has:
Better protection (>4,000
MTTDL)
Equal, often better performance
Same capacity overhead
(typically 1 parity per 6 data
drives
Outperforms any other “double-
parity” offering
Combined with SyncMirror
(RAID1), N series storage systems
are designed to survive failure of
any five disks in one disk
protection group
P
PDP
Single-parity RAID
p
rotects against any
single disk failure
RAID-DP
Protects against any
two-disk failure

 Loading...
Loading...











